Credit: ICFO/URV
Raman spectroscopy is widely used in analytical sciences to identify molecules via their structural fingerprint. In the biological context the Raman response provides a valuable label-free specific contrast that allows distinguishing different cellular and tissue contents. Unfortunately, spontaneous Raman scattering is very weak, over ten orders of magnitude weaker than fluorescence. Unsurprisingly, fluorescence microscopy is often the preferred choice for applications such as live cell imaging. Luckily, Raman can be enhanced dramatically on metal surfaces or in metallic nanogaps and this surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) can even overcome the fluorescence response. Nanometric SERS probes are thus promising candidates for biological sensing applications, preserving the intrinsic molecular specificity. Still, the effectiveness of SERS probes depends critically on the particle size, stability and brightness, and, so far, SERS-probe based imaging is rarely applied.
Now ICFO researchers Matz Liebel and Nicolas Pazos-Perez, working in the groups of ICREA professors Niek van Hulst (ICFO) and Ramon Alvarez-Puebla (Univ. Rovira i Virgili) have presented “holographic Raman microscopy”. First, they synthesized plasmonic superclusters from small nanoparticle building blocks, to generate very strong electric fields in a restricted cluster size. These extremely bright SERS nanoprobes require very low illumination light exposure in the near-infrared, thus reducing potential photo-damage of live cells to a minimum, and allow wide-field Raman imaging. Second, they took advantage of the bright SERS probes to realize 3D holographic imaging, using the scheme for incoherent holographic microscopy developed by Liebel and team in a study in Science Advances (Link). Remarkably, the incoherent Raman scattering is made to “self-interfere” to achieve Raman holography for the first time.
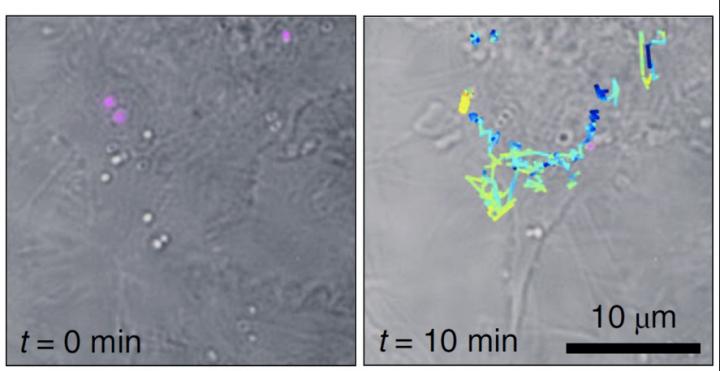
Liebel and Pazos-Perez demonstrated Fourier transform Raman spectroscopy of the wide-field Raman images and were able to localize single-SERS-particles in 3D volumes from one single-shot. The authors then used these capabilities to identify and track single SERS nanoparticles inside living cells in three dimensions.
The results, published in Nature Nanotechnology represent an important step towards multiplexed single-shot three-dimensional concentration mapping in many different scenarios, including live cell and tissue interrogation and possibly anti-counterfeiting applications.
###
Media Contact
Alina Hirschmann
[email protected]




