A multinational team led by researchers from Osaka University use experimental Kelvin probe force spectroscopy to alter the charge states on single oxygen atoms and achieve reversible conversion of oxygen atoms to molecular oxygen
Credit: Osaka University
Osaka, Japan – While pinning down a single oxygen atom sounds difficult, trying to then manipulate electrons associated with that single atom to alter its charge sounds downright impossible. However, for the first time, this achievement has been reported by an international research team led by Osaka University.
Along with collaborators from Slovakia and the United Kingdom, graduate student Yuuki Adachi from Osaka University’s Department of Applied Physics has recently published this research in ACS Nano.
Oxygen is one of the most abundant elements on Earth. Usually found in its diatomic form, O2, oxygen is highly reactive and doesn’t hang around long in a gaseous state. The ground state, or least reactive form of oxygen, is referred to as triplet oxygen because it has three possible arrangements of electron spins. However, singlet oxygen, with its one possible spin arrangement, is more reactive and plays a major role in a diverse range of chemical reactions, ranging from green fuel production to photodynamic cancer treatments.
Unsurprisingly then, there is significant interest in controlling the formation and activation of molecular oxygen.
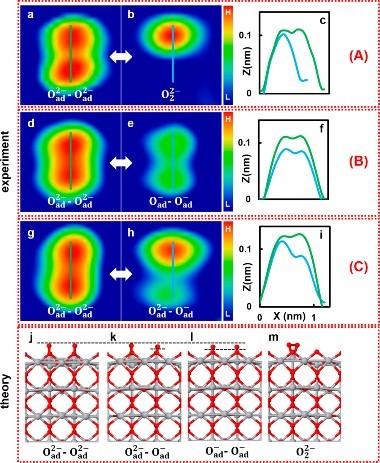
“We used Kelvin probe force spectroscopy to examine the charge states of oxygen atoms attached to a titanium dioxide rutile surface, and to then manipulate the charge through the transfer of individual electrons to and from pairs of oxygen atoms,” explains Adachi. “We identified three different charge states amongst the pairs: O–/O–, O2-/O2-, and O–/O2-. Depending on the applied voltage and where we positioned the tip of the probe relative to the atoms, we could then reversibly switch the charge between the O– and O2- states.”
The team then showed that they could use the same method to induce controlled, reversible bond formation between two adjacent oxygen atoms, forming molecular oxygen (O2).
Interestingly, they also found that the charge state could be controlled remotely by locating the tip elsewhere on the rutile surface. Electrons were transferred to the oxygen atoms via surface polarons, a phenomenon where electrons can travel through a crystal lattice.
“This level of control over the charge state of oxygen atoms has not previously been possible,” says corresponding author of the study Associate Professor Yan Jun Li. “Our work provides a novel method to examine transition-metal-oxide-based catalytic reactions, and can likely be applied to other atoms, and perhaps other surfaces, where controlled chemical reactions initiated by charge manipulation are performed.”
###
The article, “Tip-induced control of charge and molecular bonding of oxygen atoms on the rutile TiO2 (110) surface with atomic force microscopy,” was published in ACS Nano at DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.9b01792
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and now has expanded to one of Japan’s leading comprehensive universities. The University has now embarked on open research revolution from a position as Japan’s most innovative university and among the most innovative institutions in the world according to Reuters 2015 Top 100 Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017. The university’s ability to innovate from the stage of fundamental research through the creation of useful technology with economic impact stems from its broad disciplinary spectrum.
Website: https:/
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




