The 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Alain Aspect, John Clauser, and Anton Zeilinger for their works on “quantum nonlocality” in quantum mechanics. Quantum nonlocality is a phenomenon where connected particles can affect each other instantly, regardless of the distance separated.
Credit: Tohoku University
The 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Alain Aspect, John Clauser, and Anton Zeilinger for their works on “quantum nonlocality” in quantum mechanics. Quantum nonlocality is a phenomenon where connected particles can affect each other instantly, regardless of the distance separated.
Imagine you owned a pair of gloves. These gloves are a pair and therefore correlated in some way, no matter how far apart they are. One day, you place one of the gloves into your backpack and hop on a flight to travel to another country, while the other glove remains at home. According to quantum nonlocality, if you changed the color of the glove you brought with you, the color of the glove back home would instantaneously change too, despite being separated by a large distance.
Nonlocality violates many of the concepts predicted by classical physics, where particles’ properties are predetermined and change occurs only through direct physical interaction or fields propagated at a finite speed. Nonlocality has a wide array of implications for understanding the future of reality, quantum mechanics, and the development of quantum technologies.
There exist several ways to define and interpret nonlocality. For instance, a set of mathematical expressions called the Bell and CHSH inequalities demonstrates nonlocality by violating inequalities. Meanwhile, Lucien Hardy proposed an alternative interpretation of quantum nonlocality in 1992 when he developed the Hardy Paradox.
Suppose there are three quantities A, B, and C, where A is greater than B and B is greater than C. Intuitively, and according to a fundamental mathematical property known as the transitive property (or local hidden variable theories in physics), this would render A greater than C.
However, Hardy noted that there is still room for a situation where C is greater than A. This violates the transitive property, and such violations are possible in the quantum world when particles are entangled with each other. In other words, this is nonlocality.
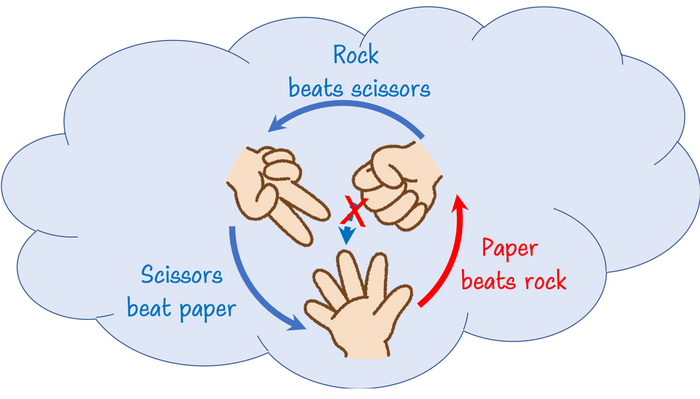
We can use “rock-paper-scissors” to imagine this. While it is evident that rock beats scissors and scissors beat paper, it is impossible for the rock to beat paper. Paper beating rock does not align with any mathematical reasoning, hence why it is a paradox.
A recent study, published in the journal American Physical Review A, has made interesting revelations about the Hardy nonlocality. The study was co-authored by Dr. Le Bin Ho from Tohoku University’s Frontier Research Institute for Interdisciplinary Sciences (FRIS).
“The Hardy nonlocality has significant implications for understanding fundamental quantum mechanics, and it is vital for strengthening the probability of nonlocal,” said Le. “We used quantum computers and methods to investigate the measurement of Hardy nonlocality to improve its probability.”
Le and his colleagues did this by proposing a theoretical framework for attaining a higher nonlocal probability. They verified this by using a theoretical model and a quantum simulation.
Despite previous studies showing the opposite, they discovered that nonlocal probability increases as the number of particles grows. This suggests that quantum effects persist even at larger scales, further challenging classical theories of physics.
Le says these findings have important ramifications for understanding quantum mechanics and its potential applications in communications. “Understanding quantum nonlocality can lead to groundbreaking technological advancements, such as the secure transmission of information through quantum communication via nonlocality resources.”
Journal
Physical Review A
DOI
10.1103/PhysRevA.107.042210
Article Title
Increased success probability in Hardy’s nonlocality: Theory and demonstration
Article Publication Date
14-Apr-2023




