Credit: TANG Yongbing
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are the dominant power source for portable electronics and electric vehicles. However, the relatively low theoretical capacity of graphite anode (372 mAh g-1) hinders the enhancement of the energy density of LIBs. Therefore, exploiting anode materials with high capacity is drawing increasing attention.
Among various anode materials, aluminum (Al) is a promising candidate due to its excellent conductivity, high theoretical capacity, low discharge potential, natural abundance, and especially low cost. However, Al-based anodes are usually investigated in half cells or full cells with low cathode areal density (Recently, a research team led by Prof. TANG Yongbing and Dr. ZHANG Miao at the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences published a paper entitled “Uniform Distribution of Alloying/Dealloying Stress for High Structural Stability of Al Anode in High Areal Density Lithium Ion Battery” on Advanced Materials, which showed how the researchers improved the cycling performance of Al-based batteries with a high areal density cathode.
In previous studies, the team developed a new lithium-ion battery configuration with high efficiency and low cost, which used an integrated design of aluminum foil to replace the graphite anode and the Cu current collector of conventional LIBs, omitting conventional anode materials. Thus, dead weight and dead volume could be greatly reduced, further improving energy densities of this battery. Nevertheless, this integrated anode also has a problem with cycling stability when assembled with a high areal density cathode.
In this work, the team found that the cracking and pulverization of the Al anode could be attributed to the uneven charge/discharge reaction along the boundaries of pristine Al, which led to the stress concentration and ultimate failure of the Al anode. They then found it was possible to extend the lifetime of the Al anode via uniform distribution of the alloying/dealloying stress.
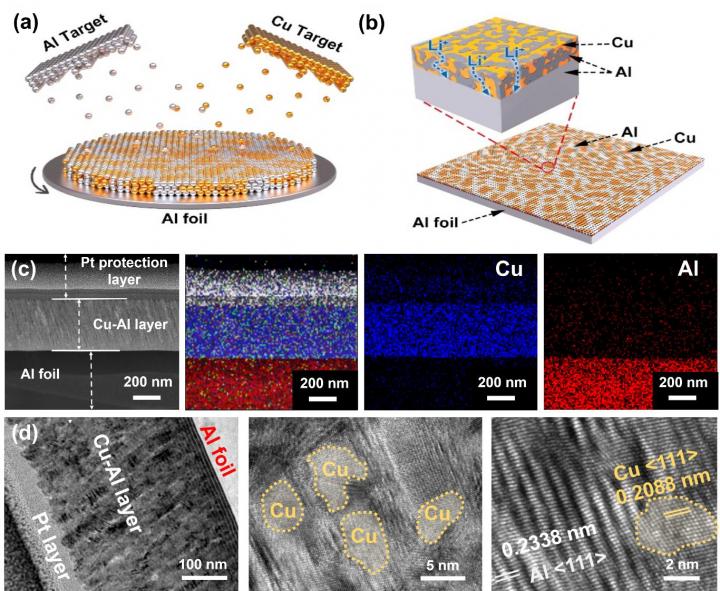
TANG and his collaborators promoted an inactive (Cu) and active (Al) codeposition strategy to homogeneously distribute the alloying sites and disperse the stress of volume expansion, which is beneficial in obtaining the structural stability of the Al anode (namely Cu-Al@Al).
Owing to the homogeneous reaction and uniform distribution of stress during the charge/discharge process, the full battery of Cu-Al@Al assembled with a high LiFePO4 cathode areal density of 7.4 mg cm-2 achieved a capacity retention of ~88% over 200 cycles, which is the best performance of Al anodes in full batteries with a cathode of such high areal density.
The study suggests that this inactive/active design provides a viable way to solve the problem of Al anodes and offers possibilities for practical applications of Al anodes.
###
Media Contact
ZHANG Xiaomin
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




