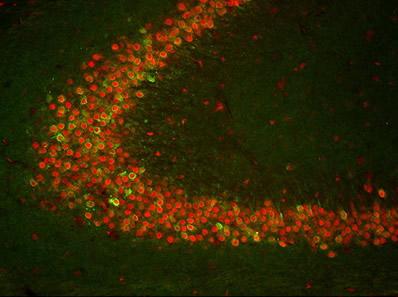
Credit: Courtesy of Elsevier
SYRACUSE, N.Y. – Seizure suppression is the focus of an original research article by researchers at the Department of Biology at Syracuse University – and they have the pictures to prove it. Their new work sheds new light on epilepsy, a chronic neurological disorder marked by recurrent, unprovoked seizures.
James Hewett, associate professor of biology, and Yifan Gong, a Ph.D. candidate in biology and neuroscience, have co-authored an article in the journal Neuroscience (Elsevier, 2018) about a protein in the brain called T-cell intracellular antigen-1 (TIA-1).
"TIA-1 is known for its ability to regulate gene expression during cellular stress," says Hewett, who studies the processes that suppress the severe electrical storms in the brain, leading to seizures. "We suspected that TIA-1 was involved with seizure suppression, but our findings suggested something else."
He and Gong are interested in the function of an enzyme in the brain called cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). This enzyme makes prostaglandins–chemical messengers that aid in the performance of normal tasks, including learning and memory.
Their research showed that seizure suppression was associated with an increase in COX-2 expression in neurons.
"Our findings raise the possibility that the level of neuronal COX-2 expression in the brain may be a determinant of the seizure threshold [a natural set-point for electrical activity, above which seizures occur]. This suggests that a better understanding of the regulation of COX-2 expression in the brain can provide new insights into molecular mechanisms that suppress seizure-induction," adds Hewett, a pharmacologist by training.
It is against this backdrop that he and Gong have sought to understand the relationship between COX-2 and TIA-1. For months, they worked in Hewett's lab, planning, conducting and analyzing their experiments. Gong even created the field's first comprehensive expression profile of TIA-1 in the normal brain. Part of his analysis is on the cover of Neuroscience. "What TIA-1 is doing there in the normal brain, if anything at all, is not entirely known," Hewett says.
"Because TIA-1 is known to suppress COX-2 expression in other cells, we reasoned that the inactivation of the TIA-1 gene would increase COX-2 expression in neurons and, consequently, would increase resistance to acute seizures," he continues. "Yifan's thesis research, however, found that TIA-1 does not influence COX-2 expression in neurons, nor play a role in seizure control in the normal brain."
Also surprising was Gong's discovery that TIA-1 appears to suppress epileptogenesis, the gradual process by which the normal brain becomes epileptic. "My research is directed at understanding the molecular mechanisms of epilepsy–specifically, identifying genes involved with seizure generation and epileptogenesis," he says.
Gong, who is Hewett's first Ph.D. student at Syracuse, plans to co-author a follow-up paper with Hewett later this summer.
"Epilepsy can be acquired at any time during our lives," says Hewett, citing brain trauma, infection and cancer as major risk factors. "Cures and preventive measures remain elusive, and the incidence of resistance to antiepileptic drugs is a clinical limitation. A better understanding of the function of neuromodulators, such as COX-2 and TIA-1, may help identify novel therapeutic targets for the treatment of epilepsy."
He and Gong belong to the Interdisciplinary Neuroscience Group, which brings together faculty members, postdoctoral fellows and students from multiple academic units across campus to foster neuroscience education and research.
###
The Interdisciplinary Neuroscience Group and the Department of Biology are part of the College of Arts and Sciences.
Media Contact
Daryl Lovell
[email protected]
313-574-5262
@syracuseu
http://www.syr.edu
Original Source
http://thecollege.syr.edu/news/2018/hewett-gong-research.html