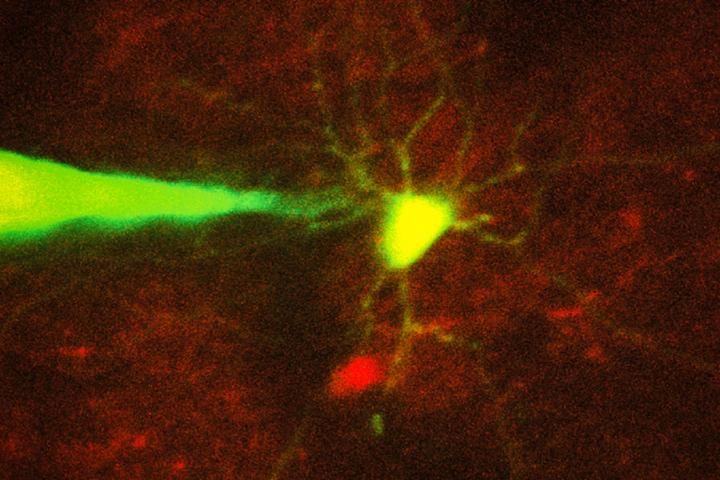
Credit: Ho-Jun Suk
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Recording electrical signals from inside a neuron in the living brain can reveal a great deal of information about that neuron's function and how it coordinates with other cells in the brain. However, performing this kind of recording is extremely difficult, so only a handful of neuroscience labs around the world do it.
To make this technique more widely available, MIT engineers have now devised a way to automate the process, using a computer algorithm that analyzes microscope images and guides a robotic arm to the target cell.
This technology could allow more scientists to study single neurons and learn how they interact with other cells to enable cognition, sensory perception, and other brain functions. Researchers could also use it to learn more about how neural circuits are affected by brain disorders.
"Knowing how neurons communicate is fundamental to basic and clinical neuroscience. Our hope is this technology will allow you to look at what's happening inside a cell, in terms of neural computation, or in a disease state," says Ed Boyden, an associate professor of biological engineering and brain and cognitive sciences at MIT, and a member of MIT's Media Lab and McGovern Institute for Brain Research.
Boyden is the senior author of the paper, which appears in the Aug. 30 issue of Neuron. The paper's lead author is MIT graduate student Ho-Jun Suk.
Precision guidance
For more than 30 years, neuroscientists have been using a technique known as patch clamping to record the electrical activity of cells. This method, which involves bringing a tiny, hollow glass pipette in contact with the cell membrane of a neuron, then opening up a small pore in the membrane, usually takes a graduate student or postdoc several months to learn. Learning to perform this on neurons in the living mammalian brain is even more difficult.
There are two types of patch clamping: a "blind" (not image-guided) method, which is limited because researchers cannot see where the cells are and can only record from whatever cell the pipette encounters first, and an image-guided version that allows a specific cell to be targeted.
Five years ago, Boyden and colleagues at MIT and Georgia Tech, including co-author Craig Forest, devised a way to automate the blind version of patch clamping. They created a computer algorithm that could guide the pipette to a cell based on measurements of a property called electrical impedance — which reflects how difficult it is for electricity to flow out of the pipette. If there are no cells around, electricity flows and impedance is low. When the tip hits a cell, electricity can't flow as well and impedance goes up.
Once the pipette detects a cell, it can stop moving instantly, preventing it from poking through the membrane. A vacuum pump then applies suction to form a seal with the cell's membrane. Then, the electrode can break through the membrane to record the cell's internal electrical activity.
The researchers achieved very high accuracy using this technique, but it still could not be used to target a specific cell. For most studies, neuroscientists have a particular cell type they would like to learn about, Boyden says.
"It might be a cell that is compromised in autism, or is altered in schizophrenia, or a cell that is active when a memory is stored. That's the cell that you want to know about," he says. "You don't want to patch a thousand cells until you find the one that is interesting."
To enable this kind of precise targeting, the researchers set out to automate image-guided patch clamping. This technique is difficult to perform manually because, although the scientist can see the target neuron and the pipette through a microscope, he or she must compensate for the fact that nearby cells will move as the pipette enters the brain.
"It's almost like trying to hit a moving target inside the brain, which is a delicate tissue," Suk says. "For machines it's easier because they can keep track of where the cell is, they can automatically move the focus of the microscope, and they can automatically move the pipette."
By combining several imaging processing techniques, the researchers came up with an algorithm that guides the pipette to within about 25 microns of the target cell. At that point, the system begins to rely on a combination of imagery and impedance, which is more accurate at detecting contact between the pipette and the target cell than either signal alone.
The researchers imaged the cells with two-photon microscopy, a commonly used technique that uses a pulsed laser to send infrared light into the brain, lighting up cells that have been engineered to express a fluorescent protein.
Using this automated approach, the researchers were able to successfully target and record from two types of cells — a class of interneurons, which relay messages between other neurons, and a set of excitatory neurons known as pyramidal cells. They achieved a success rate of about 20 percent, which is comparable to the performance of highly trained scientists performing the process manually.
Unraveling circuits
This technology paves the way for in-depth studies of the behavior of specific neurons, which could shed light on both their normal functions and how they go awry in diseases such as Alzheimer's or schizophrenia. For example, the interneurons that the researchers studied in this paper have been previously linked with Alzheimer's. In a recent study of mice, led by Li-Huei Tsai, director of MIT's Picower Institute for Learning and Memory, and conducted in collaboration with Boyden, it was reported that inducing a specific frequency of brain wave oscillation in interneurons in the hippocampus could help to clear amyloid plaques similar to those found in Alzheimer's patients.
"You really would love to know what's happening in those cells," Boyden says. "Are they signaling to specific downstream cells, which then contribute to the therapeutic result? The brain is a circuit, and to understand how a circuit works, you have to be able to monitor the components of the circuit while they are in action."
This technique could also enable studies of fundamental questions in neuroscience, such as how individual neurons interact with each other as the brain makes a decision or recalls a memory.
To help other labs adopt the new technology, the researchers plan to put the details of their approach on their web site, autopatcher.org.
###
Other co-authors include Ingrid van Welie, Suhasa Kodandaramaiah, and Brian Allen. The research was funded by Jeremy and Joyce Wertheimer, the National Institutes of Health (including the NIH Single Cell Initiative and the NIH Director's Pioneer Award), the HHMI-Simons Faculty Scholars Program, and the New York Stem Cell Foundation-Robertson Award.
Media Contact
Sarah McDonnell
[email protected]
617-253-8923
@MIT
http://web.mit.edu/newsoffice
Original Source
http://news.mit.edu/2017/robotic-system-monitors-specific-neurons-0830