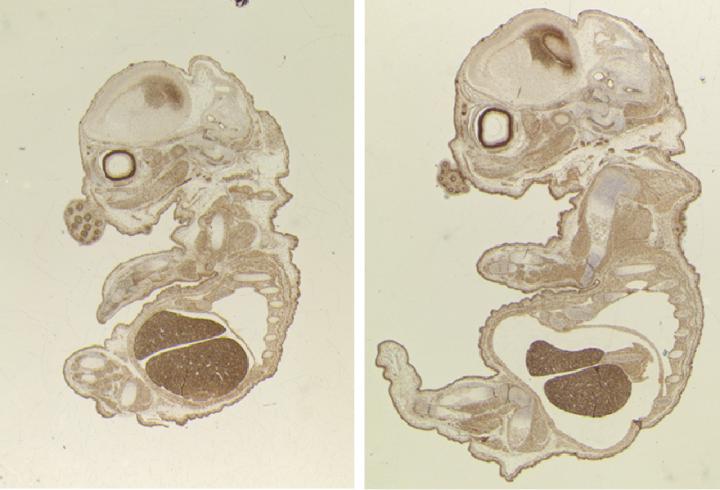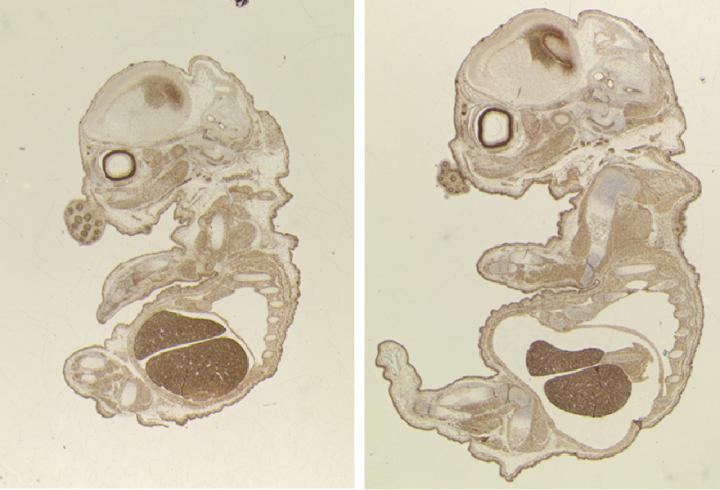
Credit: S. Segura-Bayona, IRB Barcelona
The placenta, a transient organ that links the developing embryo to its mother, is responsible for nutrient, waste and gas exchange between the foetus and the mother. Scientists at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) reveal that the TLK2 gene is vital for the development of the placenta and for embryo viability in mice. The results are published today in the journal Cell Death and Differentiation, which belongs to the Nature group.
In spite of the difference between embryo development in mice and humans, this finding may be of biomedical relevance. Recent clinical data obtained from a massive genomic analysis of people with intellectual disabilities undertaken in the Netherlands detected mutations in 10 new genes, among them TLK2.
Travis H. Stracker, researcher at IRB Barcelona and head of the study, says, "We propose that mutations in the TLK2 gene in humans could result in impaired placental function during embryo development. Placental defects could result in insufficient oxygen during development and cause neurological disorders."
Mice depleted of TLK2 produce a smaller embryo and placenta than normal mice; however, the researchers did not observe morphological defects. Defects in the placenta were found to cause embryo death at day 15 of a 20-day gestation period. The scientists detected a reduction in the expression of genes that are crucial for the differentiation of trophoblasts–a group of specialised cells that supply the embryo with nutrients–and that this reduction impairs the function of the placenta.
A non-essential gene in adults
In this study, the scientists also unveil that TLK2 is non-essential in adult mice. Its "twin" gene TLK1 substitutes for its loss. The absence of one of these genes is compensated by the presence of the other and the animals are normal and healthy and have the same life expectancy.
"It is only when we simultaneously remove both genes that we observe genomic instability, such as chromosome segregation defects or chromosomal aberrations," explains the "la Caixa" PhD student at IRB Barcelona, Sandra Segura-Bayona. She appears as first author of the study together with postdoctoral fellow Philip Knobel, and former student Helena González Burón, who started this study under a "la Caixa" fellowship in 2011 and whose thesis results are included in this article.
The researchers conclude that TLK1 and TLK2 conserve genomic integrity and cell viability and that they have largely redundant functions in adults.
TLK1 and TLK2 in cancer
In the field of cancer, it is known that TLK2 shows increased expression in a subtype of breast tumour and that this increase contributes to cancer progression. Furthermore, TLK1 and TLK2 are involved in cell proliferation, and the activity of these two genes is believed to be necessary for the growth of tumour cells. Given these considerations, both TLK1 and TLK2 may be potential anti-cancer targets.
To address this question, Stracker's lab, which is devoted to studying the relationship between Genomic Instability and Cancer, is working towards the identification of TLK1 and TLK2 inhibitors in order to examine the function of these genes in models of cancer.
###
The study published today has been done in collaboration with researchers from the University of Utrecht, The Netherlands, from the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre in Toronto, Canada, and from the University of Copenhagen, Denmark. The study has been funded through ERDFs granted by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness.
Reference article:
Sandra Segura-Bayona, Philip A Knobel, Helena González-Burón, Sameh A Youssef, Aida Peña-Blanco, Étienne Coyaud, Teresa López-Rovira, Katrin Rein, Lluís Palenzuela, Julien Colombelli, Stephen Forrow, Brian Raught, Anja Groth, Alain de Bruin, and Travis H Stracker
Differential requirement for Tousled-like kinases 1 and 2 in mammalian development
Cell Death and Differentiation (2017): doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.108
Media Contact
Sònia Armengou
[email protected]
34-934-037-255
http://www.irbbarcelona.org
Original Source
https://www.irbbarcelona.org/en/news/researchers-at-irb-barcelona-discover-a-crucial-gene-involved-in-the-development-of-the