Credit: Cassini, Dante, Baillié and Noyelles
The Solar System’s second largest planet both in mass and size, Saturn is best known for its rings. These are divided by a wide band, the Cassini Division, whose formation was poorly understood until very recently. Now, researchers* from the CNRS, the Paris Observatory – PSL and the University of Franche-Comté have shown that Mimas, one of Saturn’s moons, acted as a kind of remote snowplough, pushing apart the ice particles that make up the rings. The findings are the result of two studies supported by the International Space Science Institute and CNES, the French space agency, published simultaneously in June 2019 in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
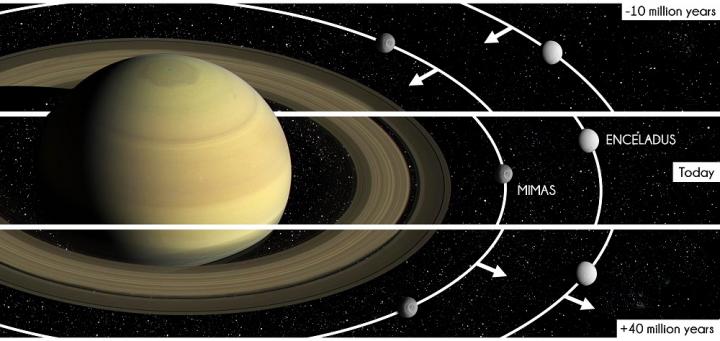
Saturn’s rings are made up of ice particles whose orbital velocity increases the closer they are to the planet. The Cassini Division is a wide, dark band located between Saturn’s two most visible rings, in which the particle density is considerably lower than that inside the rings. The researchers suspected a link between Mimas, one of Saturn’s moons, and the band, since there is a region at the inner edge of the Division where the particles orbit around Saturn exactly twice as fast as Mimas. This phenomenon, known as orbital resonance, pushes the ice particles apart, producing a relatively narrow gap. Scientists from CNRS, the Paris Observatory – PSL and the University of Franche-Comté have now shown that Mimas may have moved closer to Saturn in the recent past, making the moon a kind of remote snowplough that widened the initial gap, giving it the 4500 km width it has today. If on the other hand the orbit of Mimas moved outwards, the particles would return to their original position, rather as if a snowplough were to reverse and stop pushing the snow, letting it spread out again. Using numerical simulations, the researchers calculated that Mimas must have migrated inwards by 9000 km over a few million years in order to open up the 4500 km gap that currently makes up the Cassini Division.
A natural satellite, such as the Moon, normally tends to move away from its planet rather than closer to it. In order to migrate inwards, a moon has to be able to lose energy, particularly by heating up, which would cause its internal ice to melt and weaken its outer crust. However, the state of Mimas’ surface, which still bears the scars of relatively ancient meteorite impacts, does not tally with such a scenario. The researchers’ second hypothesis, which remains to be confirmed, is that the loss of heat was shared out between Mimas and Enceladus, another of Saturn’s moons, through orbital resonance. This would have caused the creation of the internal oceans that the Cassini spacecraft detected below the surface of both these bodies.
Today, Mimas has begun to migrate outwards again. According to the researchers’ calculations, the Cassini Division is likely to take around 40 million years to close up again. Thanks to these findings, scientists may view the presence of gaps in the rings of an exoplanet as a clue that it could have moons with oceans.
###
*The researchers belong to the Institut de Mécanique Céleste et de Calcul des Éphémérides (Observatoire de Paris – PSL / CNRS), Institut UTINAM (CNRS / Université de Franche-Comté), Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris (CNRS / Université de Paris / IPGP / IGN), Laboratoire de Planétologie et Géodynamique (Université de Nantes / CNRS / Université d’Angers), Namur Institute for Complex Systems (Université de Namur), and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (NASA).
Media Contact
Maxime DOS SANTOS
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




