Modelling reveals First Australians arrived in large groups using complex technologies
Credit: Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Australian Biodiversity and Heritage (CABAH)
New insights into how people first arrived in Australia have been revealed by a group of experts brought together to investigate the continent’s deep history.
They used sophisticated modelling to determine not only the likely routes travelled by Aboriginal people tens of thousands of years ago, but also the sizes of groups required for the population to survive in harsh conditions.
The research, published today in two companion papers (one in Scientific Reports and the other in Nature Ecology and Evolution), confirms the theory that people arrived in several large and deliberate migrations by island-hopping to reach New Guinea more than 50,000 years ago.
While many Aboriginal cultures believe people have always been here, others have strong oral histories of ancestral beings arriving from the north.
“We know that Aboriginal people have lived here for more than 50,000 years. This research offers a greater understanding of how migration events took place and further evidence of the marine and navigation capabilities used to make these deliberate journeys,” said Professor Michael Bird, from the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Australian Biodiversity and Heritage (CABAH) and James Cook University.
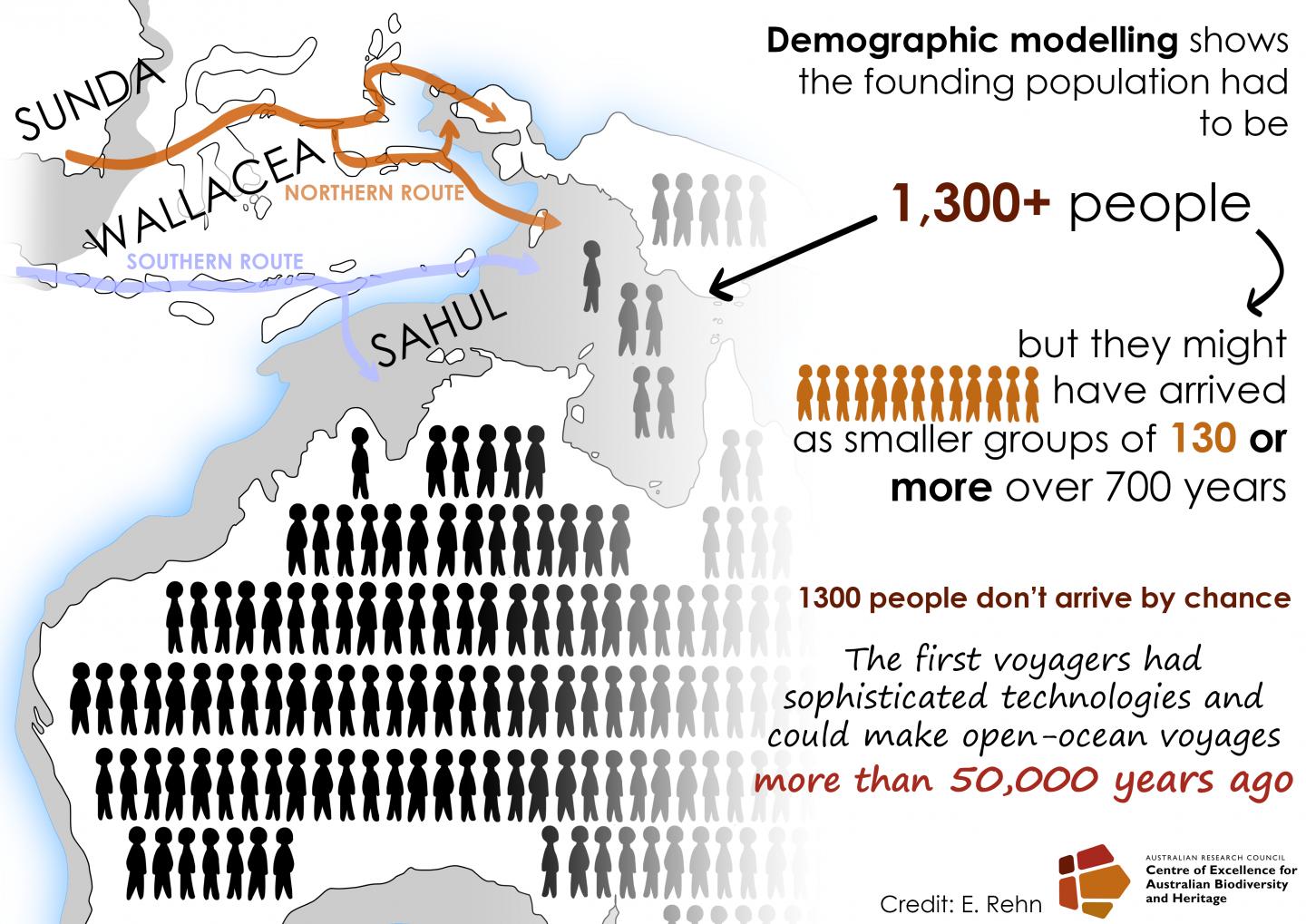
The team of multidisciplinary researchers from CABAH and the CSRIO set out to establish the most likely route travelled to reach the ancient mega-continent, known as Sahul (New Guinea, Australia and Tasmania joined at times of low sea level).
“We developed demographic models to determine which island-hopping route ancient people most likely took,” said CABAH’s Professor Corey Bradshaw, from Flinders University.
“A northern route connecting the islands of Mangoli, Buru, and Seram into West Papua New Guinea would probably have been easiest to navigate and survive. This route was easiest when compared to the southern route from Timor that leads to the now-drowned Sahul Shelf in the modern-day Kimberley region.”
The researchers also used complex mathematical modelling — considering factors including fertility, longevity, past climate conditions, and other ecological principles — to calculate the numbers of people required for the population as a whole to survive.
The simulations indicate that at least 1300 people arrived in either a single migration event or smaller, successive waves averaging at least 130 people every 70 years or so, over the course of about 700 years.
“This suggests planned and well-organised maritime migration, rather than accidental arrival” Professor Bradshaw added.
The studies confirm the ancestors of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people possessed sophisticated technology and knowledge to build watercraft. This research also showcases the remarkable ability at that time to plan, navigate, and make multiple complicated, open-ocean voyages to directly transport large numbers of people.
“Both studies are unique because they relied on past environmental information and did not use any genetic data. We are very excited to see how further archaeological and genetics studies in CABAH can contribute to this story,” says Dr Laura Weyrich, a CABAH investigator at the University of Adelaide.
The papers Early human settlement of Sahul was not an accident and Minimum founding populations for the first peopling of Sahul, were co-authored by scientists from around Australia, including Flinders University, James Cook University, University of Wollongong, University of New South Wales, University of Adelaide, Australian National University, and the CSIRO.
CABAH brings together expertise from diverse academic disciplines to answer fundamental questions about the natural and human history of our region, including how and when people first came to Australia.
###
Media Contact
Corey Bradshaw
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




