Credit: LIU Xuemei
Fear overgeneralization (i.e., deficits in the discrimination of safety and threat) is an important pathological characteristic of anxiety-related syndromes such as posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and panic disorder.
However, unlike traditional conditioned fear, the mechanism of processing innate fear is largely unknown.
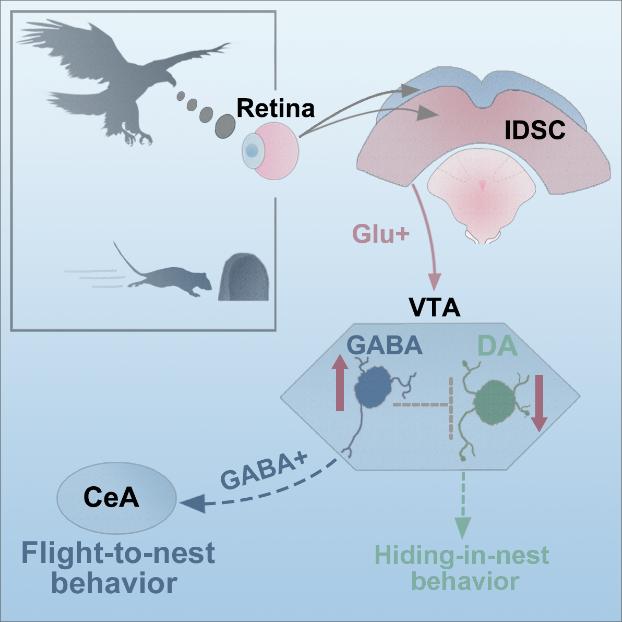
Prof. WANG Liping and his colleagues ZHOU Zheng and LIU Xuemei at the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed that the VTA (ventral tegmental area) GABAergic neural circuit mediates visually evoked innate defensive responses.
In this study, the research group identified for the first time a neural circuit related to the VTAGABA+ neurons that mediates visually evoked innate defensive responses, involving the SC Glut+_ VTAGABA+_ CeA (central nucleus of the amygdala) pathway.
It has been confirmed by neuroscientists that the VTA plays an important role in learned appetitive and aversive behaviors. Interestingly, the researchers revealed that the GABA neurons in VTA were activated by visual threats by fiber photometry. Through viral tracing and both in vivo and in vitro electrophysiological recordings, they showed that VTAGABA+ neurons received direct excitatory inputs from the superior colliculus (SC).
The researchers revealed that VTAGABA+ neurons mediated looming-evoked innate defensive behaviors. These findings demonstrated that SC glutamatergic inputs activated VTAGABA+ neurons and mediated looming-evoked innate defensive behaviors. They further showed that CeA was a downstream target of the SC-VTA GABAergic pathway and it was involved in innate defensive behavior.
This study provides new insights into potential mechanisms of survival across species, as well as the maladaptive behavior in fear- and anxiety-related mental disorders.
The team has been working on the dissection of the neural circuits mediating instinctive emotions for years. In their previous work, they have resolved a novel brain circuit controlling visually evoked innate freezing behaviors via the SC-LP-LA subcortical pathway. They also had pioneering work which first reported that the accelerated innate defensive response to visual threats induced by stress is mediated by the Locus Coeruleus (LC) directed TH+ projections to the SC. The current study published in Neuron is another key milestone in their systematic work.
###
Media Contact
ZHANG Xiaomin
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




