Bowel ischemia is a potentially fatal medical condition caused by a decrease or obstruction of blood flow to the intestine. It is linked to many serious gastrointestinal disorders that can have long-term and deadly effects. Left untreated, it quickly progresses to irreversible intestinal necrosis that, in turn, leads to fatal metabolic disorders and end-organ dysfunction. As a result, the timely surgical treatment of this condition is critical.
Credit: Yaning Wang, et al
Bowel ischemia is a potentially fatal medical condition caused by a decrease or obstruction of blood flow to the intestine. It is linked to many serious gastrointestinal disorders that can have long-term and deadly effects. Left untreated, it quickly progresses to irreversible intestinal necrosis that, in turn, leads to fatal metabolic disorders and end-organ dysfunction. As a result, the timely surgical treatment of this condition is critical.
The current intraoperative evaluation of bowel perfusion (blood flow to the intestine) is based on subjective assessment of human surgeons, owing to the lack of a reliable marker. This leaves the door open for mistakes with serious long-term health consequences. A quantitative and objective assessment of bowel perfusion is, therefore, imperative.
Now, an international research team has addressed this problem. In a recent study published in the SPIE Journal of Medical Imaging, the researchers developed a deep learning model based on a conditional generative adversarial network (cGAN) and used it to analyze data from laser speckle contrast imaging (LSCI) combined with a visible-light camera to identify regions of abnormal tissue perfusion.
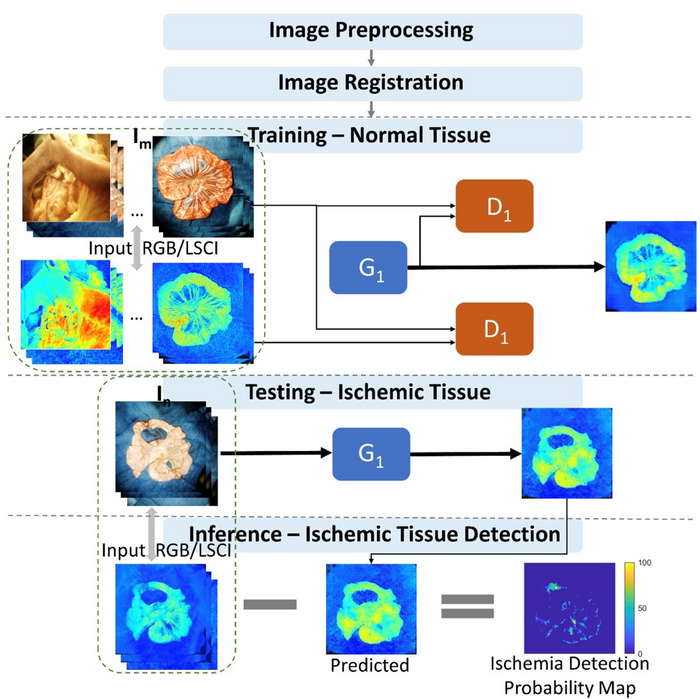
“Our vision platform is built around a dual-modality bench-top imaging system with red-green-blue (RGB) and dye-free LSCI channels. We used a preclinical model to gather data on bowel mesenteric vascular structures with normal/abnormal microvascular perfusion to create a control/experimental group. We then trained our model with the normal dataset and used the abnormal data for testing,” explains the lead author Jaepyeong Cha, Associate Professor and Principal Investigator at the Sheikh Zayed Institute for Surgical Innovation.
cGAN detects ischemic bowel regions by monitoring the erroneous reconstruction from the latent feature space, an embedding space that places items resembling one another close to each other. The main benefit of cGAN is that it is unsupervised, meaning that it does not need any prior manual tagging of data to detect patterns. “In fact, it provides well-defined segmentation results for different levels of ischemia when compared to the traditional qualitative LSCI technique,” highlights Cha.
Using a collection of 2560 RGB/LSCI image pairs, the researchers demonstrated that their model could accurately segment ischemic intestine images with an accuracy of over 93%, which compared favorably with subjective current methods. Multiple and independent estimations were used to label the images, which combined annotations from surgeons with an optimization algorithm called “fastest gradient descent” in suspicious areas of vascular images. For a 256 × 256 image, the total processing time for the deep learning method was a mere fraction (0.05) of a second. Overall, the model outperformed the raw LSCI images in terms of pixelwise probability distribution of intestinal ischemia.
The proposed model provides a pixel-wise and quantitative analysis of intestinal perfusion, making it reliable and superior to the standard procedures – and promising better surgical outcomes. “It has the potential to help surgeons improve the clinical outcomes of mesenteric ischemia and other gastrointestinal surgeries by increasing the accuracy of intraoperative diagnosis,” says Cha. “With a computer-aided detection platform combined with cGAN, they would be able to predict healthy tissue perfusion patterns from color RGB images and recognize ischemic areas at risk.”
Read the Gold Open Access article by Y. Wang et al., “Unsupervised and quantitative intestinal ischemia detection using conditional adversarial network in multimodal optical imaging,” J. Medical Imaging 9(6), 064502, doi 10.1117/1.JMI.9.6.064502.
Journal
Journal of Medical Imaging
DOI
10.1117/1.JMI.9.6.064502
Method of Research
Imaging analysis
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Unsupervised and quantitative intestinal ischemia detection using conditional adversarial network in multimodal optical imaging
Article Publication Date
28-Nov-2022




