Scholars from HSE University and the RAS Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry have demonstrated the efficiency of T-cell immune response against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. In approximately 90% of vaccinated Europeans, T-cell immunity was as effective against Omicron as with other variants. The results of the study were published in PeerJ.
Credit: S.Nersisyan et al.
Scholars from HSE University and the RAS Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry have demonstrated the efficiency of T-cell immune response against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. In approximately 90% of vaccinated Europeans, T-cell immunity was as effective against Omicron as with other variants. The results of the study were published in PeerJ.
The Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 caused a new wave of the global pandemic. The new mutations help the virus spread more effectively and avoid antibodies, which is why those who have already had the disease or who have been vaccinated are getting infected more often. At the same time, recent data shows that the severity of the disease in vaccinated patients is significantly lower than in people who have not contacted the virus.
The researchers assume that this can be explained by several factors. First, the Omicron variant is slower at infecting the human cells; second, there is a hypothesis that a lighter course of the disease is related to effective action of T-cell immunity.
To confirm this assumption, a team of researchers from the HSE Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology and the RAS Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry (Stepan Nersisyan, Anton Zhiyanov, Alexey Galatenko, Maxim Shkurnikov, Maria Zakharova, Irina Ishina, Inna Kurbatskaia, Azad Mamedov, Alexander Gabibov, and Alexander Tonevitsky) studied the Omicron variant for mutations that help it avoid the T-cell immune response.
The development of T-cell response starts from the recognition of virus peptides (short fragments of proteins) with the molecules of the human major histocompatibility complex (HLA). The more peptides that are recognised, the faster and more efficient T-cell immunity is. Virus mutations can change such peptides, which is why they can stop being recognised by HLA molecules, and the T-cell response will be less effective.
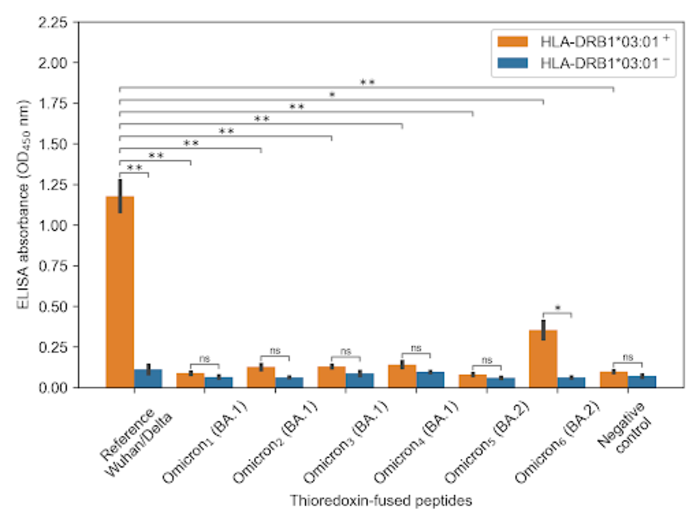
T-CoV, a bioinformatics algorithm, demonstrated that the Omicron variant avoided none of the HLA molecule variants. But it detected several HLA molecule variants that started to become less effective at recognizing the Omicron’s S-protein. An outstanding discovery was the HLA-DRB1*03:01 variant of the molecule. The most important peptide of the virus managed to avoid it. Interestingly, both types of Omicron, BA.1 and BA.2 (also known as ‘Stealth’), evaded immune response recognition, though this was achieved by completely different mutations.
The bioinformatics calculations were verified experimentally in a laboratory. The researchers proved that there is no binding between Omicron peptides and HLA-DRB1*03:01 molecule, which was expressed in vitro.
The researchers emphasise that the initial peptide from the Wuhan basic variant, as well as Delta peptide, are recognised effectively by this molecule.
The authors emphasise that the detected HLA-DRB1*03:01 variant is present in a big share of the global population: for example, in 8.9% of Europeans.
‘The population diversity of HLA molecules, as well as the specificity of their work do not let the virus avoid the T-cell immune response. But the virus has managed to hide its S-protein from one of the HLA molecules. Importantly, most of COVID-19 vaccines (Sputnik V, Pfizer, Moderna, AstraZeneca and some others) carry specifically this virus protein. This means that people with the variant HLA-DRB1*03:01 (who make up 9% of Europe’s population, for example) vaccinated by S-protein may suffer from a more severe course of the disease caused by the Omicron variant,’ said Alexander Tonevitsky, Dean of the HSE Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology.
Journal
PeerJ
DOI
10.7717/peerj.13354
Article Title
Alterations in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta peptides presentation by HLA molecules
Article Publication Date
27-Apr-2022




