Credit: Kanazawa University
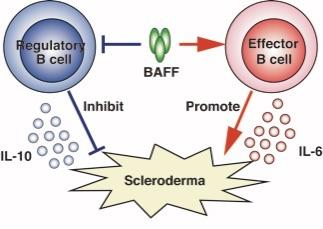
Background: Systemic sclerosis (SSc, also known as scleroderma), a connective tissue disorder of autoimmune etiology, is characterized by excessive fibrosis in the skin and various internal organs. More than 90% of SSc patients carry autoantibodies such as anti-DNA topoisomerase I, anti-centromere, and anti-RNA polymerase antibodies. In addition, B cell activating factor (BAFF) is present at elevated levels in patients with SSc and correlates with disease severity. Thus, B cells are considered to play a pathogenic role in SSc. However, B cells play critical roles in multiple aspects of immunity since they not only mature into antibody-producing cells but also present antigen and produce cytokines. Moreover, not all B cells promote the immune response; indeed, regulatory B cells (Bregs) and effector B cells (Beffs) are known to play opposing suppressive and stimulatory roles, respectively. Studies with human subjects and mouse models of autoimmune diseases have identified interleukin (IL)-10-producing Bregs as negative regulators of the immune response, inflammation, and autoimmunity. In contrast, cytokine-producing Beffs, especially those producing IL-6, positively modulate the immune response through the production of various cytokines. Here, we evaluated the role of IL-6-producing Beffs and IL-10-producing Bregs in the pathogenesis of scleroderma using B cell-specific cytokine-deficient mice.
Results: In mice with bleomycin-induced scleroderma, serum levels of IL-6, but not IL-10, increased in parallel with the development of fibrosis. The number of IL-6-producing Beffs also increased in the spleen and the inflamed skin of mice with scleroderma compared with control mice. Skin and lung fibrosis was attenuated in B cell-specific IL-6-deficient mice, whereas fibrosis was exacerbated in B cell-specific IL-10-deficient mice. Stimulation of splenocytes isolated from naive mice with BAFF caused expansion of Beffs and decreased the number of Bregs, while addition of a BAFF antagonist had the opposite effect. Finally, administration of a BAFF antagonist to mice with scleroderma attenuated the skin and lung fibrosis by modulating the balance of Bregs and Beffs.
Significance and future prospects: The current study indicates that B cells play reciprocal roles in the pathogenesis of SSc, exhibiting both pathogenic and protective functions. Some therapeutic success in SSc has been achieved by targeting B cells. B cell depletion with rituximab, a pan-B cell-depleting anti-CD20 antibody, has shown beneficial effects on skin and lung fibrosis in SSc patients. However, a phase III randomized controlled study will be required to confirm the efficacy and safety of rituximab for these patients. Two large randomized controlled trials of rituximab have been conducted in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE); however, both trials failed to achieve the primary endpoints. Our present findings suggest that these failures may have been due to dual depletion of both Beffs and Bregs by rituximab. Thus, the outcome of pan-B cell depletion may depend on the balance between Beffs and Bregs in each patient. In contrast to rituximab, the anti-BAFF antibody belimumab showed efficacy in phase III trials of patients with SLE and has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. Our results may explain why partial B cell depletion with BAFF inhibition is superior to pan-B cell depletion with a CD20 antibody, since BAFF inhibition selectively depletes Beffs while sparing Bregs. Finally, the results of the current study also suggest that BAFF inhibition and strategic alteration in the balance of Bregs and Beffs could be a potential therapeutic strategy for SSc.
###
Media Contact
Tomoya Sato
[email protected]
81-762-645-076
http://www.kanazawa-u.ac.jp/e/index.html
Original Source
https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aas9944 http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aas9944