Using data from the eruption of the underwater volcano near Tonga in 2022, a research group at Nagoya University in Japan has used disturbances in the earth’s upper atmosphere to track the airwaves that cause tsunami. Their findings may lead to speedier predictions of these giant waves.
Credit: EyePress News/Shutterstock
Using data from the eruption of the underwater volcano near Tonga in 2022, a research group at Nagoya University in Japan has used disturbances in the earth’s upper atmosphere to track the airwaves that cause tsunami. Their findings may lead to speedier predictions of these giant waves.
Every minute is crucial when warning people caught in the path of a tsunami. After the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, a tsunami in Indonesia reached Sri Lanka in less than two hours. Eight hours later, it arrived on the coast of Kenya. If there had been a way to notify people about the dangers of a tsunami in those faraway areas, it may have been possible to save at least some of the 230,000 victims.
A research group led by Assistant Professor Atsuki Shinbori, Associate Professor Yuichi Otsuka, and Associate Professor Nozomu Nishitani of the Institute for Space-Earth Environmental Research (ISEE), Nagoya University, in collaboration with the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology and the University of Electro-Communications, believes that it may be possible to predict tsunami faster by tracking the atmospheric disturbances caused by the airwaves they create. Their findings were reported in Earth, Planets and Space.
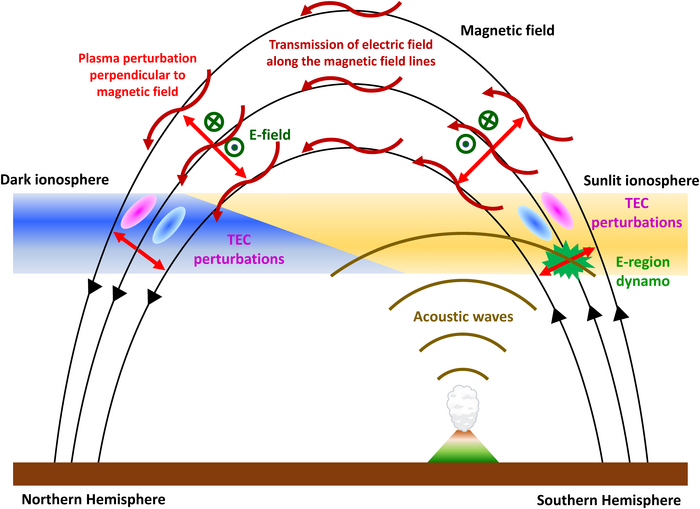
When a tsunami occurs, it deforms the lower atmosphere and generates oscillations of sound and gravity waves, causing disturbances of the electrons in the upper atmosphere, also called the ionosphere. Radio waves, such as those used in GPS and satellite broadcasting/communications, also pass through this part of the atmosphere. As a result, the disturbances caused by a natural disaster produce errors in the positional information supplied by GPS satellites.
Shinbori and his group used satellites and radar to examine these errors following the 2022 undersea volcanic eruption off the coast of Tonga in the South Pacific. They found that the eruption of the underwater volcano caused waves of air pressure that spread as far as Australia and Japan. These waves oscillated the lower part of the ionosphere. This generated an electric field that was then transmitted at high speed to the upper ionosphere. To their surprise, the researchers detected the electron changes much earlier than the air pressure waves that caused the tsunami.
The structures of the disturbance over Japan and Australia, interestingly, also mirrored each other. Despite being in different hemispheres, they occurred almost simultaneously because they disturbed the electrons in the magnetic field lines, the magnetic lines that radiate from the south to the north magnetic pole. The team calculated the speed of these disturbances and found the electromagnetic wave along the magnetic field lines travelled at 1000 kilometers (621.4 miles) per second. This was far faster than the air pressure wave, which traveled at the speed of sound (a comparatively slower 315 meters (0.2 miles) per second).
“We captured the signal of the ionospheric disturbance caused by the air pressure wave about three hours before the pressure wave originating from the volcanic eruption believed to have triggered the tsunami in Japan,” Shinbori explains. “In short, the significance of these results can be divided into two aspects: the scientific aspect of a coupled system, and the disaster prevention aspect of preparedness for severe events such as tsunamis.”
Future applications of the technique are already being considered. “Statistical analysis of ionospheric disturbances during volcanic eruptions and seismic events may make it possible to estimate tsunami wave heights and sizes from ionospheric disturbance signals in the future,” Shinbori says. “Ionospheric disturbances may be a new step forward in tsunami alerts.”
This research was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Specially Promoted Research (KAKENHI) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), which began in FY2016, “Study of dynamical variation of particles and waves in the inner magnetosphere using ground-based network observations (PWING Project)”.
Journal
Earth Planets and Space
Article Publication Date
14-Jul-2022




