Increasing awareness of emerging environmental and climate change effects has expedited the global commercialization of clean energy. Naturally, the demand for powering up several small-scale and low power devices has increased. However, the small-scale storage of electricity has encountered bottlenecks, encouraging the possibility of generating electricity from hydrogen, using fuel cells.
Credit: Kui Jiao from Tianjin University
Image source Link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enrev.2023.100017
Increasing awareness of emerging environmental and climate change effects has expedited the global commercialization of clean energy. Naturally, the demand for powering up several small-scale and low power devices has increased. However, the small-scale storage of electricity has encountered bottlenecks, encouraging the possibility of generating electricity from hydrogen, using fuel cells.
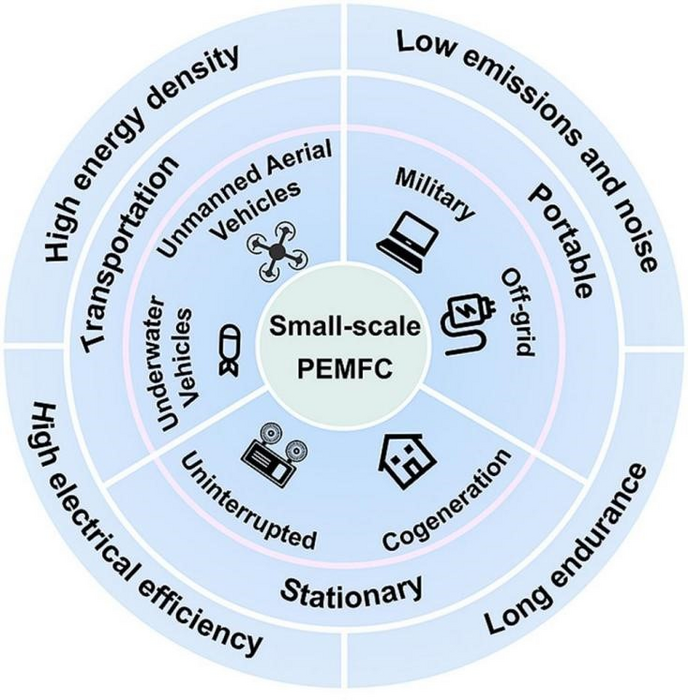
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) are promising electrochemical cells that convert the chemical energy of fuel into electrical energy. PEMFCs are used for a range of applications, but their unique attributes, including high energy densities, low pollution emissions, and low operating temperatures, make them favorable for small-scale applications. In particular, the small-scale PEMFC (<10 kW) is appropriate for applications such as portable power generation, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), light-duty vehicles, and residential power supply. Notably, improvements in the specific power of small-scale PEMFC technology can improve this cell’s market uptake.
To understand the current trends in this field, Professor Kui Jiao and his team from Tianjin University, China, reviewed the advances and challenges in the applications of PEMFCs. Their findings were made available online on 18 April 2023, in Volume 2 of Energy Reviews. In the review article, the team discusses the operation and characteristics of PEMFCs for applications in the transportation, stationary, and portable power generator fields. In addition, they provide their perspectives on future strategies for small-scale high-specific-power PEMFC’ systems.
In transportation, the successful implementation of small-scale PEMFCs in UAVs, underwater vehicles, and light traction vehicles can make them an excellent alternative power source.
The team also added that higher power density, longer endurance, mild hybrid architecture, and PEMFC range extenders are more suitable for small transportation applications.
Small-scale PEMFCs are also used for stationary applications, such as powering up uninterrupted power supply and residential co-generation systems. The pre-requisites of these power systems include reliability, durability, and affordability. In this regard, the research team concluded that the PEMFC could be used as a renewable backup power source due to its high efficiency and low pollution emissions. They also addressed fuel flexibility and reliability issues.
One must note that although lithium (Li)-ion battery systems dominate the market in portable applications, small-scale PEMFCs have additional benefits. Portable (outdoor) power generation is best suited for small-scale PEMFCs due to their longer duration, high energy density, off-grid power generation, and adaptability.
“Although several pioneering studies have been conducted to promote the application of small PEMFCs, further advancements are essential to meet the requirements for practical applications,” adds Professor Jiao. Future challenges in the development of small-scale PEMFCs will primarily be associated with optimizing fuel cell materials and the system design to obtain a high-specific power fuel cell.
Lightweight components play a crucial role in achieving advanced, high-performance PEMFC technologies, by optimizing the structural material design for greater reliability. The response time of PEMFCs can be decreased by using lightweight hybrid power sources for instant power surge.
Furthermore, proper energy management strategies for hybrid power sources help improve their efficiency and dynamics. Professor Jiao further adds, “A hydrogen storage system with a high hydrogen storage density, quick hydrogen release and charge rates, strong reversibility, and improved safety is crucial for increasing the overall device-level energy density of small-scale PEMFC systems.”
Hence, a compressed gas storage tank of large volume would not be beneficial for small-scale PEMFC applications where space and weight are important parameters. “Conversely, a long-term hydrogen storage system for small-scale PEMFC applications may instead be based on materials such as complex hydrides and metal storage systems with high volumetric densities,” Professor Jiao concludes.
***
Reference
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enrev.2023.100017
Authors: Zixuan Wanga,b, Zhi Liuaa,b, Linhao Fana,b, Qing Dua,b, and Kui Jiaoa,b
Affiliations:
aState Key Laboratory of Engines, Tianjin University, 135 Yaguan Road, Tianjin, China
bNational Industry-Education Platform of Energy Storage, Tianjin University, 135 Yaguan Road, Tianjin, China
About Professor Kui Jiao from Tianjin University
Dr. Kui Jiao currently works as a professor in the State Key Laboratory of Engines at the Tianjin University, China. He received his Ph.D. degree in 2011 from the University of Waterloo, Canada, in mechanical engineering. His research interests include low and intermediate temperature fuel cells, hydrogen storage device, lithium-ion battery, thermoelectric generator, and turbocharger compressor. He has published over 200 international journal papers and several book chapters, with more than 11746 citations and an h-index of 62. He also received the National Science Fund for Outstanding Young Scholars in 2016.
About Energy Reviews
Energy Reviews is an international, interdisciplinary, high-quality, open-access academic journal in the field of energy, which is sponsored by Shenzhen University and published by the Elsevier publishing group. Energy Reviews invites high-quality reviews at the forefront of research in a broad range of topics covering not only materials, chemistry, and engineering, but also new energy devices, applications, methods, tools, theories, policy and management. The following areas will be prioritized, but not exclusively:
1, New theories, methods and technologies for energy research
2, Interdisciplinary research of materials, physics, chemistry and biology in energy
3, Low-carbon utilization of fossil fuel and CCUS
4, Advanced hydrogen, renewable energy and energy storage technologies
5, Exploration and applications of novel energy conversion
6, Applications of AI, big data in energy
Website: https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/energy-reviews
Journal
Energy Reviews
DOI
10.1016/j.enrev.2023.100017
Method of Research
Literature review
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Application Progress of Small-scale Proton exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
Article Publication Date
18-Apr-2023
COI Statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest




