Credit: Haga-Yamanaka Lab, UC Riverside
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — A discovery by scientists at UC Riverside may open up new ways to control steroid hormone-mediated processes, including growth and development in insects, and sexual maturation, immunity, and cancer progression in humans.
Published today in Developmental Cell, the researchers used a well-studied fruit fly model to show that a transporter protein is needed for the hormone ecdysone to pass into cells. The work was led by Naoki Yamanaka, an assistant professor of entomology at UCR and a member of the university's Institute for Integrative Genome Biology.
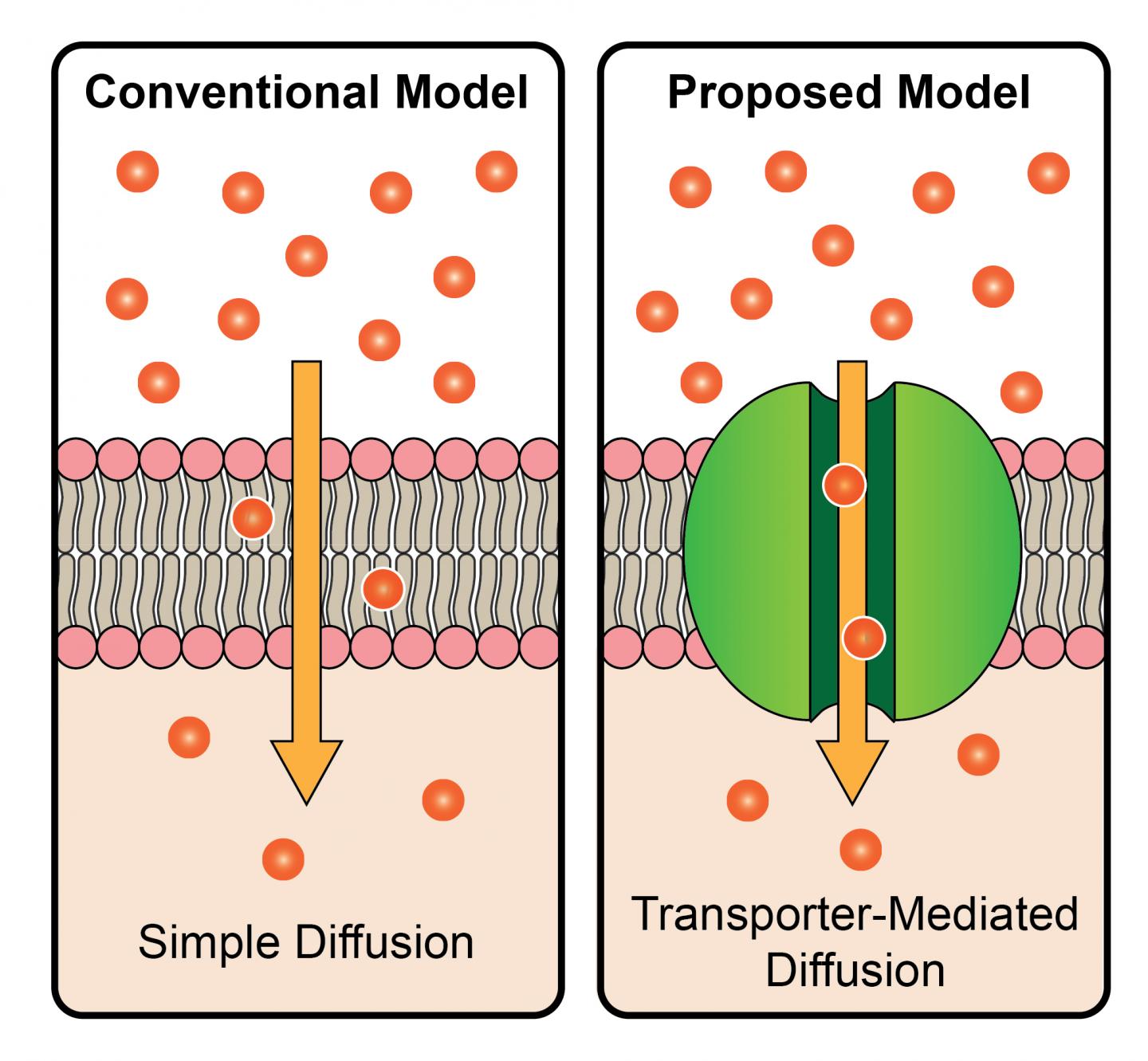
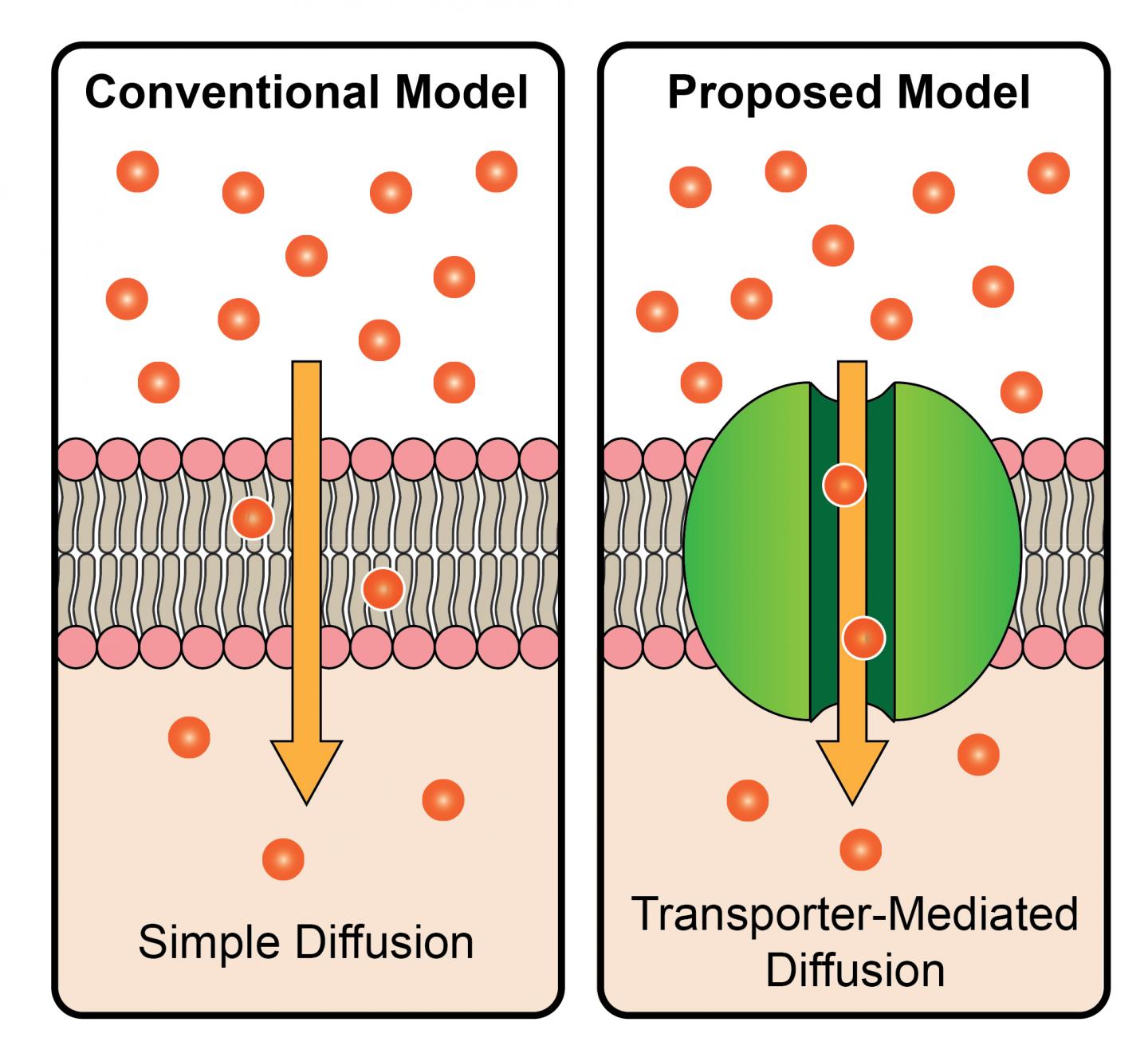
Steroid hormones, which are produced by glands of the endocrine system, must enter cells to exert their biological effects. For decades, the consensus among scientists has been that these chemicals slip freely across cell membranes with no help from cellular transporters. Yamanaka's paper challenges that, describing a defined passageway through which steroid hormones are imported into cells.
The insect hormone studied, ecdysone, activates the genes required for metamorphosis and molting as an insect moves from one stage of its life cycle to the next. Since animal development is a precise process, Yamanaka hypothesized that the intake of required hormones might be regulated.
"Although the simple diffusion model has been prominent for all steroid hormones to date, it seemed logical from a physiological perspective that cells would regulate ecdysone uptake to achieve better control of its concentration," he said.
Using two separate genetic screens, the researchers identified a potential gatekeeper–a transporter they named Ecdysone Importer (EcI). They then used the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing tool to create fruit flies without this transporter, which completely halted their development.
Supported by a $2.3 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Yamanaka will now study the same transport pathway in mosquitoes, hoping to develop chemicals that inhibit steroid hormone entry into cells as a new way of pest control. Worldwide, mosquito-borne diseases cause millions of deaths each year, with malaria alone causing more than 400,000 deaths, according to the World Health Organization.
In a collaboration led by Sachiko Haga-Yamanaka, an assistant professor of molecular, cell, and systems biology, a UCR team is also searching for similar transporters in humans–work that is funded by a $1 million grant from the W. M. Keck Foundation.
"If these transporters are found in humans, it will represent a paradigm shift in endocrinology," Yamanaka said. "It would also open up the exciting possibility of developing chemical reagents that manipulate steroid hormone entry into cells, not just in insects but in humans. This could lead to new ways to manipulate a variety of steroid-related processes ranging from immune responses to cancer progression."
###
The title of the paper is "A Membrane Transporter Is Required for Steroid Hormone Uptake in Drosophila." In addition to Yamanaka and Haga-Yamanaka, authors include Naoki Okamoto and Riyan Bittar from UCR and Raghuvir Viswanatha, Zhongchi Li, and Norbert Perrimon from Harvard Medical School.
The work is funded by the National Institutes of Health (R00 HD073239), the W.M. Keck Foundation and a Pew Biomedical Scholars Award.
Media Contact
Sarah Nightingale
[email protected]
951-827-4580
@UCRiverside
http://www.ucr.edu
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2018.09.012