Queen Mary University of London has become the first university outside of North America to acquire a Cell DIVE imager, providing access to the latest technology and ensuring that we remain world-leading in the fast-moving area of single-cell approaches.
Credit: Queen Mary University of London/Dr Adrian Biddle
Queen Mary University of London has become the first university outside of North America to acquire a Cell DIVE imager, providing access to the latest technology and ensuring that we remain world-leading in the fast-moving area of single-cell approaches.
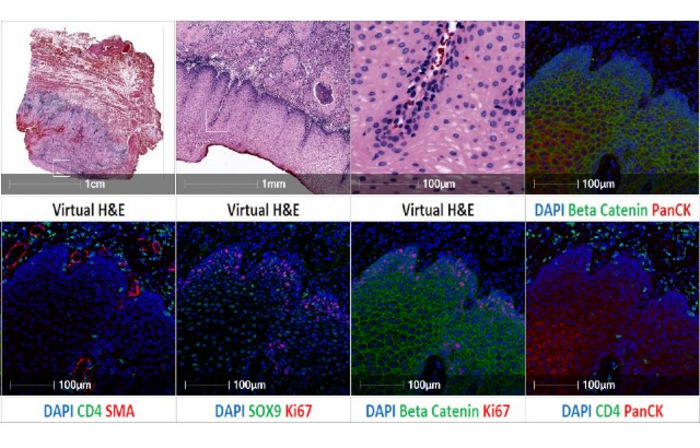
The Cell DIVE provides multiplexed imaging of tissue sections enables high-dimensional tissue imaging for quantitative analysis of at least 60 biomarkers, visualising the inner workings of single cells on a level that was previously unattainable.
What makes this technology platform significant is the integration of biology, precision imaging, sophisticated analysis software to enable deep insights at the single cell level. This offers a powerful approach to understanding the molecular and cellular processes driving tissue pathology in human disease.
The Cell DIVE is the latest addition to the Phenotypic Screening Facility at Queen Mary which is open to all staff across the University and external users and is fully supported by dedicated staff.
Prof. Cleo Bishop, Director of the Queen Mary University of London Phenotypic Screening Facility, said: “We’re excited to have this new technology available for use at the University following a successful Wellcome Trust multi-user equipment grant. The equipment will help us further our understanding of health tissues and heterogeneity within disease.”
“In the past researchers have been able to study how two to three different proteins relate to one another, but the Cell DIVE enables us to visualise more than 60 different proteins on a ‘cell-by-cell’ basis. We can directly relate each of these proteins to one and another within an individual cell, between cells and within the tissue microenvironment. This powerful approach can be used to shed new light on any area of medical research.”
As part of its 2030 strategy, the University is providing a world-class virtual and physical research infrastructure, which is available to all researchers, supported by internal and significant external funding to support academics to pioneer research and innovation.
Queen Mary has been ranked joint seventh in the UK for the quality of its research, according to the Research Excellence Framework 2021; and across the University, 92 per cent of Queen Mary’s research has been assessed as internationally excellent or world-leading according to the REF21 results.
Subject of Research
Cells




