Physicists from UNIGE have discovered a new quantum property: By placing 3 pairs of photons in a network, it is possible to entangle them and create new ultra-strong correlations
Credit: © UNIGE
Entanglement is one of the properties specific to quantum particles. When two photons become entangled, for instance, the quantum state of the first will correlate perfectly with the quantum state of the second, even if they are at a distance from one another. But what happens when three pairs of entangled photons are placed in a network? Researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, working in partnership with Tehran’s Institute for Research in Fundamental Sciences (IPM), have proved that this arrangement allows for a new form of quantum correlation in theory. When the scientists forced two photons from separate pairs to become entangled, the connection was also made with their twin photon present elsewhere in the network, forming a highly-correlated triangle. These results, which you can read all about in the journal Physical Review Letters, create the potential for new applications in cryptography while reviving quantum physics at its most fundamental level.
Entanglement involves two quantum particles – photons, for example – forming a single physical system in spite of the distance between them. Every action performed on one of the two photons has an impact on its “twin” photon. This principle of entanglement leads to quantum non-locality: the measurements and statistics of the properties observed on one of the photons are very closely correlated with the measurements made on the other photon. “Quantum non-locality was discovered theoretically by John Stewart Bell in 1964,” begins Nicolas Brunner, associate professor in the Department of Applied Physics in UNIGE’s Faculty of Science. “This showed that photon correlations are exclusively quantum in nature, and so can’t be explained by conventional physics. This principle could be used to generate ultra-secure encryption keys.”
Is it possible to force photons in a network to become entangled?
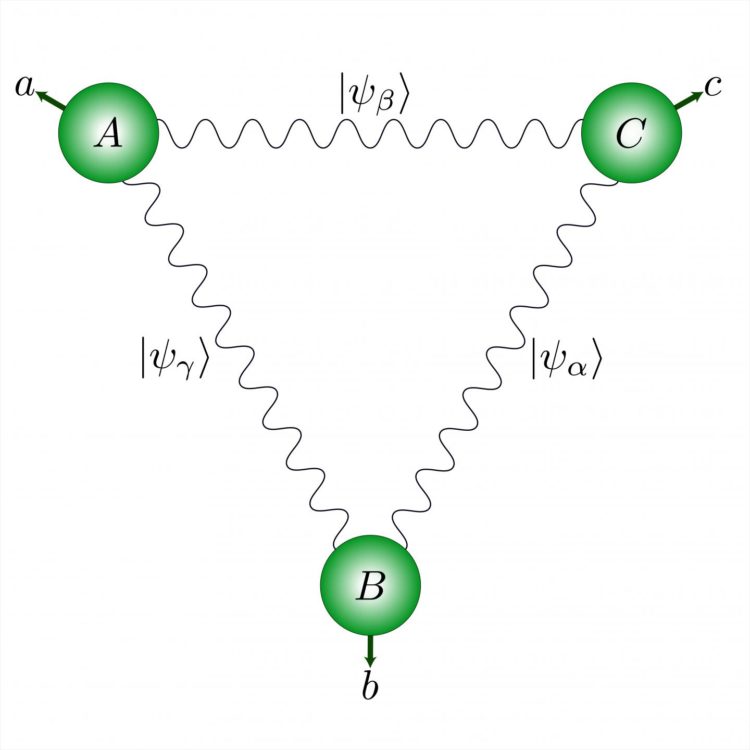
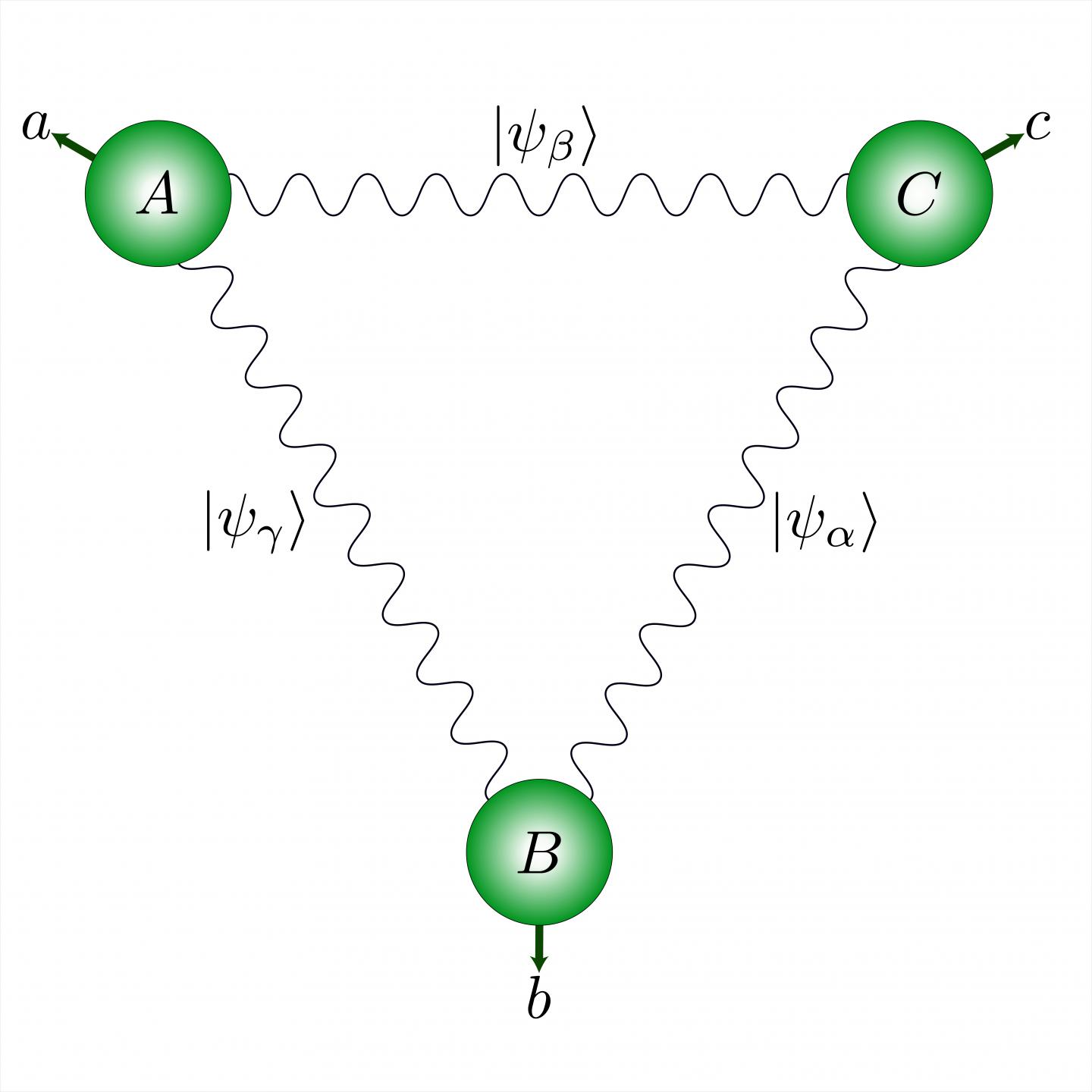
But what are the implications of this principle of quantum non-locality when several pairs of photons are placed in a network? “To answer this question, we devised an experiment involving three pairs of photons that were then separated and dispersed to three points forming a triangle”, explains Marc-Olivier Renou, who is also a researcher in the Department of Applied Physics. “At each vertex, two photons from a different pair are processed together.”
The physicists subsequently forced the two photons at each vertex of the triangle to entangle by making them interact with each other, before measuring them. They finally showed that the statistics arising from these measurements cannot be explained by any local physical theory. In addition, these statistics are so strongly correlated that they could represent a new form of quantum correlations. “It could become a new version of Bell’s theorem, specific to quantum networks”, enthuses Nicolas.
This important theoretical discovery underlines the power of quantum correlations in networks, which far exceeds what researchers had originally thought possible. The next step will be to observe these phenomena in the laboratory. “It’s not going to be child’s play, because conducting an experiment like this is still extremely difficult for the time being”, concludes Nicolas Gisin, a professor in UNIGE’s Department of Applied Physics.
###
Media Contact
Nicolas Brunner
[email protected]
41-223-794-368
Related Journal Article
http://dx.