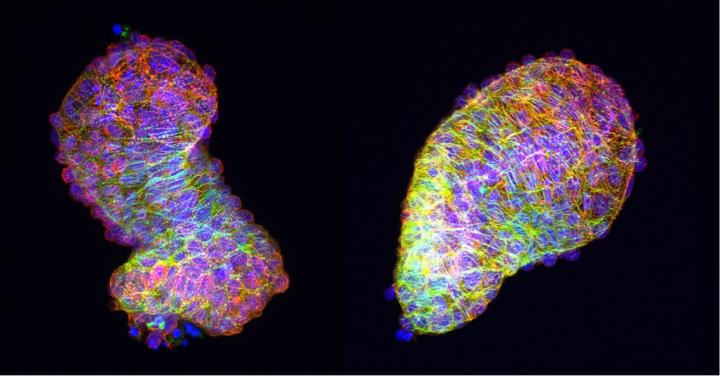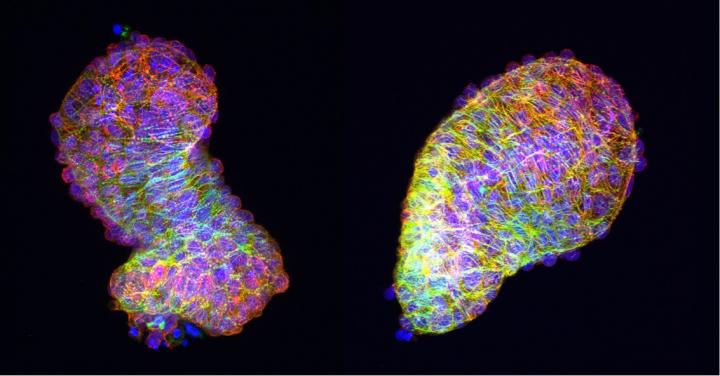
Credit: Anne M. Merks, MDC
When it first starts to develop, the heart is a simple tube. Reporting in the journal Nature Communications, researchers at MDC have now described how it forms itself into a its characteristic S-shape and how the ventricles and atria finally develop. Their findings will help scientists to better understand the development of congenital heart diseases.
In Germany, nearly one child in 100 is born with a heart defect. Until recently, little was known about the causes of congenital heart disease. But now important new insights have been provided by research on embryonic heart development by an international team led by Dr. Daniela Panáková, leader of the Electrochemical Signalling in Development and Disease working group at the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) in Berlin.
By conducting experiments with zebrafish, Panáková and her colleagues at MDC and the universities of Potsdam and Zürich have identified the mechanisms by which the heart takes on its fully developed form. Their study was published together with another article on early heart development in the zebrafish in the same issue of Nature Communications. In this paper, a team led by Prof. Christian Mosimann from the Institute of Molecular Life Sciences at the University of Zürich, with the participation of Panáková's team, reports how the heart first develops into a tube-like form through the continuous flow of heart precursor cells.
Heart cells must find new neighbours
"We then turned to the question of how the linear tube loops round into the characteristic S-shape, which ultimately goes on to form the ventricle and the atrium of the zebrafish heart," says one of the study's two lead authors, Anne Margarete Merks from Panáková's lab. "For this process to occur, the second-generation heart cells need to integrate into the linear heart and identify their correct place." She explains that this involves relocations of the cells. "They change their neighbours and find new cells to share the cell boundaries with," says Merks.
As she and her colleagues report, this process is controlled by a signalling pathway – a chain of chemical reactions that cause the cells to react to external signals – known as the PCP signalling pathway. PCP stands for 'planar cell polarity'. Two components are especially important to this pathway: the molecules Fzd7a and Vangl2. "When we deactivated the genes for these molecules in zebrafish, the heart was unable to develop properly," says Merks. "Clearly, the cells were unable to locate their future neighbours."
Tissue tension is crucial
The PCP signalling pathway influences not just individual cells but also the tissue as a whole. "If the signalling pathway is disrupted in some way, the tissue tension changes," says Merks. Without the correct tension, the looping process cannot take place and the formation of the heart is impaired. As the researchers discovered in further experiments, the change in tissue tension is due to the fact that the defective PCP signalling pathway alters the cytoskeleton of the heart muscle cells. The cytoskeleton consists of the proteins actin and myosin and enables muscle cells and therefore an entire muscle to contract.
"Normally we observe that the cytoskeleton in the heart cells doesn't look the same everywhere, but exhibits polarity," explains Merks. "The surface of the cells differ from their base." If the PCP signalling pathway is disrupted, this polarity is lost. As a result, the tube-shaped heart cannot take on its new form properly. "The outflow tract, in particular, is unable to develop correctly," Merks explains. Most congenital heart diseases are due to problems in this part of the organ.
Results transferable to humans
Merks and her colleagues carried out their experiments on zebrafish, because these animals have the important advantage that the heart develops very quickly and starts to beat just 24 hours after fertilisation. "But we're confident that our findings can be transferred to mammals, including humans," says Panáková. "The PCP signalling pathway is highly conserved in evolutionary terms and the genes involved in it have already been identified in humans and associated with congenital heart disease."
Next, Panáková and her team are planning to carry out studies with heart tissue from patients with the congenital heart diseases tetralogy of Fallot and DORV (double outlet right ventricle). They will source the tissue from a biobank run by the Competence Network for Congenital Heart Defects. Through their experiments, the researchers at MDC aim to identify exactly to what extent a disrupted PCP signalling pathway is implicated in the development of these diseases.
###
Anne Margarete Merks, et al. (2018): "Planar cell polarity signalling coordinates heart tube remodelling through tissue-scale polarisation of actomyosin activity." Nature Communications. doi: 10.1038/10.1038/s41467-018-04566-1
About the Max Delbrück Center
The Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association was founded in January 1992 on the recommendation of the German Council of Science and Humanities ("Wissenschaftsrat") with the goal of linking basic science to clinical research. The MDC integrated parts of three former Central Institutes of the GDR Academy of Sciences and was named for Max Delbrück, a physicist, biologist, and Nobel Prize winner. Currently the institute employs more than 1600 people from nearly 60 countries; over 1300 of those are directly involved in research. The MDC's annual budget is over 80 million Euros, along with substantial third-party funding obtained by individual scientific groups. As is the case with all Helmholtz institutes, the MDC receives 90 percent of its funding from the federal government and 10 percent from Berlin, the state where it resides. http://www.mdc-berlin.de
Media Contact
Jana Schlütter
[email protected]
49-309-406-2121
http://www.mdc-berlin.de
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/10.1038/s41467-018-04566-1