Niigata, Japan—Scientists have made significant progress in understanding the signals involved in regulating oral keratinocyte cell motility and proliferative capacity, offering new insights into potential pharmacological manipulation for regenerative medicine. A recent study, published in FEBS Open Bio, elucidated the role of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) and its downstream signaling cascade in controlling the behavior of oral keratinocytes.
Credit: Niigata University
Niigata, Japan—Scientists have made significant progress in understanding the signals involved in regulating oral keratinocyte cell motility and proliferative capacity, offering new insights into potential pharmacological manipulation for regenerative medicine. A recent study, published in FEBS Open Bio, elucidated the role of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) and its downstream signaling cascade in controlling the behavior of oral keratinocytes.
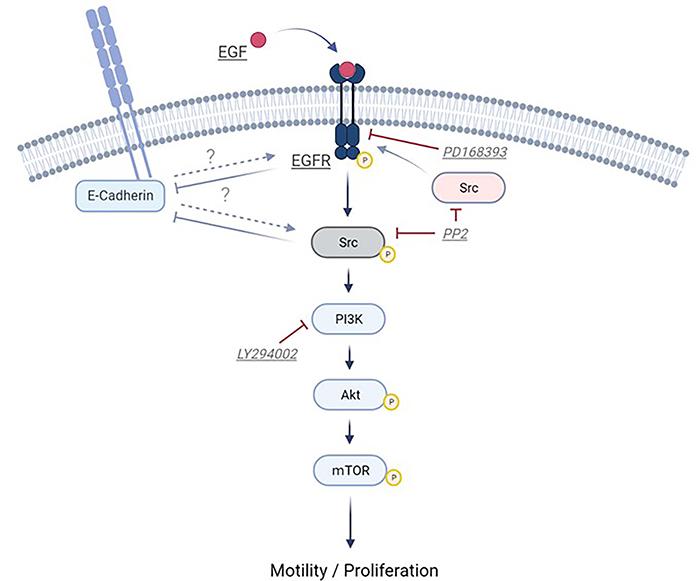
Oral keratinocytes, which play a crucial role in the formation of the oral mucosa epithelial cell sheet, have long been enigmatic in terms of their signaling regulation. However, this study, conducted by a team of researchers based at the Division of Biomimetics, Faculty of Dentistry & Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Niigata University, Japan, highlights the significant involvement of the epidermal growth factor/epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF/EGFR) axis and its downstream signaling cascade, particularly Src/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, in the modulation of oral keratinocyte cell motility and proliferative capacity.
Professor Kenji Izumi and his team examined the impact of growth supplements on oral keratinocyte behavior. They discovered that EGF in the supplement significantly affected cell motility and proliferation. This finding indicates the crucial role of EGF in regulating the behavior and quality of oral keratinocytes.
Interestingly, the study also revealed that the STAT3 and ERK1/2 pathways, previously thought to be major contributors to oral keratinocyte behavior, showed only minor effects. This finding challenges previous studies that reported the motogenic and mitogenic activity of these pathways in normal epithelial cells.
Moreover, the researchers observed reciprocal interaction between Src and EGFR in oral keratinocytes. The activation of Src, a non-receptor tyrosine kinase, appeared to transduce signals from various receptors to internal signaling pathways, affecting cellular events such as survival, adhesion, proliferation, and migration. This interaction between Src and EGFR suggests a potential upstream signal transduction from Src to the EGF/EGFR axis in oral keratinocytes.
The study investigated the connection between EGFR signaling and E-cadherin expression, a crucial molecule for cell adhesion. The researchers discovered that EGFR and Src suppressed E-cadherin expression, thereby affecting cell migration. Understanding this interplay between EGFR signaling and cell adhesion is crucial for future advancements.
The findings of this study provide a foundation for potential pharmacological manipulation of oral keratinocytes for regenerative medicine. By activating the EGF/EGFR signaling pathway and downstream cascades, such as Src/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, it may be possible to enhance the motility and proliferative capacity of oral keratinocytes during ex vivo cell expansion. However, caution must be exercised, as the activation of EGFR/Src signaling may also stimulate oncogenic signals. Speaking in an interview, Prof. Izumi said, “Our results are useful for expanding and culturing cells efficiently. This is because oral mucosa epithelial cell sheets (oral keratinocytes) have been clinically applied to treat diseases and reconstruct tissue defects in cornea, esophagus and urethra.”
This breakthrough research opens up new avenues for the efficient isolation, expansion, and sheet formation of cultured oral keratinocytes, which are essential for the successful clinical translation of epithelial cell sheets. Furthermore, these findings contribute to the understanding of oral keratinocyte behavior and pave the way for future investigations into the complex interplay between different signaling pathways in oral keratinocytes. “Our results provide a clue on pharmacological manipulation of oral keratinocytes for use in regenerative medicine”, added Prof. Izumi.
As the field of regenerative medicine continues to advance, studies like this will be instrumental in developing innovative approaches for tissue engineering and therapeutic applications, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Journal
FEBS Open Bio
DOI
10.1002/2211-5463.13653
Article Title
The EGF/EGFR axis and its downstream signaling pathways regulate the motility and proliferation of cultured oral keratinocytes
Article Publication Date
27-May-2023




