Credit: DTU/DTU Biosustain
To win the war against antibiotic resistant super bugs, scientists seek to find the origin of resistance genes. Further, they try to identify how the genes are introduced to disease-causing bacteria – so-called pathogens. Identifying where resistance genes come from and how they spread somewhat compares to finding patient zero in an outbreak, which is not an easy task.
For more than 30 years, scientists have proposed that resistance genes actually originate from the microorganisms producing the antibiotic. But even though this has been a hypothesis, scientists have not been able to find direct proof of this transfer.
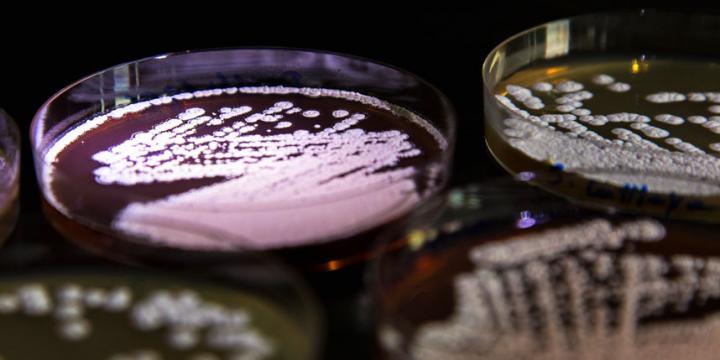
Now, research conducted at The Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Biosustainability – DTU Biosustain – at Technical University of Denmark for the very first time shows that antibiotic resistance genes originate from the same place as the antibiotic compounds, i.e. from a group of soil bacteria called Actinobacteria.
The study is now published in Nature Communications.
More than three fourths of all current antibiotics used to treat human infections are produced by Actinobacteria, which at the same time carry antibiotic resistance genes.
In these experiments, the researchers surprisingly found that many resistance genes in disease-causing microbes (gram negative pathogens) were very similar to resistance genes found in Actinobacteria. Especially in one case, the genes were 100% identical.
"It has been suspected that pathogens can obtain resistance genes from Actinobacteria for half a century. So now with the 100 % identical genes we find the smoking gun," says Postdoc Xinglin Jiang from DTU Biosustain.
Gram negative pathogens constitute a big group of different species; amongst others pseudomonas, which can cause lung and urinary tract infections.
At first, it was difficult to imagine how pathogens can acquire genes from Actinobacteria, because they are so different and not at all related with each other. But by investigating the DNA sequence around the resistance genes, the team figured out how the resistance genes transfer occurred through a new mechanism named "carry back", where the pathogen basically has a primitive form of "sex" with the Actinobacterium and takes up its resistance genes after it dies.
This gene transfer by carry back could in principle happen where pathogens come into contact with Actinobacteria, like in an animal farm or in soil polluted with untreated hospital waste. In this way, the pathogen can become resistant and endanger human lives in the next round of infection.
Understanding the origin is hence key to counteracting the spread of antibiotic resistance, explains Senior Researcher Tilmann Weber from DTU Biosustain:
"We can't stop this gene transfer, but when you know, which resistance genes pathogens may harbor, you can personalize the antibiotic treatment. Also, with this knowledge you can try to develop new antibiotics with other properties that the pathogens don't have a defense against."
Bacterial sex act reveals the mechanism:
By following the DNA-transfer, scientists for the very first time showed an unknown mechanism called carry back in which pathogens were able to snatch genes from far-related bacteria via the carry back mechanism. Here is how, in short, the carry back process works:
1. The Gram negative pathogen injects its DNA into the Actinobacteria. Gram negative bacteria naturally have an ability called conjugation by which bacterial cells can inject their own DNA into other bacterial cells. It is called the bacterial equivalent of sex, because it is usually used to exchange gene information between Gram negative bacteria. But sometimes Gram negative bacteria can also use this mechanism to inject DNA into far-related Gram positive bacteria like Actinobacteria.
2. Inside the Actinobacteria, the injected DNA recombines with the host's DNA containing resistance genes. After the Actinobacterium dies, the recombinant DNA is released into the environment.
3. Lastly, the injected DNA can act as "gluing DNA" and mediate the uptake of resistance gene back to the pathogens through a phenomenon called natural transformation.
###
Media Contact
Tilmann Weber
[email protected]
45-24-89-61-32
@DTUtweet
http://www.dtu.dk
Original Source
http://www.biosustain.dtu.dk/english/nyhedsbase/nyhed?id=9B924680-693F-47E2-8D7F-03C6CECFE473 http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15784
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag