Widespread adoption of hydrogen-powered vehicles over traditional electric vehicles requires fuel cells that can convert hydrogen and oxygen safely into water – a serious implementation problem.
Researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder are addressing one aspect of that roadblock by developing new computational tools and models needed to better understand and manage the conversion process. Hendrik Heinz, an associate professor in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, is leading the effort in partnership with the University of California Los Angeles. His team recently published new findings on the subject in Science Advances.
Fuel cell electric vehicles combine hydrogen in a tank with oxygen taken from the air to produce the electricity needed to run. They don’t need to be plugged in to charge and have the added benefit of producing water vapor as a byproduct. Those, plus other factors, have made them an intriguing option in the green and renewable energy transportation areas.
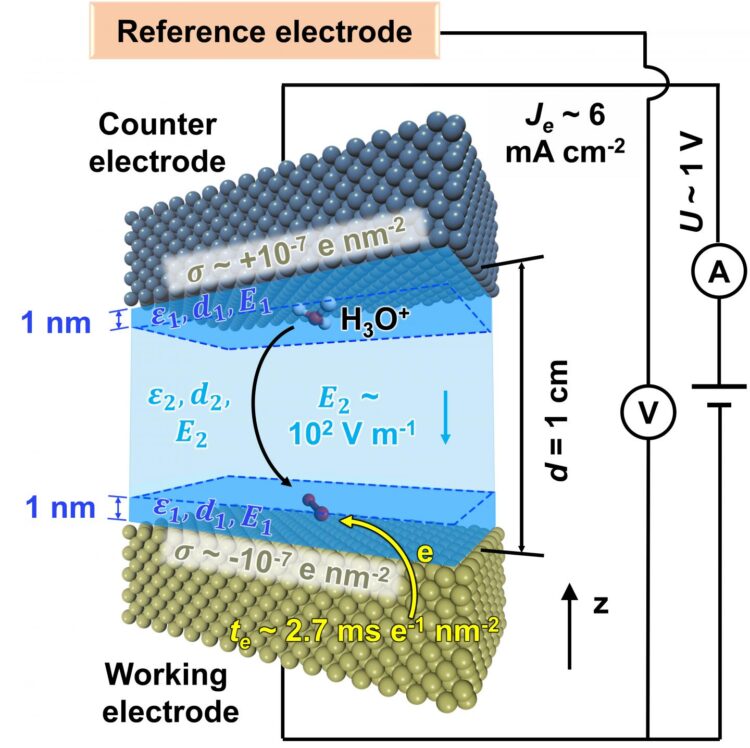
“For decades, researchers have struggled to predict the complex processes needed for this work, though enormous progress has been made using nanoplates, nanowires and many other nanostructures,” Heinz said. “To address this, we have developed models for metal nanostructures and oxygen, water and metal interactions that exceed the accuracy of current quantum methods by more than 10 times. The models also enable the inclusion of the solvent and dynamics and reveal quantitative correlations between oxygen accessibility to the surface and catalytic activity in the oxygen reduction reaction.”
Heinz said the quantitative simulations his team developed show the interaction between oxygen molecules as they encounter different barriers by molecular layers of water on the platinum surface. These interactions make the difference between a slow or fast follow-on reaction and need to be controlled for the process to work efficiently. These reactions happen quite fast – the conversion into water takes about a millisecond per square nanometer to complete – and happen on a tiny catalyst surface. All of those variables come together in an intricate, complex “dance” that his team has found a way to model in predictive ways.
The computational and data-intensive methods described in the paper can be used to create designer-nanostructures that would max out the catalytic efficiency, as well as possible surface modifications to further optimize the cost-benefit ratio of fuel cells, Heinz added. His collaborators are exploring the commercial implication of that aspect, and he is applying the tools to help to study a wider range of potential alloys and gain further insights into the mechanics at play.
“The tools described in the paper, especially the interface force field for order-of-magnitude more reliable molecular dynamics simulations, can also be applied to other catalyst and electrocatalyst interfaces for similar groundbreaking and practically useful advances,” he said.
###
This work was funded by the National Science Foundation. Other partners include the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility and Research Computing at the University of Colorado Boulder.
Media Contact
Kelsey Simpkins
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.