Credit: Osaka University
Osaka, Japan – Hydrogen gas is a promising alternative energy source to overcome our reliance on carbon-based fuels, and has the benefit of producing only water when it is reacted with oxygen. However, hydrogen is highly reactive and flammable, so it requires careful handling and storage. Typical hydrogen storage materials are limited by factors like water sensitivity, risk of explosion, difficulty of control of hydrogen-generation. Hydrogen gas can be produced efficiently from organosilanes, some of which are suitably air-stable, non-toxic, and cheap. Catalysts that can efficiently produce hydrogen from organosilanes are therefore desired with the ultimate goal of realizing safe, inexpensive hydrogen production in high yield. Ideally, the catalyst should also operate at room temperature under aerobic conditions without the need for additional energy input.
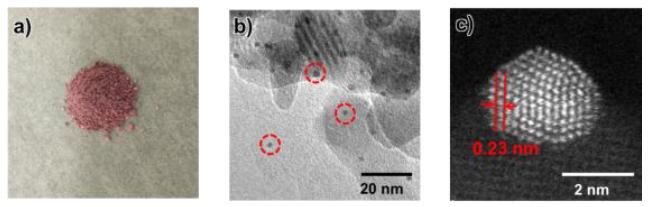
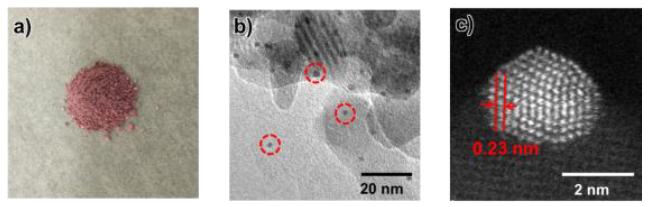
A research team led by Kiyotomi Kaneda and Takato Mitsudome at Osaka University have now developed a catalyst that realizes efficient environmentally friendly hydrogen production from organosilanes. The catalyst is composed of gold nanoparticles with a diameter of around 2 nm supported on hydroxyapatite. The catalyst was synthesized from chloroauric acid using glutathione as a capping agent to prevent nanoparticle aggregation, resulting the formation of small size of gold nanoparticles. Glutathione-capped gold nanoparticles were then adsorbed on hydroxyapatite and glutathione was removed by subsequent calcination.
The team then added the nanoparticle catalyst to solutions of different organosilanes to measure its ability to induce hydrogen production. The nanoparticle catalyst displayed the highest turnover frequency and number attained to date for hydrogen production catalysts from organosilanes. For example, the nanoparticle catalyst converted 99% of dimethylphenylsilane to the corresponding silanol in just 9 min at room temperature, releasing an equimolar amount of hydrogen gas at the same time. Importantly, the catalyst was recyclable without loss of activity. On/off switching of hydrogen production was achieved using the nanoparticle catalyst because it could be easily separated from its organosilane substrate by filtration. The activity of the catalyst increased as the nanoparticle size decreased.
A prototype portable hydrogen fuel cell containing the nanoparticle catalyst and an organosilane substrate was fabricated. The fuel cell generated power in air at room temperature and could be switched on and off as desired. Images of the catalyst after use in the fuel cell resembled those of the unused catalyst, indicating that the hydroxyapatite-supported nanoparticle catalyst readily resisted aggregation.
Generation of hydrogen from inexpensive organosilane substrates under ambient conditions without additional energy input represents an exciting advance towards the goal of using hydrogen as a green energy source.
###
The article "On-demand Hydrogen Production from Organosilanes at Ambient Temperature Using Heterogeneous Gold Catalysts" was published in Scientific Reports (DOI: 10.1038/srep37682).
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
@osaka_univ_e
http://www.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag