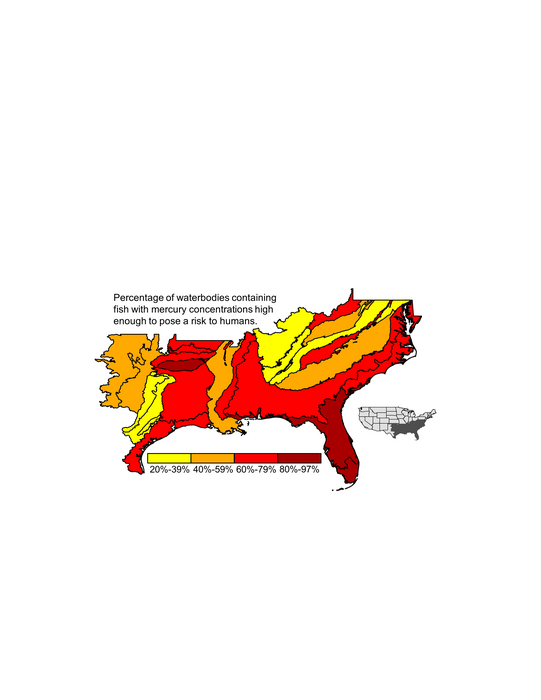
Consuming methylmercury-contaminated fish poses a hazard to human health. New research published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry may help environmental resource management officials predict which regions are likely to have fish with high concentrations of this toxin, without the need for extensive testing.
Credit: Effect of Land Cover on Ecoregion-Scale Spatial Patterns of Mercury Contamination of Largemouth Bass in the Southeastern US
Chumchal, M. et al
First published: 17 August 2022
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/etc.5426
Consuming methylmercury-contaminated fish poses a hazard to human health. New research published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry may help environmental resource management officials predict which regions are likely to have fish with high concentrations of this toxin, without the need for extensive testing.
Investigators found that 72% of the variance in average concentrations of methylmercury in largemouth bass between regions of the Southeastern U.S. could be explained by the percent coverage of land by evergreen forests, emergent herbaceous wetlands, and pasture/hay.
The scientists explain that inorganic mercury from the atmosphere is deposited across the landscape, but that land cover determines how much of this inorganic mercury will be transported to freshwater systems and converted to methylmercury in aquatic environments.
“Our study suggests that monitoring efforts should focus on ecoregions with land cover types that increase the ‘sensitivity’ of water bodies to atmospheric mercury deposition,” said lead author Ray Drenner, PhD, of Texas Christian University. “We hope our study helps resource managers tasked with issuing fish consumption advisories for mercury.”
Journal
Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry
DOI
10.1002/etc.5426
Article Title
Effect of Land Cover on Ecoregion-Scale Spatial Patterns of Mercury Contamination of Largemouth Bass in the Southeastern US
Article Publication Date
17-Aug-2022




