Credit: Marc Montagut
Very recently, researchers led by Markus Aspelmeyer at the University of Vienna and Lukas Novotny at ETH Zurich cooled a glass nanoparticle into the quantum regime for the first time. To do this, the particle is deprived of its kinetic energy with the help of lasers. What remains are movements, so-called quantum fluctuations, which no longer follow the laws of classical physics but those of quantum physics. The glass sphere with which this has been achieved is significantly smaller than a grain of sand, but still consists of several hundred million atoms. In contrast to the microscopic world of photons and atoms, nanoparticles provide an insight into the quantum nature of macroscopic objects. In collaboration with experimental physicist Markus Aspelmeyer, a team of theoretical physicists led by Oriol Romero-Isart of the University of Innsbruck and the Institute of Quantum Optics and Quantum Information of the Austrian Academy of Sciences is now proposing a way to harness the quantum properties of nanoparticles for various applications.
Briefly delocalized
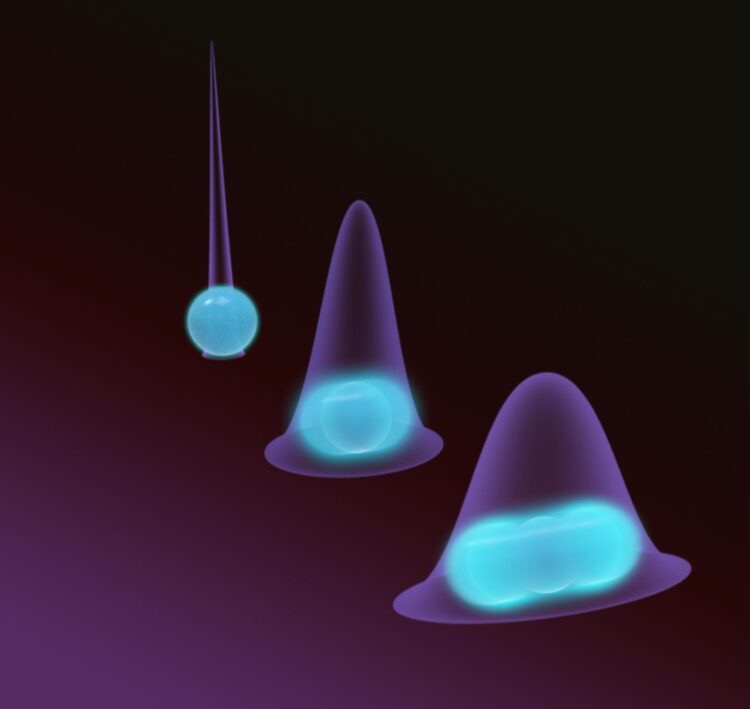
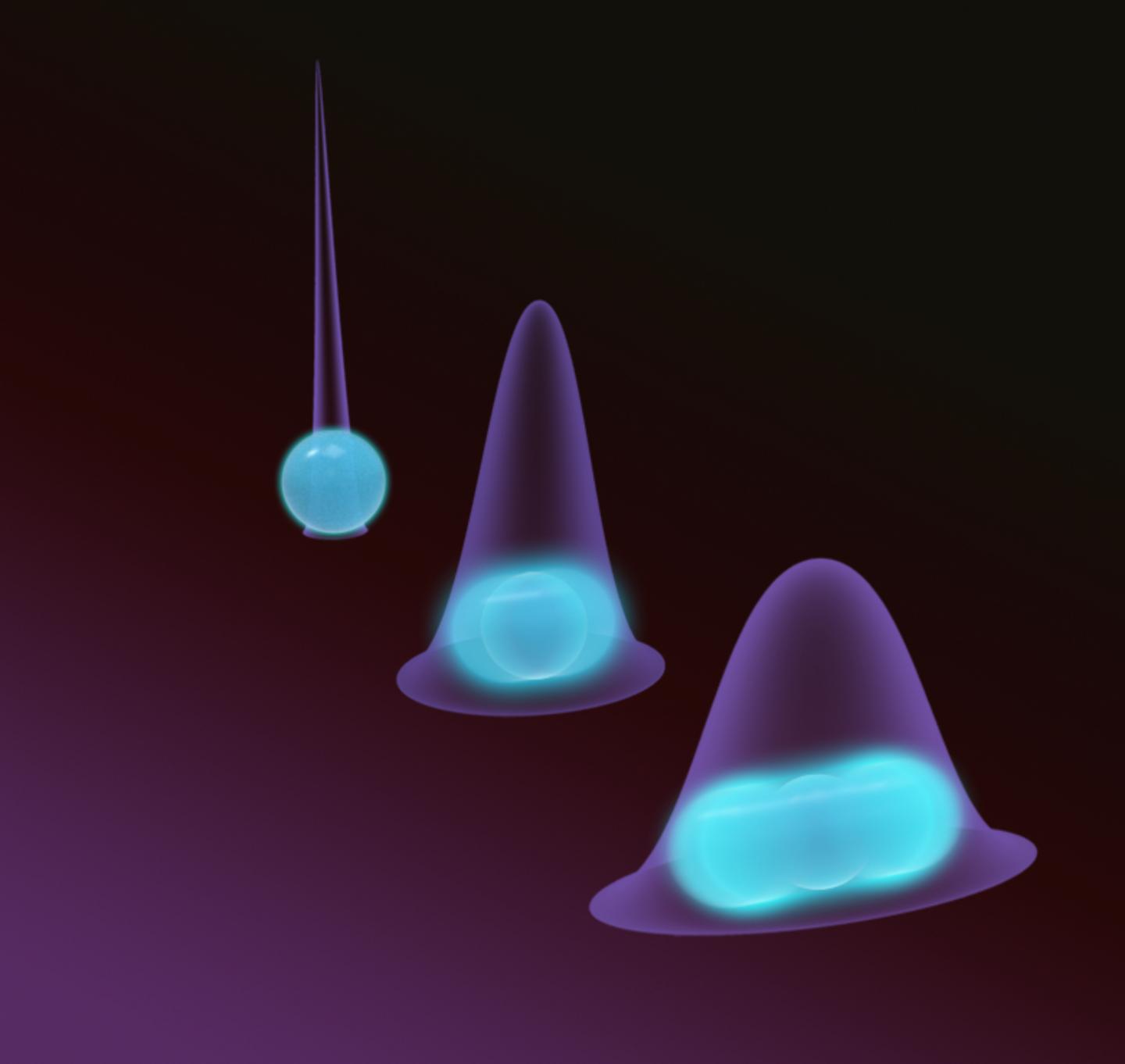
“While atoms in the motional ground state bounce around over distances larger than the size of the atom, the motion of macroscopic objects in the ground state is very, very small,” explain Talitha Weiss and Marc Roda-Llordes from the Innsbruck team. “The quantum fluctuations of nanoparticles are smaller than the diameter of an atom.” To take advantage of the quantum nature of nanoparticles, the wave function of the particles must be greatly expanded. In the Innsbruck quantum physicists’ scheme, nanoparticles are trapped in optical fields and cooled to the ground state. By rhythmically changing these fields, the particles now succeed in briefly delocalizing over exponentially larger distances. “Even the smallest perturbations may destroy the coherence of the particles, which is why by changing the optical potentials, we only briefly pull apart the wave function of the particles and then immediately compress it again,” explains Oriol Romero-Isart. By repeatedly changing the potential, the quantum properties of the nanoparticle can thus be harnessed.
Many applications
With the new technique, the macroscopic quantum properties can be studied in more detail. It also turns out that this state is very sensitive to static forces. Thus, the method could enable highly sensitive instruments that can be used to determine forces such as gravity very precisely. Using two particles expanded and compressed simultaneously by this method, it would also be possible to entangle them via a weak interaction and explore entirely new areas of the macroscopic quantum world.
Together with other proposals, the new concept forms the basis for the ERC Synergy Grant project Q-Xtreme, which was granted last year. In this project, the research groups of Markus Aspelmeyer and Oriol Romero-Isart, together with Lukas Novotny and Romain Quidant of ETH Zurich, are pushing one of the most fundamental principles of quantum physics to the extreme limit by positioning a solid body of billions of atoms in two places at the same time.
###
Media Contact
Oriol Romero-Isart
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.