Credit: ©Science China Press
In recent years, with the rapid development of flexible electronic skins, high-performance flexible tactile sensors have received more attention and have been used in many fields such as artificial intelligence, health monitoring, human-computer interaction, and wearable devices. Among various sensors, flexible capacitive tactile sensors have the advantages of high sensitivity, low energy consumption, fast response, and simple structure. Sensitivity is an important parameter of the sensor. A common way to improve sensitivity is to introduce microstructures and use ionic dielectric materials at the interface to form a nano-scale ion-electronic interface with ultra-high specific capacitance. However, due to the incompressibility of the material and the high stability design of the structure, the linearity of the sensing signal is poor and the pressure response range is narrow. The sensor with high linearity facilitates the conversion between capacitance and pressure. It can greatly simplify the circuit design and data processing system, and improve the response speed of the sensing system. Therefore, the production of flexible pressure sensors with high linearity and high sensitivity has become a key issue in the development of flexible electronic skin.
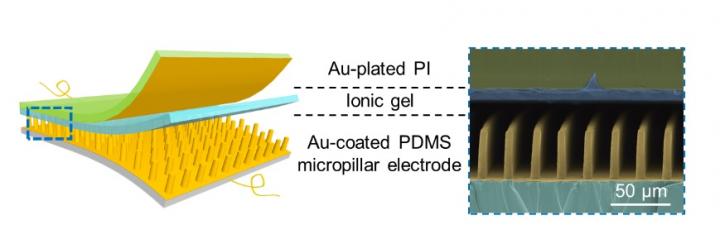
Recently, Chuan Fei Guo’s research group from the Department of Materials Science and Technology of Southern University of Science and Technology has made progress in the research of highly linear flexible pressure sensors. They improved the deformability of the structure by designing a flexible electrode with a surface micropillared structure with a large aspect ratio that is easy to buckle and lose stability (as shown in Fig. 1). Combined with the ionic gel dielectric layer, the sensor has high linearity (R2~0.999) and high sensitivity (33.16 kPa-1) in a wide pressure range of 12-176 kPa.
The micropillars undergo three deformation stages under pressure; initial contact (0-6 kPa), structural buckling (6-12 kPa) and post-buckling stage (12-176 kPa). In the post-buckling stage, the signal exhibits high linearity and high sensitivity, as shown in Fig. 2a.
The high linearity lies in the matching of the modulus of the micropillared structure electrode and the dielectric layer. The micropillars are made of silicone rubber polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) with an elastic modulus of 1 MPa, and the elastic modulus of the ion gel membrane is 5 MPa. Through finite element analysis (FEA), it can be known that a material with a modulus of MPa will produce a linear contact area change (as shown in Fig. 2b) when the material is extruded with a micropillared structure, which matches the linear sensitivity obtained in the experiment.
In addition to high linear sensitivity, the sensor also has a low detection limit (0.9 Pa), low response time (9 ms), and high stability (during 6000 compression/bending cycles, the signal remains stable). According to the performance of the sensor, they make a series of applied experiments. A sensor is attached on the middle finger segment of an artificial hand to lift weights of different weights, and the sensor signal shows a step change with a uniform increase in weight (~372 pF/g). Then, multiple (21) sensors are attached to the manipulator to carry out the object grasping experiment. The sensor array can better reflect the pressure distribution of the grasped object. The sensor is also used in the detection of the human radial artery, and the pulse signal is relatively stable under different pre-pressures (10.23 ~ 17.75 kPa), as shown in Fig. 3. In the plantar pressure distribution test, the sensor array can clearly feedback the difference of pressure distribution in different state.
The high linearity sensitivity of the sensor is derived from the design of the surface micropillared structure and the matching of the mechanical properties of the electrodes and dielectric materials. The combination of Euler’s stability principle, FEA and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) characterization explains the reason for linear sensitivity. The weight-lifting experiment and grasping experiment of the manipulator, human pulse detection and plantar pressure distribution test show that the sensor has great application potential in the fields of intelligent robots, human-computer interaction, and health monitoring. This work also provides new design ideas for the research of flexible linear sensors.
###
This work is recently published online in Science Bulletin. Associate Professor Chuan Fei Guo is the only corresponding author of the paper, and Southern University of Science and Technology is the first and the communication unit. The first author of the paper is the research assistant Peng Lu of the research group (2017 SUSTech-Harbin Institute of Technology combined training master graduate). The postdoctoral researcher Liu Wang makes important contributions to this work. Research assistants Pang Zhu, Jun Huang and others also make a great contribution to this work.
The research was supported by the funds of the “Science Technology and Innovation Committee of Shenzhen Municipality”, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the “Guangdong Innovative and Entrepreneurial Research Team Program”, the Shenzhen Sci-Tech Fund, and the “Tencent Robotics X Lab Rhino-Bird Focused Research Program”.
See the article:
P. Lu, L. Wang, P. Zhu, J. Huang, Y. Wang, N. Bai, Y. Wang, G. Li, J. Yang, K. Xie, J. Zhang, B. Yu, Y. Dai, C. F. Guo. “Iontronic pressure sensor with high sensitivity and linear response over a wide pressure range based on soft micropillared electrodes.” Sci. Bull. (2021)
https:/
Media Contact
Guo Chuan Fei
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




