A team of researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) has identified a mechanism that causes mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s patients resulting in a reduction of the supply of energy to the brain. “This effect is attributable to an RNA modification which has not previously been reported,” said Professor Kristina Friedland of the Institute of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences at JGU. She supervised the related study in collaboration with her colleague Professor Mark Helm. Their results contribute to the better understanding of the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Also involved in the research were groups at the Mainz University Medical Center, the Institute of Molecular Biology (IMB), Université de Lorraine, and the Medical University of Vienna. The corresponding paper has been published in Molecular Psychiatry.
Credit: ill./©: Kristina Friedland / JGU
A team of researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) has identified a mechanism that causes mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s patients resulting in a reduction of the supply of energy to the brain. “This effect is attributable to an RNA modification which has not previously been reported,” said Professor Kristina Friedland of the Institute of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences at JGU. She supervised the related study in collaboration with her colleague Professor Mark Helm. Their results contribute to the better understanding of the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Also involved in the research were groups at the Mainz University Medical Center, the Institute of Molecular Biology (IMB), Université de Lorraine, and the Medical University of Vienna. The corresponding paper has been published in Molecular Psychiatry.
The ‘powerhouse of the cell’ affected by functional disorder
Mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell, are organelles inside cells that are in charge of the provision of energy throughout the body and particularly in the brain. For 95 percent of its energy, the brain is reliant on the metabolism of glucose in the mitochondria. It has long been known that impairment of glucose metabolism occurs in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. This impairment is due to dysfunctioning of the mitochondria induced by the aging process and the build-up of amyloid-beta.
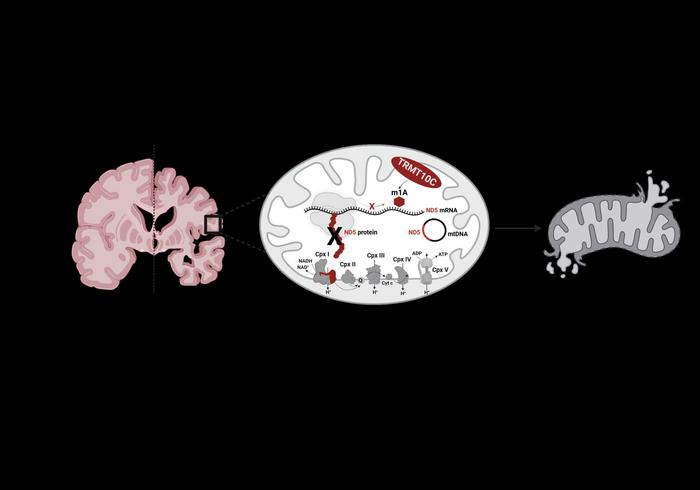
A source of energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is formed in the inner mitochondrial membrane by means of a sequence of reactions known as the respiratory chain. Involved in this process are more than one thousand proteins that are transported from the cellular nuclei to the mitochondria. “But there are also proteins that are synthesized by the mitochondria themselves. One of these is ND5, a subunit of complex I of the respiratory chain,” explained Professor Kristina Friedland. A substance called NADH gives electrons to complex I, which transfers these to ubiquinone, resulting in ubiquinol. During this process, four proteins are pumped from the matrix into the intermembrane space. ND5 plays an important role in this connection and any mutations of the mitochondrial encoded gene of this subunit can result in serious mitochondrial disorders, such as Leigh syndrome.
It has already been demonstrated that the mRNA that provides the instructions for the synthesis of this protein can undergo methylation. In body cells, mRNA carries the genetic information and – together with tRNA – is responsible for its translation into proteins. Methylation of mRNA leads to a change to its chemical structure so that it can no longer correctly interact with tRNA. “The synthesis process is undermined and fewer proteins of the subunit ND5, which is of central relevance to complex I, are formed because the whole process commences with the respiratory chain,” added Friedland.
TRMT10C enzyme causes methylation and thus inhibition of the synthesis of ND5
The teams of Friedland and Helm at the Institute of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences at Mainz University were able to show that it is an enzyme called TRMT10C that induces this methylation and thus the subsequent repression of ND5. The researchers observed suppression of the biosynthesis of proteins of the ND5 subunit in a suitable cell model as well as in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients.
As the authors stated in their article in Molecular Psychiatry: “As a consequence, here demonstrated for the first time, TRMT10C induced m1A methylation of ND5 mRNA leads to mitochondrial dysfunction. Our findings suggest that this newly identified mechanism might be involved in Aβ-induced mitochondrial dysfunction.” The research was funded as part of the Collaborative Research Center / Transregio 319 “RMaP: RNA Modification and Processing”.
Related links:
- https://ak-friedland.pharmakologie.uni-mainz.de/ – Research group of Professor Kristina Friedland at the JGU Institute of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences
- https://www.blogs.uni-mainz.de/fb09-ak-helm-en/ – Research group of Professor Mark Helm at the JGU Institute of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences
- https://www.blogs.uni-mainz.de/fb09-pharmacy/pharmacy/ – Institute of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz
- https://www.imb.de/ – Institute of Molecular Biology (IMB)
- https://www.unimedizin-mainz.de/index.php?id=240&L=1 – Mainz University Medical Center
- https://www.trr319-rmap.de/ – Collaborative Research Center / Transregio 319 “RMaP: RNA Modification and Processing”
Journal
Molecular Psychiatry
DOI
10.1038/s41380-024-02421-y
Article Title
N1-methylation of adenosine (m1A) in ND5 mRNA leads to complex I dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease
Article Publication Date
29-Jan-2024




