Researchers from the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering have unveiled an artificial intelligence-based model for computational imaging and microscopy without training with experimental objects or real data.
Credit: Credit: Ozcan Research Lab/UCLA
Researchers from the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering have unveiled an artificial intelligence-based model for computational imaging and microscopy without training with experimental objects or real data.
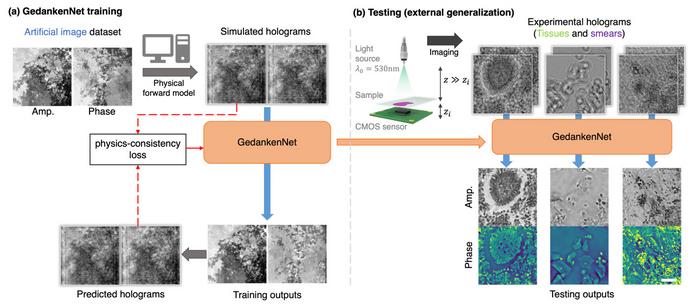
In a recent paper published in Nature Machine Intelligence, UCLA’s Volgenau Professor for Engineering Innovation Aydogan Ozcan and his research team introduced a self-supervised AI model nicknamed GedankenNet that learns from physics laws and thought experiments.
Artificial intelligence has revolutionized the imaging process across various fields — from photography to sensing. The application of AI in microscopy, however, has continued to face persistent challenges. For one, existing AI-powered models rely heavily on human supervision and large-scale, pre-labeled data sets, requiring laborious and costly experiments with numerous samples. Moreover, these methodologies often struggle to process new types of samples or experimental set-ups.
With GedankenNet, the UCLA team was inspired by Albert Einstein’s hallmark Gedanken experiment (German for “thought experiment”) approach using visualized, conceptual thought experiments in creating the theory of relativity.
Informed only by the laws of physics that universally govern the propagation of electromagnetic waves in space, the researchers taught their AI model to reconstruct microscopic images using only random artificial holograms — synthesized solely from “imagination” without relying on any real-world experiments, actual sample resemblances or real data.
Following GedankenNet’s “thought training,” the team tested the AI model using 3D holographic images of human tissue samples captured with a new experimental set-up. In its first attempt, GedankenNet successfully reconstructed the microscopic images of human tissue samples and Pap smears from their holograms.
Compared with state-of-the-art microscopic image reconstruction methods based on supervised learning using large-scale experimental data, GedankenNet exhibited superior generalization to unseen samples without relying on any experimental data or prior information on samples. In addition to providing better microscopic image reconstruction, GedankenNet also generated output light waves that are consistent with the physics of wave equations, accurately representing the 3D light propagation in space.
“These findings illustrate the potential of self-supervised AI to learn from thought experiments, just like scientists do,” said Ozcan, who holds faculty appointments in the departments of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Bioengineering at UCLA Samueli. “It opens up new opportunities for developing physics-compatible, easy-to-train and broadly generalizable neural network models as an alternative to standard, supervised deep learning methods currently employed in various computational imaging tasks.”
The other authors of the paper are graduate students Luzhe Huang (first author) and Hanlong Chen, as well as postdoctoral scholar Tairan Liu from the UCLA Electrical and Computer Engineering Department. Ozcan also holds a faculty appointment at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and is an associate director of the California NanoSystems Institute.
Journal
Nature Machine Intelligence
DOI
10.1038/s42256-023-00704-7
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
‘Self-supervised learning of hologram reconstruction using physics consistency’
Article Publication Date
7-Aug-2023




