Credit: Viacheslav Dremov et al./Nature Communications
MIPT physicists have learned how to locally control Josephson vortices. The discovery can be used for quantum electronics superconducting devices and future quantum processors. The work has been published in the prestigious scientific journal Nature Communications.
A Josephson vortex is a vortex of currents occurring in a system of two superconductors separated by a weak link — a dielectric, a normal metal, etc. — in the presence of an external magnetic field. In 1962, Brian Josephson predicted the flow of a supercurrent through a thin layer of insulating material separating two pieces of superconducting material. This current was named the Josephson current, and the coupling of superconductors was dubbed a Josephson junction. A so-called weak link occurs between the two superconductors through a dielectric or a nonsuperconducting metal, and macroscopic quantum coherence develops.
When this system is placed in a magnetic field, the superconductors push the magnetic field out. The greater the magnetic field applied, the more the superconductivity resists the magnetic field penetrating into the Josephson system. However, the weak link is a place in which the field can penetrate in the form of individual Josephson vortices carrying magnetic flux quanta. Josephson vortices are often seen as real topological objects, 2 pi-phase singularities that are hard to observe and manipulate.
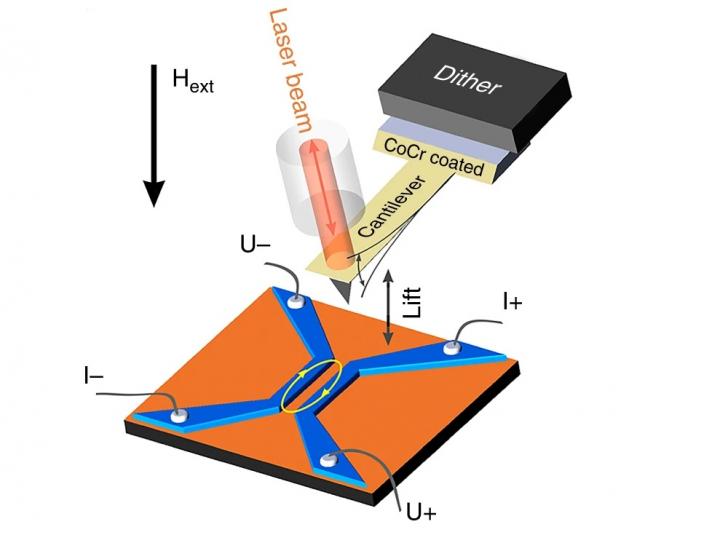
Researchers from the MIPT Laboratory of Topological Quantum Phenomena in Superconducting Systems applied a magnetic force microscope to study Josephson vortices in a system of two superconducting niobium contacts interlaid with a copper layer acting as a weak link.
“We have demonstrated that in the planar (flat) superconductor-normal metal-superconductor contacts, Josephson vortices have a unique imprint,” said the paper’s senior author, Vasily Stolyarov of MIPT. “We found this by observing these structures with a magnetic force microscope. Based on this discovery, we demonstrated the possibility of locally generating Josephson vortices, which can be manipulated by the magnetic cantilever of a microscope. Our research is yet another step toward creating future superconducting quantum computing machines.”
The variety of ultrasensitive superconducting devices, qubits, and architectures for quantum computing is growing rapidly. It is expected that superconducting quantum electronic devices will challenge conventional semiconductor devices very soon. These new devices will rely on Josephson junctions like the one indicated by the yellow closed arrow in figure 1.
“It is quite difficult to visualize Josephson vortices, as they are poorly localized,” Stolyarov added. “We discovered a way to measure the dissipation that occurs during the creation and destruction of such a vortex in the weak link area. Dissipation is a minor release of energy. In our case, the energy is released when a vortex moves in a planar Josephson contact. Thus, using our magnetic force microscope, we can successfully detect not only the static magnetic portrait of the superconducting structure but also the dynamic processes in it.”
The authors of the paper demonstrated a method for remote generation, detection, and manipulation of Josephson vortices in planar Josephson junctions using a low-temperature magnetic force microscope. With certain parameters (probe location, temperature, external magnetic field, electric current flow through the sample), the team observed a particular response of the microscope cantilever. This was followed by the appearance of sharp rings/arcs in the images. The researchers identified these features as bifurcation points between adjacent Josephson states characterized by a different number or position of Josephson vortices inside the junction. The process is accompanied by the exchange of energy between the cantilever and the sample at the bifurcation points and demonstrates that a magnetic force microscope can provide unique information on the state of a Josephson vortex.
It is expected that the results of the research will serve as an impetus and a basis for developing new methods of local noncontact diagnostics and management of modern superconducting devices and superconducting quantum electronics.
###
The study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation and the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation.
Media Contact
Varvara Bogomolova
[email protected]
7-916-147-4496
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




