Credit: YANG Nailiang
The Chinese puzzle ball is an ornate decorative artwork consisting of several concentric shells that move independently of each other. In the recent decade, Chinese scientists provided a universal method for the fabrication of a conceptually similar micronanoscale structure, called the hollow multishell structure (HoMS).
A new study led by Prof. WANG Dan from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposes a novel concept of temporal-spatial ordering and dynamic smart behavior in HoMSs. It was published in Nature Reviews Chemistry on Feb. 11.
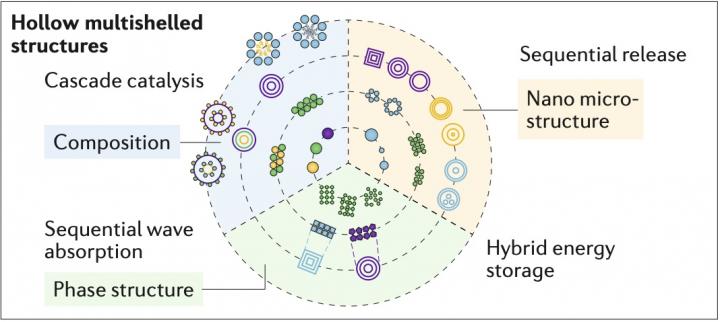
Unlike the single shell hollow sphere or nanoparticles, HoMS has potential applications in fields ranging from energy conversion and storage to catalysis, since it avoids easy agglomeration of nanoparticles, maintains the advantage of effective surface area, and benefits the mass transmission.
In the first phase of their work, the group developed a facile sequential templating approach (STA) for the fabrication of HoMS. This approach realized precise control of the shell number, thickness, distance, and facet exposure, thus modulating surface properties and the interface of HoMS materials.
Specifically, multishells separate space into various, relatively isolated subspaces. At the same time, the heterogeneous pores on each shell facilitate the transmission of small molecules.
“When a molecule or electromagnetic wave diffuses through HoMS, it experiences a set order of environments and spends a controllable time in each one,” said WANG. “Based on the understanding of structure property relationship, we name this specific feature of HoMS as ‘temporal-spatial ordering’.”
Interestingly, in the antenna system of cyanobacteria, different antenna pigments are loaded in a certain order to realize the sequential collection of light energy, which is the example for natural temporal-spatial ordering. This specific structure ensures the fast and precise route to accumulate large amount of oxygen to significant amounts for oxygenic life.
“Inspired by nature, we believe the unique structure suggests promising applications for HoMS in sequential electromagnetic wave harvesting, cascade catalytic reactions, sustained drug release, and hybrid energy storage technologies,” said WANG.
The group also proposed another promising proposition: HoMS with isolated spaces in multiple chemical environments could express dynamic smart behavior.
Through chemical modification, HoMSs can bind the target and perhaps also self-evolve to have desired properties at a desired time, which would be highly desirable in chemical engineering and biochemistry fields.
###
Media Contact
LI Xiangyu
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




