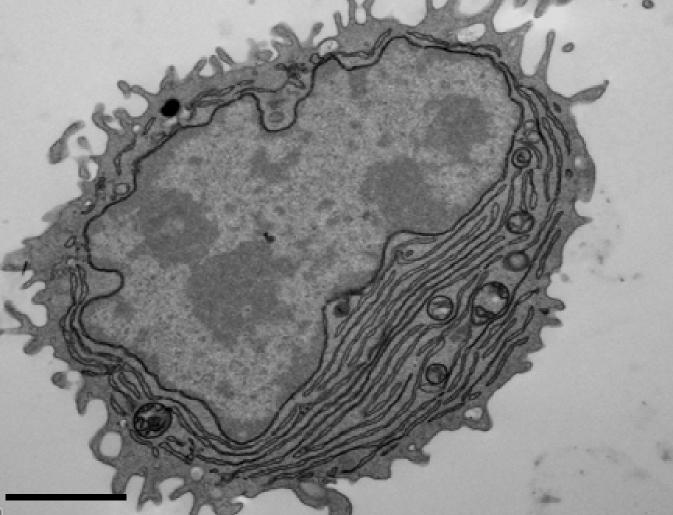
Credit: Sanjuan Nandin et al., 2017
An international team of scientists has developed a method to rapidly produce specific human antibodies in the laboratory. The technique, which will be described in a paper to be published July 24 in The Journal of Experimental Medicine, could speed the production of antibodies to treat a wide range of diseases and facilitate the development of new vaccines.
Antibodies are produced by the body's B cells to fight off infections by bacteria, viruses, and other invasive pathogens. When an individual B cell recognizes a specific pathogen-derived "antigen" molecule, it can proliferate and develop into plasma cells that secrete large amounts of antibody capable of binding to the antigen and fending off the infection.
Researchers have sought to replicate this process in the laboratory to produce specific antibodies from B cells isolated from patient blood samples. However, in addition to encountering a specific antigen, B cells need a second signal to start proliferating and developing into plasma cells. This second signal can be provided by short DNA fragments called CpG oligonucleotides, which activate a protein inside B cells named TLR9. But treating patient-derived B cells with CpG oligonucleotides stimulates every B cell in the sample, not just the tiny fraction capable of producing a particular antibody.
A team of researchers led by Facundo Batista, from the Francis Crick Institute in London and the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT, and Harvard, have been able to produce specific human antibodies in the laboratory by treating patient-derived B cells with tiny nanoparticles coated with both CpG oligonucleotides and the appropriate antigen. With this technique, CpG oligonucleotides are only internalized into B cells that recognize the specific antigen, and these cells are therefore the only ones in which TLR9 is activated to induce their proliferation and development into antibody-secreting plasma cells.
The team successfully demonstrated their approach using various bacterial and viral antigens, including the tetanus toxoid and proteins from several strains of influenza A. In each case, the researchers were able to produce specific, high-affinity antibodies in just a few days. Some of the anti-influenza antibodies generated by the technique recognized multiple strains of the virus and were able to neutralize its ability to infect cells.
The procedure does not depend on the donors having been previously exposed to any of these antigens through vaccination or infection; the researchers were able to generate anti-HIV antibodies from B cells isolated from HIV-free patients.
Batista and colleagues hope that their approach will help researchers rapidly generate therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of infectious diseases and other conditions such as cancer.
"Specifically, it should allow the production of these antibodies within a shorter time frame in vitro and without the need for vaccination or blood/serum donation from recently infected or vaccinated individuals," Batista says. "In addition, our method offers the potential to accelerate the development of new vaccines by allowing the efficient evaluation of candidate target antigens."
###
Sanjuan Nandin et al., 2017. J. Exp. Med. http://jem.rupress.org/cgi/doi/10.1084/jem.20170633?PR
About The Journal of Experimental Medicine
The Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM) features peer-reviewed research on immunology, cancer biology, stem cell biology, microbial pathogenesis, vascular biology, and neurobiology. All editorial decisions are made by research-active scientists in conjunction with in-house scientific editors. JEM provides free online access to many article types from the date of publication and to all archival content. Established in 1896, JEM is published by The Rockefeller University Press. For more information, visit jem.org.
Visit our Newsroom, and sign up for a weekly preview of articles to be published. Embargoed media alerts are for journalists only.
Follow JEM on Twitter at @JExpMed and @RockUPress.
Media Contact
Ben Short
[email protected]
212-327-7053
@RockUPress
http://www.rupress.org/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1084/jem.20170633