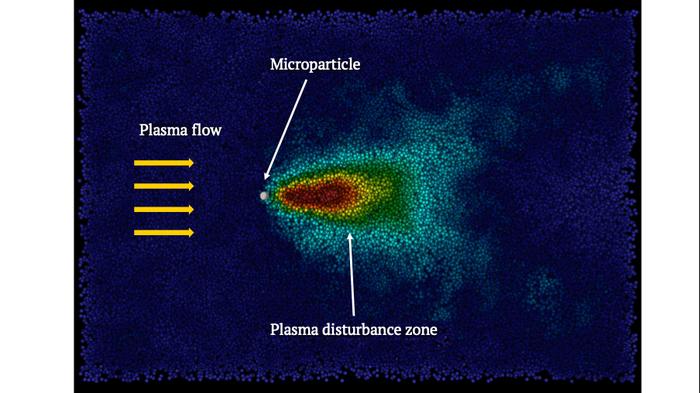
Understanding the mechanisms of interaction between plasma and microparticles is of a critical importance in various fields, including astrophysics, microelectronics, and plasma medicine. A common experimental approach for studying interactions between plasma and microparticles is to place microparticles in a flowing plasma of a gas discharge. In order to achieve a more accurate understanding of the processes occurring in such systems, scientists need fast and efficient tools for calculating forces acting on microparticles in a plasma flow.
Credit: HSE
Understanding the mechanisms of interaction between plasma and microparticles is of a critical importance in various fields, including astrophysics, microelectronics, and plasma medicine. A common experimental approach for studying interactions between plasma and microparticles is to place microparticles in a flowing plasma of a gas discharge. In order to achieve a more accurate understanding of the processes occurring in such systems, scientists need fast and efficient tools for calculating forces acting on microparticles in a plasma flow.
Typically, plasma-physicists have to independently develop software tailored to a specific task, which is a significant investment of time and resources. Existing open-source programs frequently encounter challenges related to installation, documentation, and sluggish performance. A group of scientists from the JIHT, the HSE and, MIPT have developed a novel solution: a fast, open-source code which is easy to install and extensively documented.
The outcome—OpenDust—performs ten times faster than existing analogues. In order to accelerate calculations, the algorithm uses multiple GPUs simultaneously.
“OpenDust has a flexible, user-friendly interface written in Python. Users can define the parameters of a simulated system and configure computational resources. For instance, users have the ability to specify the plasma flow rate and the number of GPU accelerators needed for a calculation. The backend, which is the server component of the product responsible for the internal logic, is optimised for the high-performance computations and harnesses the power of multiple GPUs. This capability enables substantially increase calculations and process larger amount of data”, explains Daniil Kolotinskii, study co-author and OpenDust developer, Junior Researcher at the Joint Institute for High Temperatures RAS.
The code, OpenDust, simulates dynamics of plasma media surrounding a system of microparticles. Scientists can use it to explore intricate physical phenomena within complex plasma, including self-organisation effects and instabilities. Additionally, the code can be applied in various fields of science and industry, such as simulation of plasma purification processes within industrial extreme ultraviolet lithography machines or studying active particle systems.
“Our code is the first-ever open-source program for the multiscale self-consistent simulation of microparticle motion in a plasma flow. OpenDust can serve as a versatile tool for simulating and studying diverse physical phenomena associated with microparticle motion in a plasma flow. The code has both academical and industrial applications. For example, it can facilitate the development of novel methods for efficiently removing dust from plasma in industrial lithography machines”, says Alexey Timofeev, Leading Research Fellow, HSE International Laboratory for Supercomputer Atomistic Modelling and Multi-scale Analysis.
Journal
Computer Physics Communications
DOI
10.1016/j.cpc.2023.108746
Article Title
OpenDust: A fast GPU-accelerated code for the calculation of forces acting on microparticles in a plasma flow
Article Publication Date
29-May-2023




