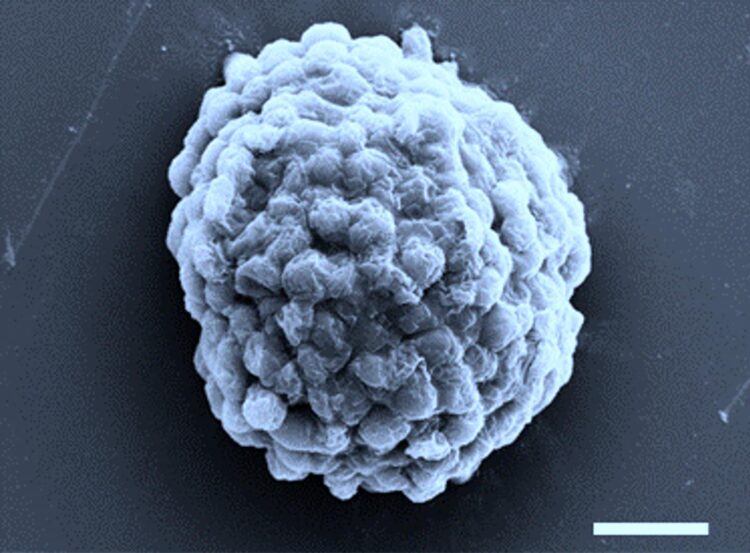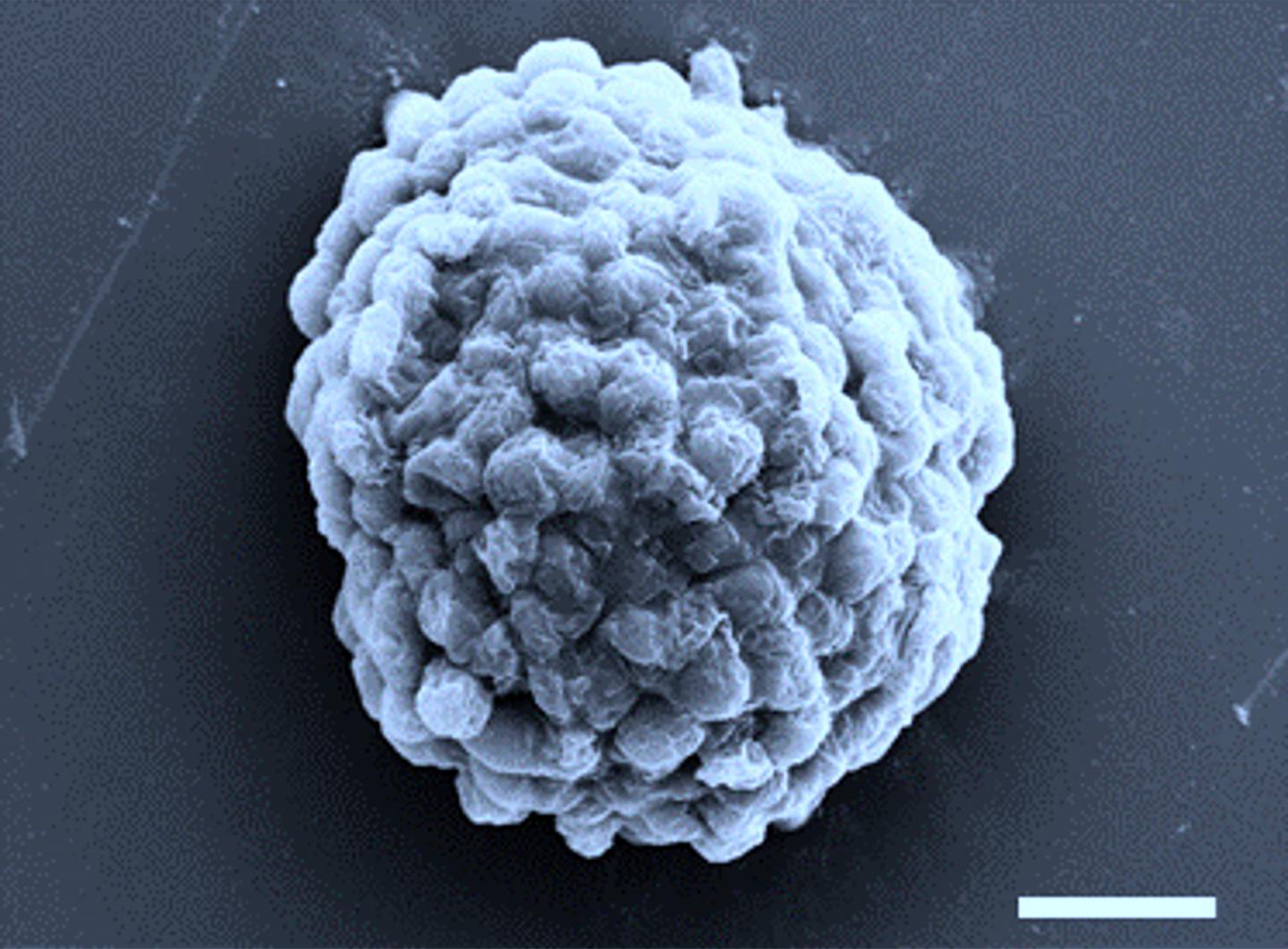
Credit: Prof Xin Huang, Harbin Institute of Technology
Scientists have built tiny droplet-based microbial factories that produce hydrogen, instead of oxygen, when exposed to daylight in air.
The findings of the international research team based at the University of Bristol and Harbin Institute of Technology in China, are published today in Nature Communications.
Normally, algal cells fix carbon dioxide and produce oxygen by photosynthesis. The study used sugary droplets packed with living algal cells to generate hydrogen, rather than oxygen, by photosynthesis.
Hydrogen is potentially a climate-neutral fuel, offering many possible uses as a future energy source. A major drawback is that making hydrogen involves using a lot of energy, so green alternatives are being sought and this discovery could provide an important step forward.
The team, comprising Professor Stephen Mann and Dr Mei Li from Bristol’s School of Chemistry together with Professor Xin Huang and colleagues at Harbin Institute of Technology in China, trapped ten thousand or so algal cells in each droplet, which were then crammed together by osmotic compression. By burying the cells deep inside the droplets, oxygen levels fell to a level that switched on special enzymes called hydrogenases that hijacked the normal photosynthetic pathway to produce hydrogen. In this way, around a quarter of a million microbial factories, typically only one-tenth of a millimetre in size, could be prepared in one millilitre of water.
To increase the level of hydrogen evolution, the team coated the living micro-reactors with a thin shell of bacteria, which were able to scavenge for oxygen and therefore increase the number of algal cells geared up for hydrogenase activity.
Although still at an early stage, the work provides a step towards photobiological green energy development under natural aerobic conditions.
Professor Stephen Mann, Co-Director of the Max Planck Bristol Centre for Minimal Biology at Bristol, said: “Using simple droplets as vectors for controlling algal cell organization and photosynthesis in synthetic micro-spaces offers a potentially environmentally benign approach to hydrogen production that we hope to develop in future work.”
Professor Xin Huang at Harbin Institute of Technology added: “Our methodology is facile and should be capable of scale-up without impairing the viability of the living cells. It also seems flexible; for example, we recently captured large numbers of yeast cells in the droplets and used the microbial reactors for ethanol production.”
###
“Photosynthetic hydrogen production by droplet-based microbial micro-reactors under aerobic conditions” by Xu Z, Wang S, Li S, Liu X, Wang L, Li M, Huang X and Mann S in Nature Communications.
Media Contact
Victoria Tagg
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.