Researchers at the University of Tsukuba use radio-frequency waves to image “spin-locked” defects in diamond with record-breaking resolution, which may lead to advances in material characterization and quantum computing
Credit: University of Tsukuba
Tsukuba, Japan – Scientists from the Division of Physics at the University of Tsukuba used the quantum effect called “spin-locking” to significantly enhance the resolution when performing radio-frequency imaging of nitrogen-vacancy defects in diamond. This work may lead to faster and more accurate material analysis, as well as a path towards practical quantum computers.
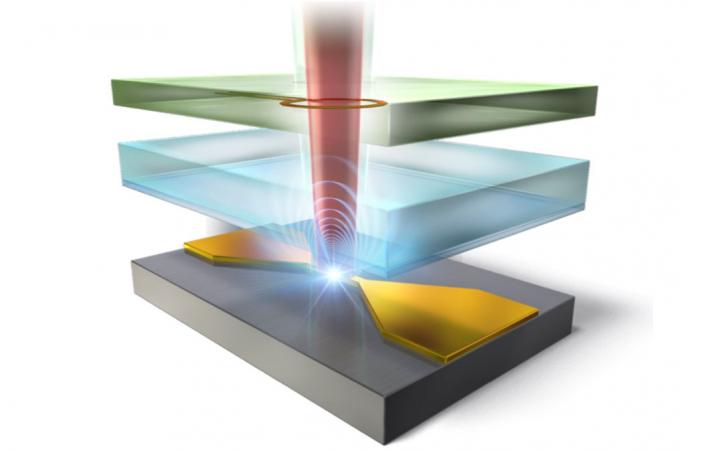
Nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers have long been studied for their potential use in quantum computers. A NV center is a type of defect in the lattice of a diamond, in which two adjacent carbon atoms have been replaced with a nitrogen atom and a void. This leaves an unpaired electron, which can be detected using radio-frequency waves, because its probability of emitting a photon depends on its spin state. However, the spatial resolution of radio wave detection using conventional radio-frequency techniques has remained less than optimal.
Now, researchers at the University of Tsukuba have pushed the resolution to its limit by employing a technique called “spin-locking.” Microwave pulses are used to put the electron’s spin in a quantum superposition of up and down simultaneously. Then, a driving electromagnetic field causes the direction of the spin to precess around, like a wobbling top. The end result is an electron spin that is shielded from random noise but strongly coupled to the detection equipment. “Spin-locking ensures high accuracy and sensitivity of the electromagnetic field imaging,” first author Professor Shintaro Nomura explains. Due to the high density of NV centers in the diamond samples used, the collective signal they produced could be easily picked up with this method. This permitted the sensing of collections of NV centers at the micrometer scale. “The spatial resolution we obtained with RF imaging was much better than with similar existing methods,” Professor Nomura continues, “and it was limited only by the resolution of the optical microscope we used.”
The approach demonstrated in this project may be applied in a broad variety of application areas–for example, the characterizations of polar molecules, polymers, and proteins, as well as the characterization of materials. It might also be used in medical applications–for example, as a new way to perform magnetocardiography.
###
The work is published in Journal of Applied Physics as “Near-field radio-frequency imaging by spin-locking with a nitrogen-vacancy spin sensor” selected as a Featured Article (DOI: 10.1063/5.0052161).
This work was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (Nos. JP18H04283,
291 JP18H01243, JP18K18726, and JP21H01009) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of
292 Science.
Media Contact
Naoko Yamashina
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




