Intensive lifestyle intervention with plenty of exercise helps people with prediabetes improve their blood glucose levels over a period of years and thus delay or even prevent type 2 diabetes. In particular, individuals with prediabetes at highest risk benefited from intensive lifestyle intervention. This is shown by the evaluation of the Prediabetes Lifestyle Intervention Study (PLIS) of the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD), which was conducted at 8 sites of the center throughout Germany. The results have now been published in the journal Diabetes.
Credit: DZD
Intensive lifestyle intervention with plenty of exercise helps people with prediabetes improve their blood glucose levels over a period of years and thus delay or even prevent type 2 diabetes. In particular, individuals with prediabetes at highest risk benefited from intensive lifestyle intervention. This is shown by the evaluation of the Prediabetes Lifestyle Intervention Study (PLIS) of the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD), which was conducted at 8 sites of the center throughout Germany. The results have now been published in the journal Diabetes.
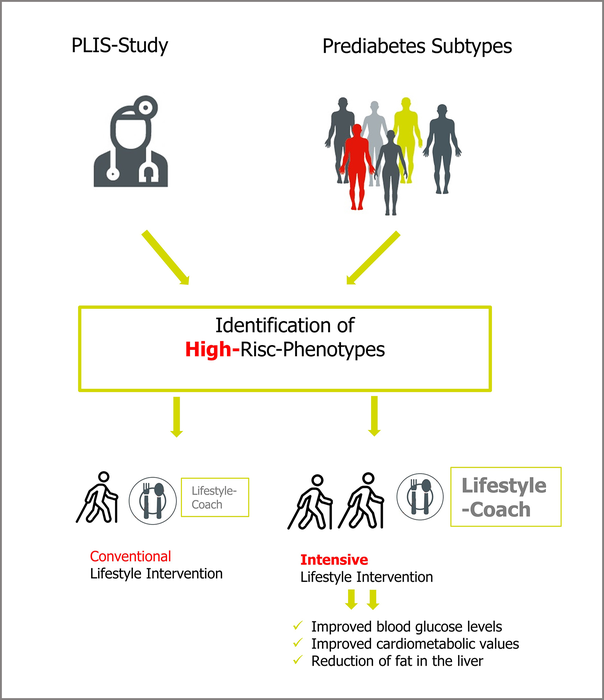
More exercise and healthy eating behavior help many people with prediabetes to normalize their blood glucose levels and avoid developing type 2 diabetes. However, not everyone benefits from a conventional lifestyle intervention (LI). Recent studies show that already in prediabetes, there are different subtypes with different risk profiles. Researchers at the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) have therefore investigated in a multicenter randomized controlled trial whether people with prediabetes and a high risk benefit from an intensification of the intervention and how people with a low risk are affected by a conventional LI compared to no lifestyle changes.
The LI lasted 12 months in each case and the follow-up period was a further two years. A total of 1,105 individuals with prediabetes were investigated at various study sites in Germany and assigned to a high-risk or low-risk phenotype based on insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity, and liver fat content. 82% of participants completed the study.
A lot helps a lot – more exercise improves blood glucose and cardiometabolic values
People at high risk – these individuals produce too little insulin or suffer from fatty liver with insulin resistance –- were randomly assigned to receive conventional LI according to the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) or a more intensive intervention with double the amount of required exercise. The results showed that more exercise, i.e. more intensive LI, helps people at high risk improve their blood glucose and cardiometabolic levels and reduce liver fat content to within the normal range. Conventional LI is less effective.
Low-risk participants completed a conventional LI or took part in a control group that received only a one-time brief consultation. “After three years, glucose tolerance was more likely to normalize in participants with conventional LI than in those in the control group,” said Professor Hans-Ulrich Häring of the German Center for Diabetes Research and last author of the study. There were hardly any differences in insulin sensitivity and secretion, liver fat content and cardiometabolic risk.
Lifestyle intervention based on risk phenotype improves diabetes prevention
“Our study results show that an individualized LI based on the risk phenotype is beneficial for diabetes prevention,” said study leader Professor Andreas Fritsche from the Institute of Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases of Helmholtz Munich at the University of Tübingen (IDM) and the Department of Diabetology, Endocrinology and Nephrology (Director: Professor Andreas Birkenfeld, MD) at Tübingen University Hospital, summarizing the results. “For successful prevention, we need to identify high-risk patients in the future and focus on providing them with an intensified lifestyle intervention.”
Journal
Diabetes
DOI
10.2337/db21-0526
Article Title
Different effects of lifestyle intervention in high- and low-risk prediabetes.




