Everyone is familiar with glass—from putting on eyeglasses, pushing open the window, standing in front of a mirror, to holding a water glass. Glass is ubiquitous in nature and essential to human life.
Credit: XING Ruirui
Everyone is familiar with glass—from putting on eyeglasses, pushing open the window, standing in front of a mirror, to holding a water glass. Glass is ubiquitous in nature and essential to human life.
But the widespread use of persistent, non-biodegradable glass that cannot be naturally eliminated causes long-term environmental hazards and social burdens.
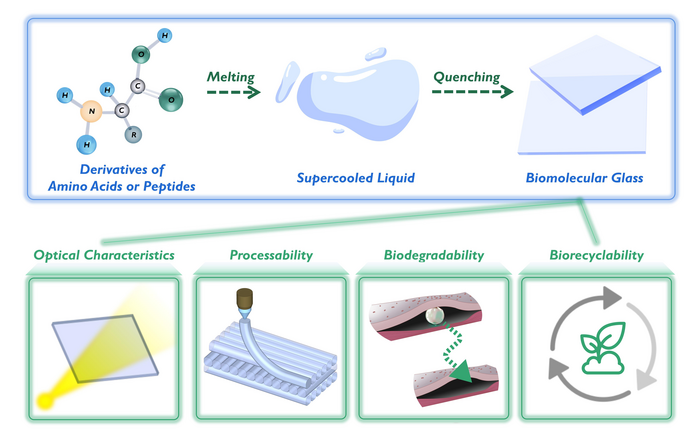
To solve this problem, a research group led by Prof. YAN Xuehai from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a family of eco-friendly glass of biological origin fabricated from biologically derived amino acids or peptides. The proposed glass is biodegradable and biorecyclable.
This study was published in Science Advances on Mar. 17.
Traditional glass, such as commercial inorganic glass and poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) organic glass, etc., is biologically incompatible and not readily degraded in nature. The development of biodegradable and biorecyclable glass is expected to have a minimal environmental footprint.
Unfortunately, manufacturing such eco-friendly glass of biological origin is very challenging because biomolecules possess poor thermal stability and decompose easily at the high temperatures typically used in glass manufacturing.
In this study, the researchers used chemically modified amino acids and peptides to fabricate biomolecular glass with biodegradability and biorecyclability features through the classic “heating-quenching” procedure.
The researchers tracked the glass-forming ability, glass-transition-related kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the material, as well as glass performance in vitro and in vivo.
Surprisingly, the biomolecular glass based on derivatives of amino acids or peptides showed a unique combination of functional properties and eco-friendly features, including excellent optical characteristics, good mechanical properties and flexible processability, as well as the desired biodegradability and biorecyclability. “The concept of biomolecular glass, beyond the commercially-used glasses or plastics, may underlie a green-life technology for a sustainable future,” said Prof. YAN. “However, the biomolecular glass is currently in the laboratory stage, and far from large-scale commercialization.”
Journal
Science Advances
DOI
10.1126/sciadv.add8105
Article Title
Biomolecular glass with amino acid and peptide nanoarchitectonics
Article Publication Date
17-Mar-2023




