Credit: by Yanfeng Dai, Xiang Yu, Jianshuang Wei, Fanxin Zeng, Yiran Li, Xiaoquan Yang, Qingming Luo, Zhihong Zhang
Accurate detection and characterization of SLNs are crucial in cancer staging and making therapeutic decisions. At present, the clinical gold standard used to detect SLNs is to label them with blue dye or a radioactive nanocolloid and then perform SLN biopsy. But these methods have drawbacks, radioscintigraphy has relatively poor spatial resolution, and blue dye will quickly label downstream LNs, leading to difficulties recognized SLN from other nodes. In addition, the removal of the SLN may cause some side effects, such as lymphedema, shoulder dysfunction, and arm numbness. Therefore, the ideal method for detecting SLN needs to have the following characteristics: 1) The probe can quickly enter the lymphatic system and retain in the SLN for a while. 2) The probe should contain a specific ligand for the selective targeting of breast cancer cells. 3) Imaging technique requires sufficient sensitivity and spatial resolution to detect the distribution of tumor cells in the entire SLN.
LN enlargement can occur during both tumour cell invasion and under inflammatory conditions. Therefore, the accurately identify the status of the SLN intraoperatively will help surgeons choose appropriate treatment regimen and minimize the complications caused by unnecessary LN removal. Although various nanoprobes based on passively targeting macrophages in SLN combined with imaging techniques have been developed to predict the metastatic status of SLNs, few can distinguish metastatic SLNs from inflamed LNs in vivo.
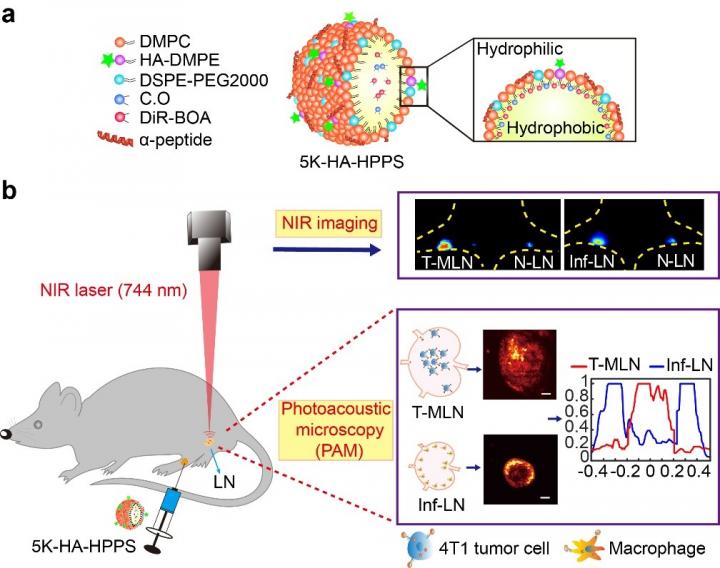
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Zhihong Zhang and Professor Qingming Luo from Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics-Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China, and School of Biomedical Engineering, Hainan University, Haikou, Hainan, China, and co-workers have developed a CD44 and SR-B1 dual-targeting hyaluronic acid nanoparticle (5K-HA-HPPS) loaded with the near-infrared fluorescent/photoacoustic dye DiR-BOA for imaging SLNs in breast cancer. Due to the small size, negative charge, and target ligand, 5K-HA-HPPS can rapidly (12 h) in pLN. More interestingly, they found that photoacoustic signals from 5K-HA-HPPS showed a significantly distinct spatial distribution among LNs of different statuses, which the signals were mainly distributed within tumour metastatic SLNs but at the peripheries of normal and inflamed LNs. The ratio of PA intensity (R) at the centre of the LNs compared with that at the periphery in the 5K-HA-HPPS group was 5.93 ± 0.75 for T-MLNs, which was much higher than that for the Inf-LNs (R = 0.2 ± 0.07) and N-LNs (R = 0.45 ± 0.09). The reported method and technique provide a new strategy for accurately identifying the status of SLNs during breast cancer surgery and facilitate the implementation of appropriate tumour treatment strategies.
Fluorescence imaging showed that 5K-HA-HPPS enhanced in both T-MLNs and Inf-LNs, indicating that T-MLNs and Inf-LNs cannot be distinguished according to their fluorescence intensities. Here wide-field fluorescence imaging is two-dimensional imaging, which possesses the advantage of sensitivity, convenience, and non-invasiveness for long-term monitoring, but it cannot distinguish whether the fluorescent signal is located inside the LN or at the periphery of the LN. By providing deep penetration and a high spatial resolution, photoacoustic microscopy has a great potential for the 3D visualization of photoacoustic signal distribution in intact LNs.
Both tumour cell infiltration and inflammation result in the enlargement of SLNs. Therefore, whether SLN enlargement is caused by the metastasis of tumour cells or inflammation should be determined before SLN resection. The presented technique possess the ability to distinguish metastatic SLNs from inflamed LNs, thus will expected to provide an in vivo detection method for quickly identifying whether the SLN has tumor metastasis and will reduce the complications caused by unnecessary LN removal during breast cancer surgery, which has potential clinical application value.
###
Media Contact
Zhihong Zhang
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




