Credit: Aalto University
Platinum is a very expensive metal and it is therefore one of the bottlenecks hindering the growth of renewable energy. Platinum is used as the catalyst in electrolysers that store electric energy as chemical compounds, and it also plays an important role in fuel cells, catalytic converters and many chemical processes used in industry.
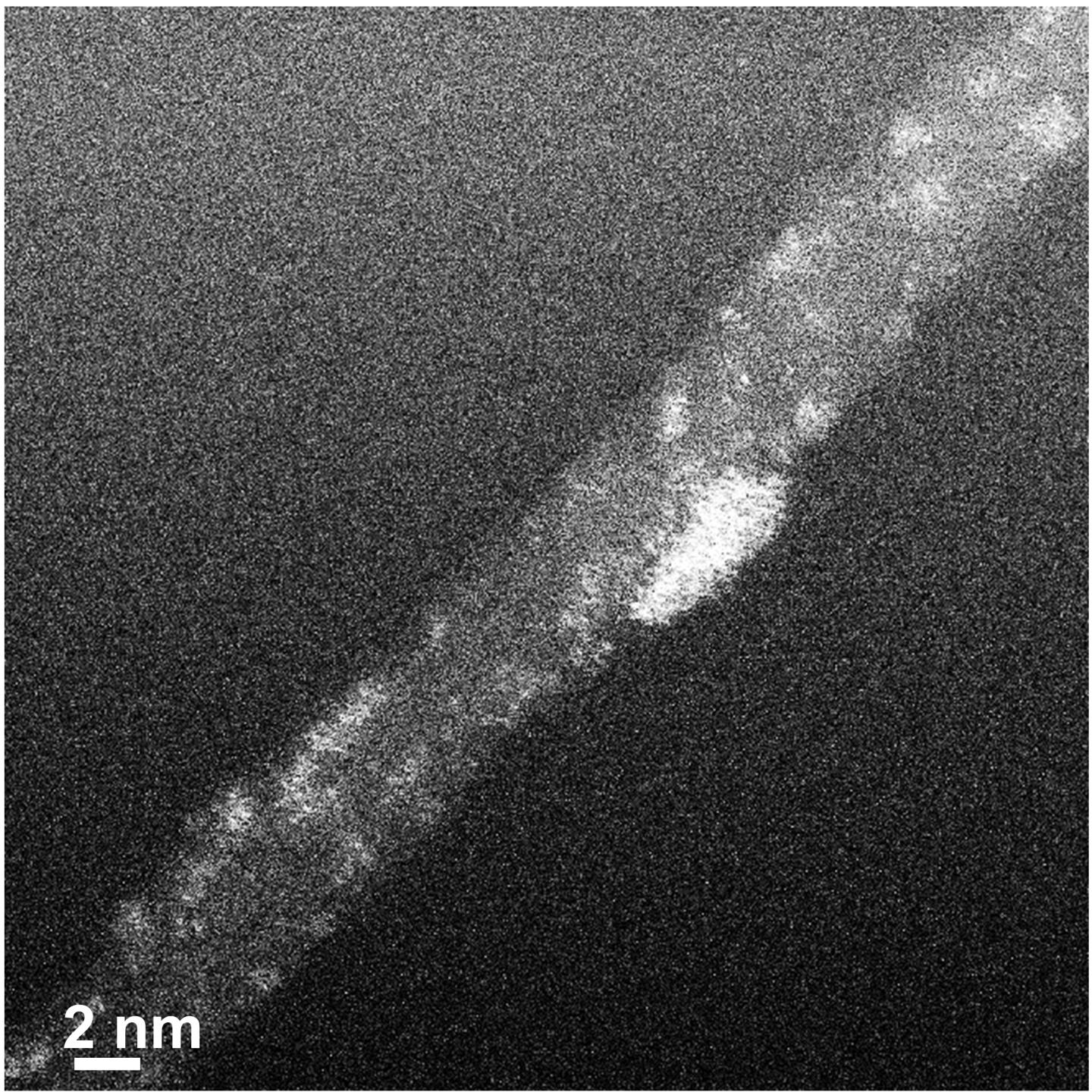
A group of Aalto University researchers led by professors Tanja Kallio and Kari Laasonen has developed a manufacturing method for electrocatalysts that only uses one hundredth of the amount of platinum generally used in commercial products. The activity achieved using the new material is similar to that of commercial electrocatalysts. The method is based on the special characteristics of carbon nanotubes.
'When platinum is electrodeposited on the surface of carbon nanotubes, it forms particles consisting of a couple of atoms. On other materials, such as graphene, platinum forms larger nanoparticles', Tanja Kallio explains.
'We believe this is because the carbon atoms of the curved surface are in a strained state, which makes them prone to stabilising platinum on the surface of the nanotube. This ensures that the platinum atoms form small and catalytically active particles. Our modelling showed that the more strained the carbon bonds are, the better the stabilisation of the platinum. Smaller tubes are more curved, which makes the strain greater, so the diameter of the nanotubes is also important.'
One third of the price
Electrolysers store electrical energy in the form of hydrogen bond energy. In practice, this mechanism is used to store fluctuating energy, such as wind energy, and balance the difference between demand and production. Since the electrocatalyst forms approximately one third of the price of the electrolyser, reducing the amount of platinum needed would make the process significantly less expensive.
'In addition to the price of platinum, the availability of the metal is also a problem. Platinum is on the EU list of critical raw materials, which means that its use is problematic either due to its scarceness or due to geopolitical problems. This is why the EU is aiming to reduce the use of platinum', Kallio says and emphasises that so far the functionality of the electrocatalyst developed at Aalto University has only been proven in laboratory conditions.
'In small-scale conditions and at room temperature, the electrocatalyst is stable and usable for a long time. The next step is to increase the scale of production and test the functionality of the electrocatalyst in practical applications, which are often carried out at a higher temperature.'
The research results have just been published in the scientific journal ACS Catalysis. Link to the article: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acscatal.7b00199
###
Further information:
Professor Tanja Kallio
tel. +358 50 563 7567
[email protected]
Professor Kari Laasonen (modelling)
tel. +358 40 557 0044
[email protected]
Media Contact
Tanja Kallio
[email protected]
358-505-637-567
@aaltouniversity
http://www.aalto.fi/en/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag