Credit: Vikas Nanda/Rutgers University-New Brunswick
How did life arise on Earth? Rutgers researchers have found among the first and perhaps only hard evidence that simple protein catalysts – essential for cells, the building blocks of life, to function – may have existed when life began.
Their study of a primordial peptide, or short protein, is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
In the late 1980s and early 1990s, the chemist Günter Wächtershäuser postulated that life began on iron- and sulfur-containing rocks in the ocean. Wächtershäuser and others predicted that short peptides would have bound metals and served as catalysts of life-producing chemistry, according to study co-author Vikas Nanda, an associate professor at Rutgers' Robert Wood Johnson Medical School.
Human DNA consists of genes that code for proteins that are a few hundred to a few thousand amino acids long. These complex proteins – needed to make all living-things function properly – are the result of billions of years of evolution. When life began, proteins were likely much simpler, perhaps just 10 to 20 amino acids long. With computer modeling, Rutgers scientists have been exploring what early peptides may have looked like and their possible chemical functions, according to Nanda.
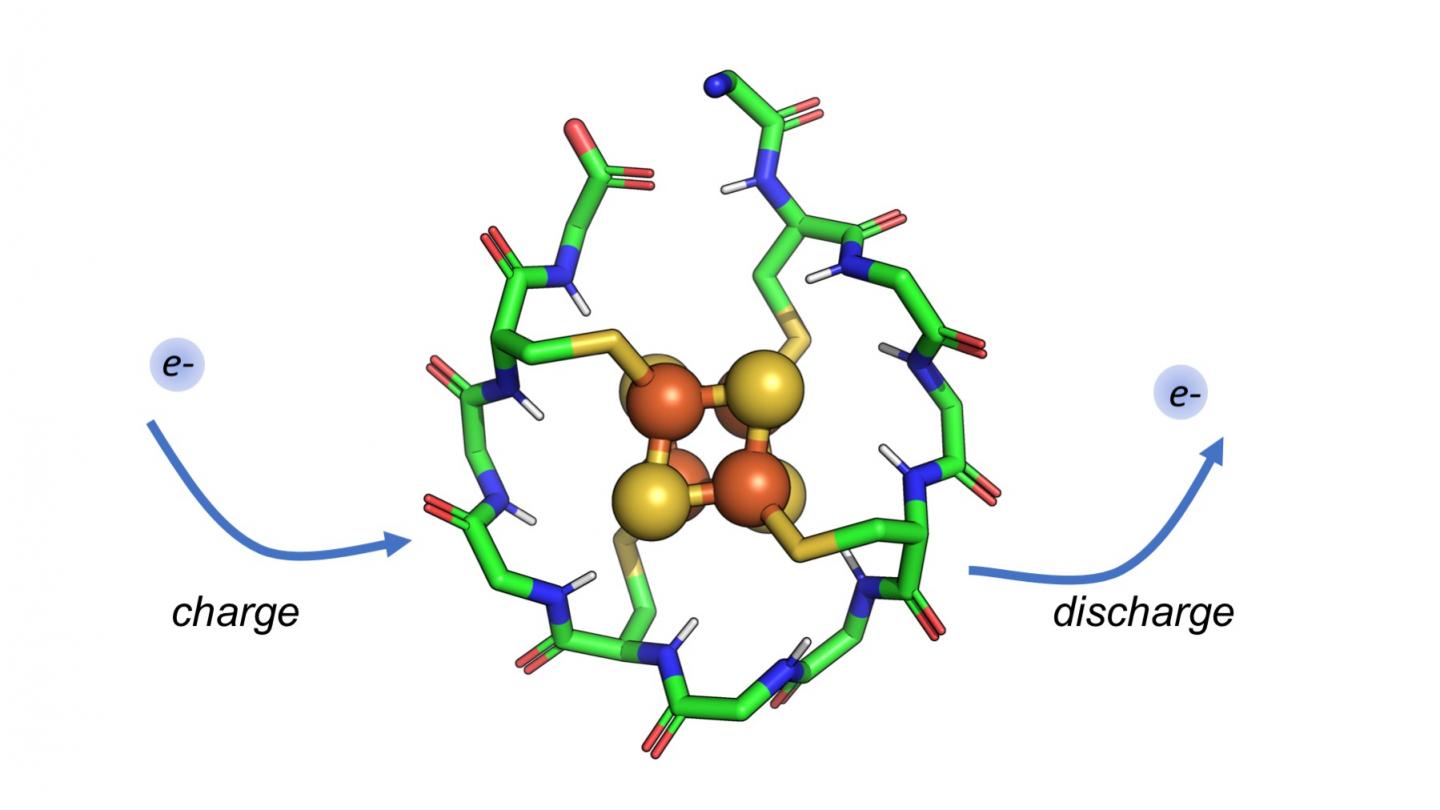
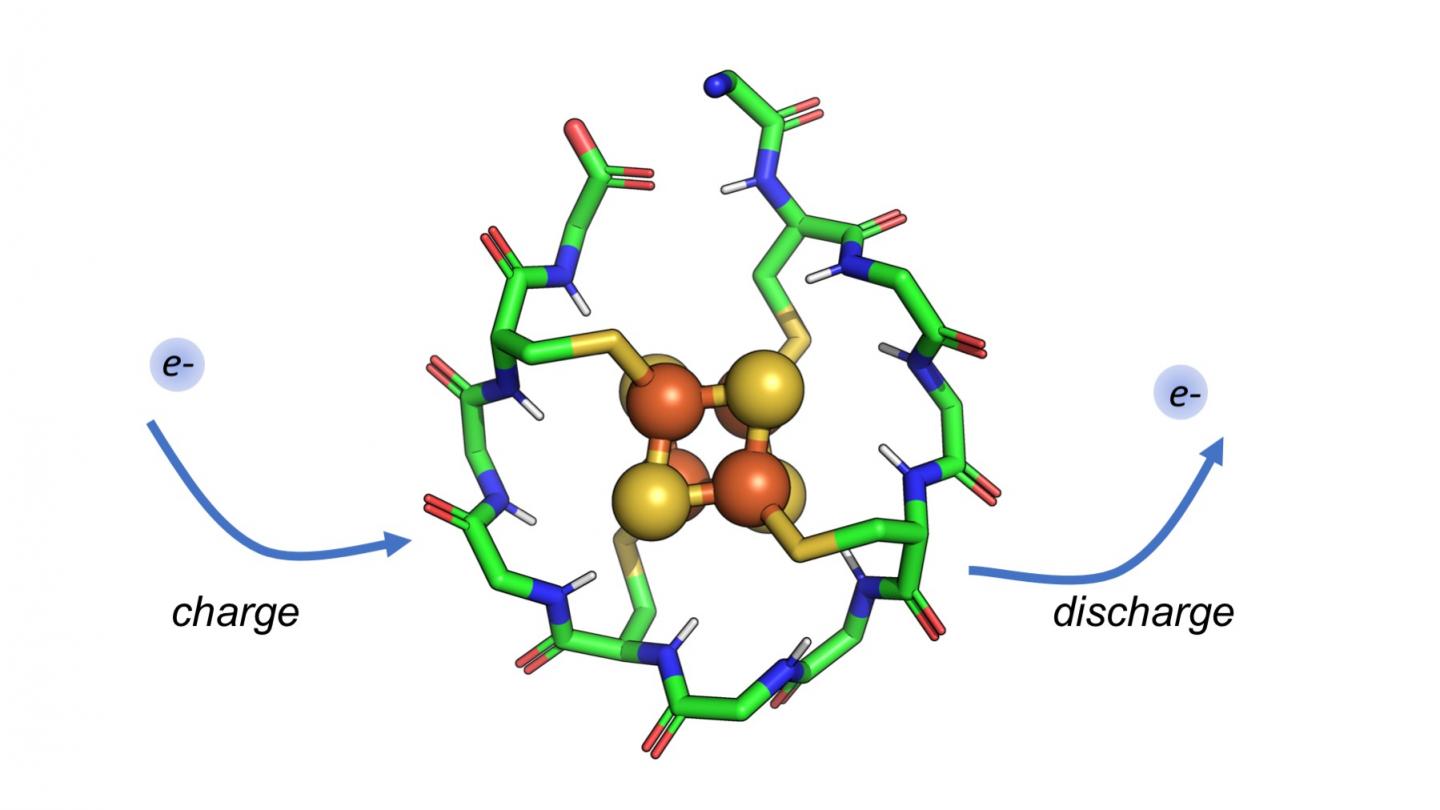
The scientists used computers to model a short, 12-amino acid protein and tested it in the laboratory. This peptide has several impressive and important features. It contains only two types of amino acids (rather than the estimated 20 amino acids that synthesize millions of different proteins needed for specific body functions), it is very short and it could have emerged spontaneously on the early Earth in the right conditions. The metal cluster at the core of this peptide resembles the structure and chemistry of iron-sulfur minerals that were abundant in early Earth oceans. The peptide can also charge and discharge electrons repeatedly without falling apart, according to Nanda, a resident faculty member at the Center for Advanced Technology and Medicine.
"Modern proteins called ferredoxins do this, shuttling electrons around the cell to promote metabolism," said senior author Professor Paul G. Falkowski, who leads Rutgers' Environmental Biophysics and Molecular Ecology Laboratory. "A primordial peptide like the one we studied may have served a similar function in the origins of life."
Falkowski is the principal investigator for a NASA-funded ENIGMA project led by Rutgers scientists that aims to understand how protein catalysts evolved at the start of life. Nanda leads one team that will characterize the full potential of the primordial peptide and continue to develop other molecules that may have played key roles in the origins of life.
With computers, Rutgers scientists have smashed and dissected nearly 10,000 proteins and pinpointed four "Legos of life" – core chemical structures that can be stacked to form the innumerable proteins inside all organisms. The small primordial peptide may be a precursor to the longer Legos of life, and scientists can now run experiments on how such peptides may have functioned in early-life chemistry.
###
Study co-lead authors are John Dongun Kim, postdoctoral researcher, and graduate student Douglas H. Pike. Other authors include Alexei M. Tyryshkin and G.V.T. Swapna, staff scientists; Hagai Raanan, postdoctoral researcher; and Gaetano T. Montelione, Jerome and Lorraine Aresty Chair and distinguished professor in the Department of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry. He is also a resident faculty member at the Center for Advanced Technology and Medicine.
Media Contact
John Cramer
[email protected]
848-932-7311
@RutgersU
http://www.rutgers.edu
Original Source
https://news.rutgers.edu/rutgers-scientists-identify-protein-may-have-existed-when-life-began/20180829#.W4gyjuhKi70 http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b07553