Credit: Houston Methodist
Houston Methodist cancer researchers are now closer to creating a blood test that can identify breast cancer patients who are at increased risk for developing brain metastasis, and also monitor disease progression and response to therapy in real time.
The discovery of identifying a distinct group of cells in the bloodstream of patients who have breast cancer brain metastases could lead to the creation of more sensitive screening tools.
[Click here for research explanation by Dario Marchetti, Ph.D.]
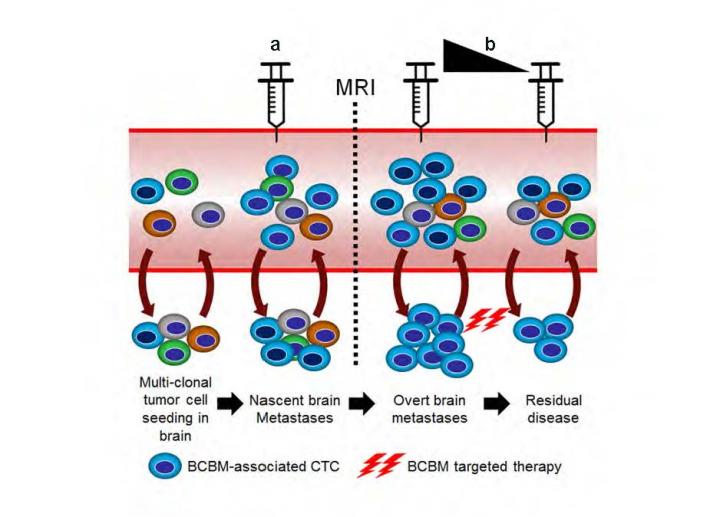
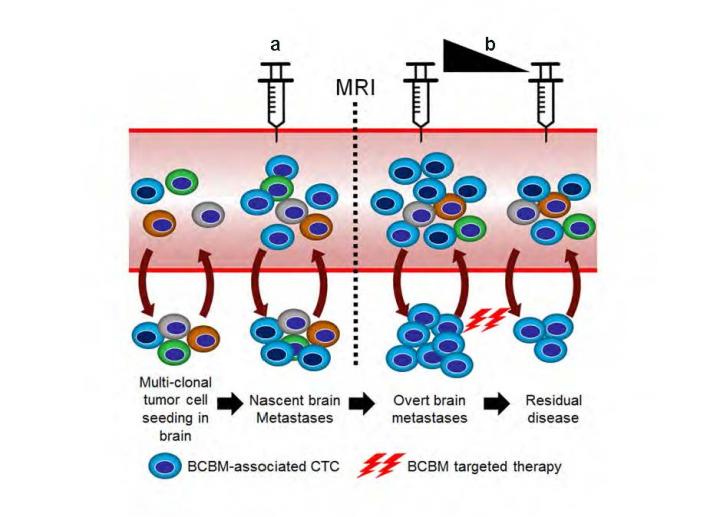
In the Aug. 4 online issue of Nature Communications, a proof-of-concept study led by Dario Marchetti, Ph.D., detected a distinct group of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) associated with brain metastasis. The finding brings cancer researchers closer to understanding how the "seeds" of metastatic disease can thrive in breast cancer patients and cause it to spread to the brain.
"Our research confirmed that CTCs in breast cancer brain metastases are distinct from other circulating tumor cells. Moreover, unlocking the mystery of how these seeds of metastatic disease survive and thrive over a period of years, sometimes decades, is an enigma in cancer," said Marchetti, senior author and director of the Biomarker Research Program at Houston Methodist Research Institute. "Now we can take this information and develop a more sensitive screening tool to detect metastatic cancer in the blood, possibly even before metastasis is radiologically detectable by MRI."
Magnetic resonance imaging is the accepted standard-of-care to diagnose breast cancer brain metastasis (BCBM) in patients. However, in most cases, by the time MRI detects the metastatic mass, the cancer has progressed to a stage where few curative treatment options are available, leading to poor overall survival. According to extensive clinical studies, approximately 20 percent of breast cancer patients will develop brain metastasis over their lifetime, and, in general, metastatic disease to the brain is estimated to become the number one cancer killer within the next decade.
"Our lab is the first in this field to perform a comprehensive report of patient-derived circulating tumor cells at the gene expression level, so we now have a clearer picture of the signaling pathways that allows them to establish brain metastases. By comparing the whole genome expression patterns of CTCs isolated from patient blood samples diagnosed with or without BCBM, we uncovered a 126 gene-signature that is specific to these brain metastatic CTCs," said Debasish Boral, Ph.D., the paper's first author and a research associate with the Biomarker Research Program at Houston Methodist Research Institute.
This research builds on a 2015 research paper where Marchetti's lab isolated four distinct circulating tumor cell subsets that were implicated in breast cancer cell dormancy. Viable breast cancer cells can remain dormant in the patients' bone marrow or other organs like the brain, lungs and liver, even decades after a primary tumor is surgically removed. These scattered cells are often undetectable by traditional clinical tools, making it nearly impossible to detect and treat metastatic disease while still amenable to therapy.
The Houston Methodist researchers are now focused on broadening the study patient population, with the end goal of transforming this information into the development of two kinds of non-invasive liquid biopsies that could be used by treating physicians: a screening method to predict brain metastasis before the disease is detectable by current diagnostic standards (MRI); and another to monitor treatment efficacy in real-time in those patients diagnosed with brain metastasis.
###
Other researchers collaborating on the Nature Communications paper were: Monika Vishnoi, Haowen N. Liu, Wei Yin, and Marc L. Sprouse (Houston Methodist Research Institute, Houston, TX); Jenny C. Chang (Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX); Antonio Scamardo and David S. Hong (The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX); and Tuan Z. Tan and Jean P. Thiery (Cancer Science Institute of Singapore, National University of Singapore).
To speak with Dario Marchetti, Ph.D., contact Gale Smith, Houston Methodist, at 281.627.0439 or [email protected]. For more information about Houston Methodist, visit houstonmethodist.org. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook.
For more information: Molecular characterization of breast cancer CTCs associated with brain metastasis. Nature Communications DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00196-1. (Online Aug. 4, 2017) D. Boral, M. Vishnoi, H. N. Liu, W. Yin, M. L. Sprouse, A. Scamardo, D. S. Hong, T. Z. Tan, J. P. Thiery, J. C. Chang, and D. Marchetti.
Media Contact
Gale Smith
[email protected]
281-627-0439
@MethodistHosp
http://methodisthealth.com
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00196-1