A team of researchers from the Keck School of Medicine of USC have published the first detailed description of the interplay between two cell types that allow lizards to regenerate their tails. This research, funded by the National Institutes of Health and published on August 10 in Nature Communications, focused on lizards’ unusual ability to rebuild cartilage, which replaces bone as the main structural tissue in regenerated tails after tail loss.
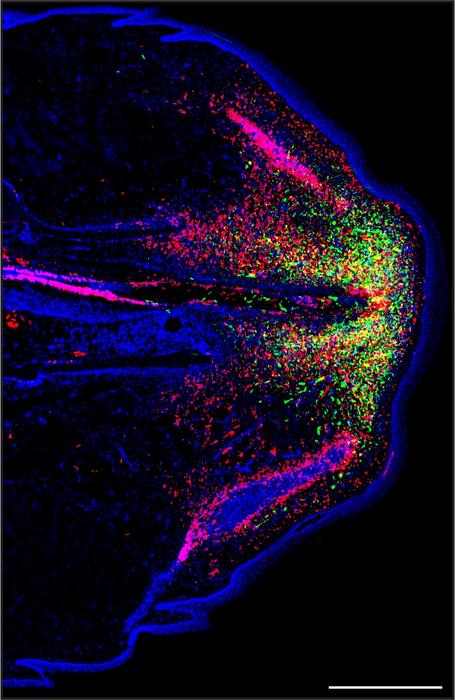
Credit: Ariel Vonk/Lozito Lab
A team of researchers from the Keck School of Medicine of USC have published the first detailed description of the interplay between two cell types that allow lizards to regenerate their tails. This research, funded by the National Institutes of Health and published on August 10 in Nature Communications, focused on lizards’ unusual ability to rebuild cartilage, which replaces bone as the main structural tissue in regenerated tails after tail loss.
The discovery could provide insight for researchers studying how to rebuild cartilage damaged by osteoarthritis in humans, a degenerative and debilitating disease that affects about 32.5 million adults in the United States, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. There is currently no cure for osteoarthritis.
“Lizards are kind of magical in their ability to regenerate cartilage because they can regenerate large amounts of cartilage and it doesn’t transition to bone,” said the study’s corresponding author Thomas Lozito, assistant professor of orthopaedic surgery and stem cell biology and regenerative medicine at the Keck School of Medicine of USC.
Lizards are among the only higher vertebrates capable of regenerating cartilage that does not ossify and are the closest relatives to mammals that can regenerate an appendage with multiple tissue types, including cartilage. Humans, by contrast, cannot repair cartilage that has been damaged once they reach adulthood.
Lozito explained that understanding how organisms with super healing powers regenerate tissue could help researchers find ways to recreate those processes in mammals.
“The dream is to find a way to translate that process in humans because they cannot repair cartilage,” said Lozito. “This represents an important step because we need to understand the process in great detail before we can try to recreate it in mammals.”
Key cells identified
First author Ariel Vonk, who is a PhD student in the Lozito Lab, and the research team determined that cells called fibroblasts, which help build tissue, are the critical cell type that builds cartilage in the lizard’s regenerated tail, the skeletons of which are almost entirely made of cartilage. The research described the changes in gene activity that took place among certain fibroblast cells that enabled cartilage building.
They also discovered that a type of immune cell called a septoclast plays an important role in inhibiting fibrosis, or scarring, allowing the process of regeneration to take place.
“Those two cell types working together laid the foundation for the beginning of the regenerative process,” said Lozito, who noted that a major difference between humans and lizards is that human tissue tends to scar and that scarring prevents tissue regeneration.
One future avenue for research, said Lozito, is to use single-cell RNA sequencing to better describe the molecular mechanisms that halt scarring in lizards so that they can try to recreate the process in mammals.
Cartilage regeneration induced in lizard limbs
Given what they learned about the cell types and molecular processes involved, the team ran tests to determine if they could recreate the process of rebuilding cartilage in lizard limbs which, unlike tails, do not regenerate after a loss.
They extracted septoclasts from lizard tails and implanted them into limbs, which were deficient in pro-regenerative immune cells found to be responsible for inhibiting scarring. They were able to successfully induce cartilage building in a lizard limb by recreating a tail-like signaling environment.
Lozito added that they hope to test whether they can induce cartilage building in mammals, beginning with mice, using the techniques they employed in their experiments on lizard limbs.
About the study
Additional authors of the study include Ariel Vonk, Xiaofan Zhao, Zheyu Pan, Megan Hudnall, Conrad Oakes, Gabriela Lopez, Sarah Hasel-Kolossa, Alexander Kuncz, Sasha Sengelmann, and Darian Gamble from the Keck School of Medicine of USC.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health (R01GM115444), and support from the Molecular Genomics Core at the USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center.
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-023-40206-z
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Single-cell analysis of lizard blastema fibroblasts reveals phagocyte-dependent activation of Hedgehog- responsive chondrogenesis
Article Publication Date
10-Aug-2023




