Credit: Argonne National Laboratory
Chemists spend a great deal of time and energy trying to get chemical reactions to begin or to speed up — but sometimes it can be just as important to stop them before they go too far.
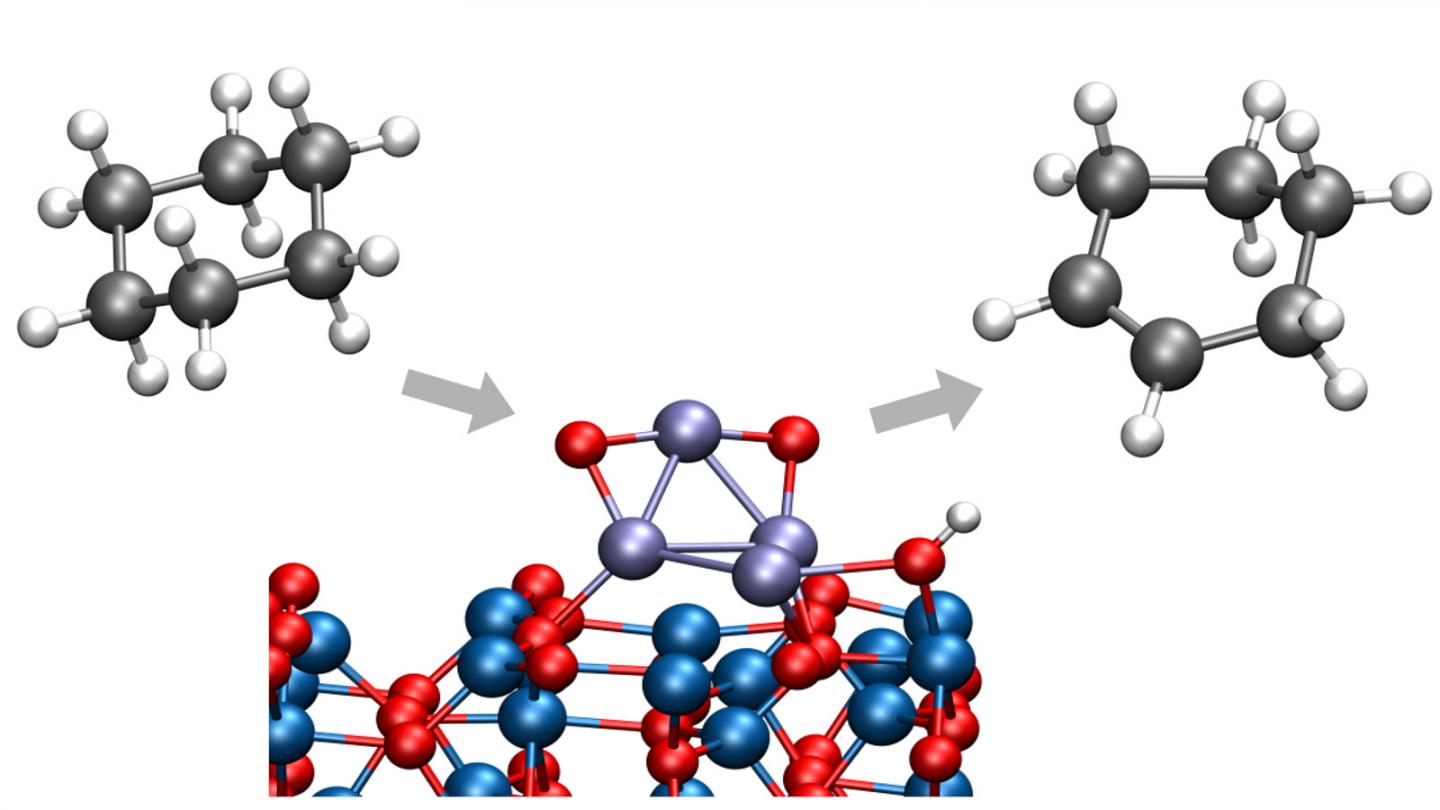
In a recent study from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, chemists have identified a way to convert cyclohexane to cyclohexene or cyclohexadiene, important chemicals in a wide range of industrial processes. Importantly, this process takes place at low temperatures, eliminating the creation of carbon dioxide that would have resulted from an unwanted breaking of carbon-carbon bonds.
“The fact that we can make this conversion happen at lower temperatures protects the intermediate dehydrogenation products cyclohexene and cyclohexadiene from being further converted unwanted products.” — Stefan Vajda
Cyclohexane is an important starting molecule in a wide range of chemical reactions, according to Argonne chemist Stefan Vajda, now at the J. Heyrovský Institute of Physical Chemistry in Prague. However, without a suitable catalyst to initiate the reaction, converting cyclohexane into useful products typically requires elevated temperatures generated through the expenditure of a great deal of energy, and the process may suffer from poor selectivity as well.
In the study, Vajda and Argonne chemist Larry Curtiss and their international team of collaborators examined a type of reaction called oxidative dehydrogenation, in which hydrogen molecules are stripped off a larger molecule. By cutting a limited number of hydrogen-carbon bonds, the reaction can produce cyclohexene and cyclohexadiene before combustion to carbon dioxide takes place.
The work improved on previous studies by the Argonne team on the dehydrogenation of cyclohexane and cyclohexene by introducing two key components: a sub-nanometer-sized cobalt oxide catalyst on an aluminum oxide support and a controlled oxygen environment.
The researchers employed X-ray scattering techniques at Argonne’s Advanced Photon Source (APS), a DOE Office of Science User Facility, to monitor the nature and stability of the catalysts during the catalytic testing of the clusters in real time. They discovered that the clusters carried out partial dehydrogenation of the cyclohexane at temperatures right around 100 degrees Celsius — far lower than had been previously observed for this kind of reaction, and the clusters retained their oxidized nature and stability at reaction temperatures up to 300°C.
“The fact that we can make this conversion happen at lower temperatures protects the intermediate dehydrogenation products cyclohexene and cyclohexadiene from being further converted to unwanted products,” Vajda said.
Vajda and Curtiss noted that the highly selective catalyst is long-lived and does not get poisoned or degraded by the reaction. In theoretical and experimental investigation of the size of the catalyst, the researchers found that clusters of size four and twenty-seven atoms were roughly equally efficient in carrying out the reaction. “It seems as though as long as the catalyst is below roughly one nanometer in size, this composition works well — an important factor for the potential scaleup of this class of catalysts by more traditional, though less size-selective, synthesis routes.” Vajda said.
To better understand the basic mechanisms behind the activity and selectivity of the cobalt catalysts, the researchers used density functional theory calculations to model the reaction pathways. “The excellent performance of the cobalt clusters can be explained by theoretical calculations, which reveal highly active cobalt atoms in the clusters and show that the oxidized nature of the clusters causes the low-temperature formation of the product,” Curtiss explained.
###
A paper based on the study, “Subnanometer cobalt oxide clusters as selective low temperature oxidative dehydrogenation catalysts,” was published in the February 27 online issue of Nature Communications.
Other authors of the paper included Argonne scientists Sungsik Lee, Avik Halder, Glen Ferguson, Sönke Seifert, and Randall Winans. Other contributors included Detre Teschner and Robert Schlögl from the Fritz-Haber-Institut and the Max-Planck-Institute for Chemical Energy Conversion in Germany, Vasiliki Papaefthimiou from the University of Strasbourg in France, and Jeffrey Greeley from Purdue University.
The research was funded by the DOE’s Office of Science and by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation’s first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America’s scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit the Office of Science website.
Media Contact
Chris Kramer
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




