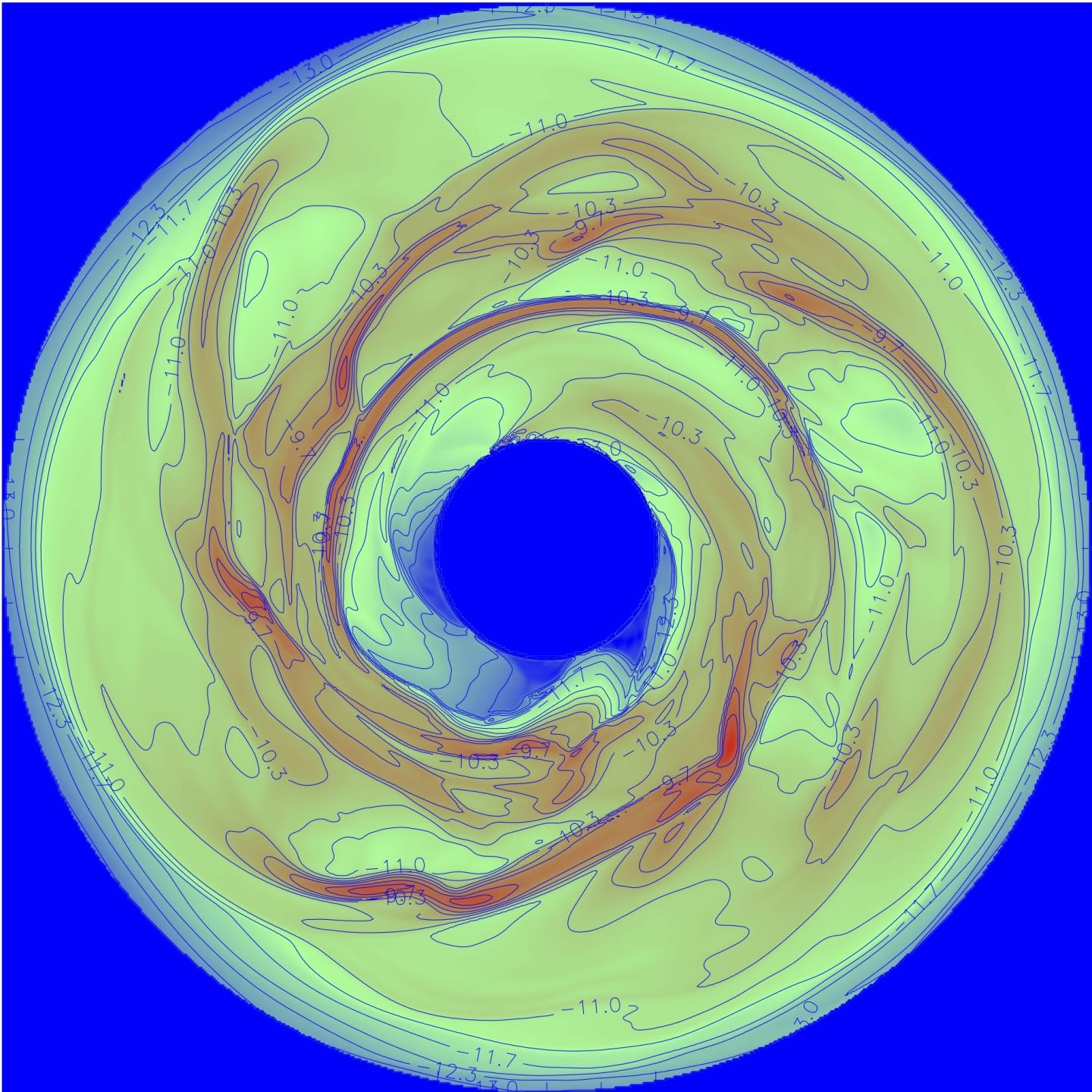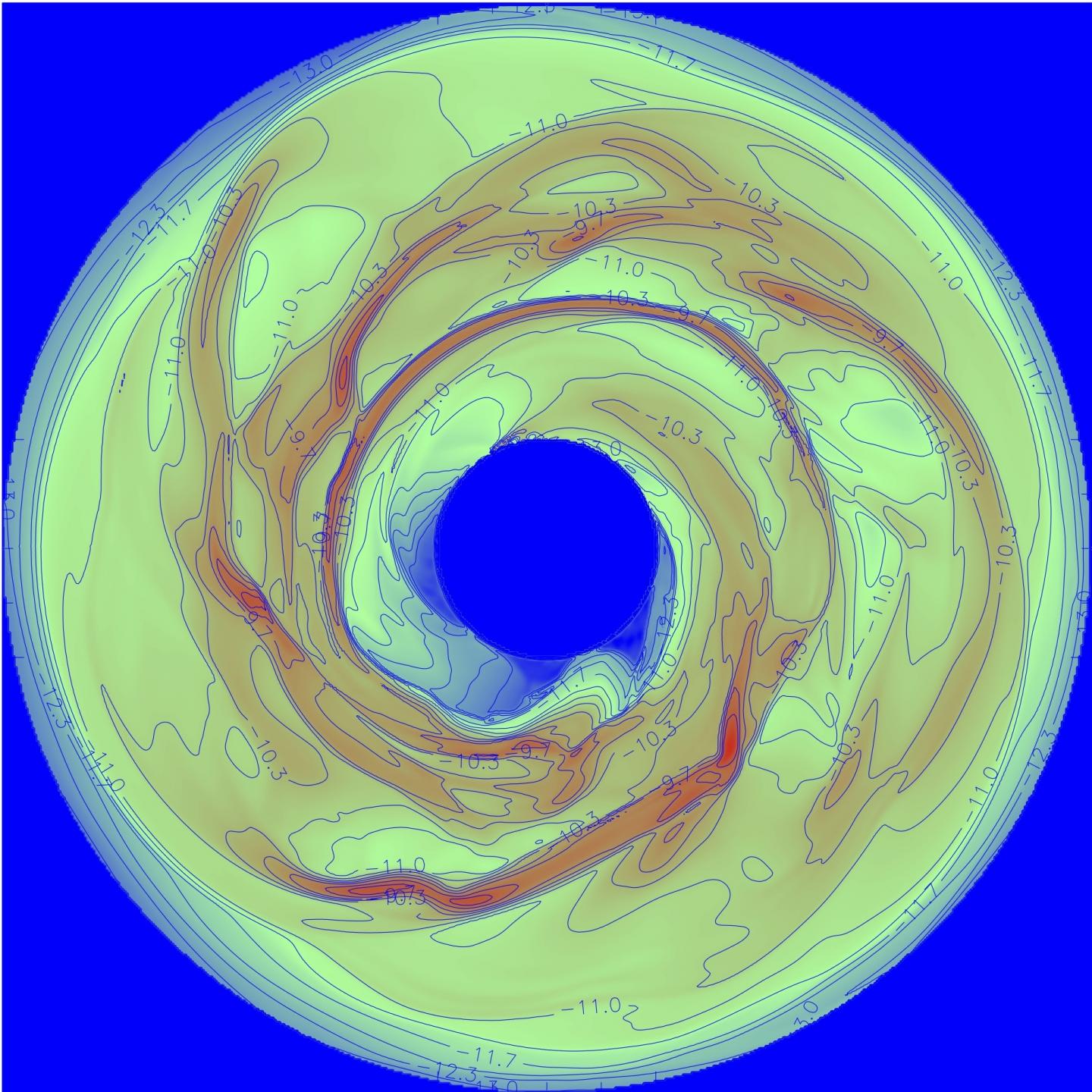
Credit: Alan Boss
Washington, DC–New planetary formation models from Carnegie's Alan Boss indicate that there may be an undiscovered population of gas giant planets orbiting around Sun-like stars at distances similar to those of Jupiter and Saturn. His work is published by The Astrophysical Journal.
The population of exoplanets discovered by ongoing planet-hunting projects continues to increase. These discoveries can improve models that predict where to look for more of them.
The planets predicted by Boss in this study could hold the key to solving a longstanding debate about the formation of our Solar System's giant planets out of the disk of gas and dust that surrounded the Sun in its youth.
One theory holds that gas giants form just like terrestrial planets do–by the slow accretion of rocky material from the rotating disk–until the object contains enough material to gravitationally attract a very large envelope of gas around a solid core. The other theory states that gas giant planets form rapidly when the disk gas forms spiral arms, which increase in mass and density until distinct clumps form that coalesce into baby gas giant planets.
One problem with the first option, called core accretion, is that it can't explain how gas giant planets form beyond a certain orbital distance from their host stars–a phenomenon that is increasingly found by intrepid planet hunters. However, models of the second theory, called disk instability, have indicated the formation of planets with orbits between about 20 and 50 times the distance between the Earth and the Sun.
"Given the existence of gas giant planets on such wide orbits, disk instability or something similar must be involved in the creation of at least some exoplanets," Boss said. "However, whether or not this method could create closer-orbiting gas giant planets remains unanswered."
Boss set out to use his modeling tools to learn if gas giant planets can form closer to their host stars by taking a new look at the disk-cooling process. His simulations indicate that there may be a largely unseen population of gas giant planets orbiting Sun-like stars at distances between 6 and 16 times that separating the Earth and the Sun. (For context Jupiter is just over five times as distant from the Sun as Earth is, and Saturn is over nine times as distant.)
"NASA's upcoming Wide Field Infrared Survey Telescope may be ideally suited to test my predictions here," Boss added.
###
Media Contact
Alan Boss
[email protected]
202-478-8858
@carnegiescience
https://carnegiescience.edu/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag