Credit: University of Illinois
Research at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign has provided the first evidence that viruses and hosts share highly similar regulatory sequences in their promoters–the initiation sequences of human genes that code for functional proteins.
"To date viral-host networks include protein and mRNA interactions between viruses and their hosts at later stages of gene expression, but our discovery of genetically coupled promoters is novel. They present an additional layer of regulatory synchrony between virus and host, established and poised before either expresses their protein products," explained Roy Dar, an assistant professor of bioengineering at Illinois.
Latent or dormant HIV infected cell reservoirs have been identified as the major barrier towards a cure due to their ability to spontaneously reactivate after removal of antiretroviral therapy. Leading strategies for eradication of HIV attempt to reactivate the whole latent reservoir and clear it with current drug cocktails, a process referred to as 'shock and kill' therapy.
"Promoters of genes coded within our DNA and the HIV-1 viral promoter which initiates active replication of the virus are strongly coupled in their regulation leading to co-expression–potentially for a viral fitness advantage. In this study, we investigated a specific T-cell migratory pathway that HIV has coupled to, gaining therapeutic insights currently unknown to the HIV cure research community," Dar added.
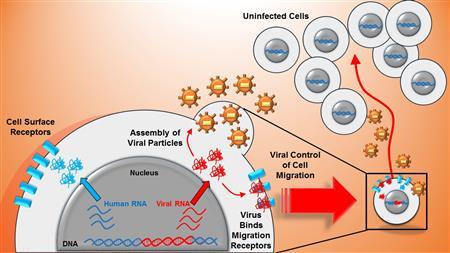
Promoter similarity of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and a human surface receptor allows shared activators to co-regulate viral-host gene expression (blue and red in the cell nucleus). Viral proteins bind cell surface receptors enabling viral control of host cell migration (right side). Those same viral proteins form viral offspring which are shed from the host cell and increase infectious risk to the moving cell's environment.
Promoter similarity of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and a human surface receptor allows shared activators to co-regulate viral-host gene expression (blue and red in the cell nucleus). Viral proteins bind cell surface receptors enabling viral control of host cell migration (right side). Those same viral proteins form viral offspring which are shed from the host cell and increase infectious risk to the moving cell's environment.
Within the systems and synthetic biology fields, the group's findings reveal an additional layer of regulation with which viruses co-evolve with coding-genes and interlace pathways in their hosts.
"The study also presents a mechanism for synchronizing initiation of gene expression in synthetic gene circuitry," stated Kathrin Bohn-Wippert, a postdoctoral researcher and first author of the paper, "Genetic coupling of viral-host gene expression presents migratory challenges in HIV therapies" (10.1038/NCOMMS15006), appearing in Nature Communications. "Specifically, in this framework of viral-host genetic coupling we found that the HIV and human CXCR4 promoters are co-regulated and co-expressed. CXCR4 is a chemokine receptor involved in one of the major migratory pathways throughout our body."
"We have demonstrated, for the first time, that the virus co-expresses with the receptor in order to control infected cell migration and its importance in HIV 'shock and kill' eradication strategies (therapies towards a cure). We also demonstrated how drug treatments can differentially control infected cell migration and/or reactivation of the virus from its latent and inactive state," she said.
According to the researchers, additional network mapping of the coevolution of virus and host-cell gene regulatory coupling will guide future therapeutic strategies, expand systems biology efforts on viral-host networks, and provide novel design principles to reverse bioengineer viral circuitry for synthetic biology and gene therapies.
"For the HIV Cure Community we hope this study will raise awareness to the added challenges facing leading strategies towards a cure," remarked Dar, who is also affiliated with the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology and the Center for Biophysics and Quantitative Biology at Illinois. "We hope this study will provide new insights to exploit viral-host relationships and viral control of cell migration for advanced therapeutic strategies."
###
Co-authors include Melina Megaridis and Erin Tevonian, both bioengineering undergraduate researchers, in the Illinois Cancer Scholars Program, and in the Dar "Noise Biology" Lab.
Media Contact
Roy Dar
[email protected]
217-265-0708
@EngineeringAtIL
http://engineering.illinois.edu/
Original Source
http://engineering.illinois.edu/news/article/21785 http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/NCOMMS15006