NYU Tandon researchers implant ‘digital watermarks’ using a neural network to easily spot manipulated photos and video
Credit: NYU Tandon
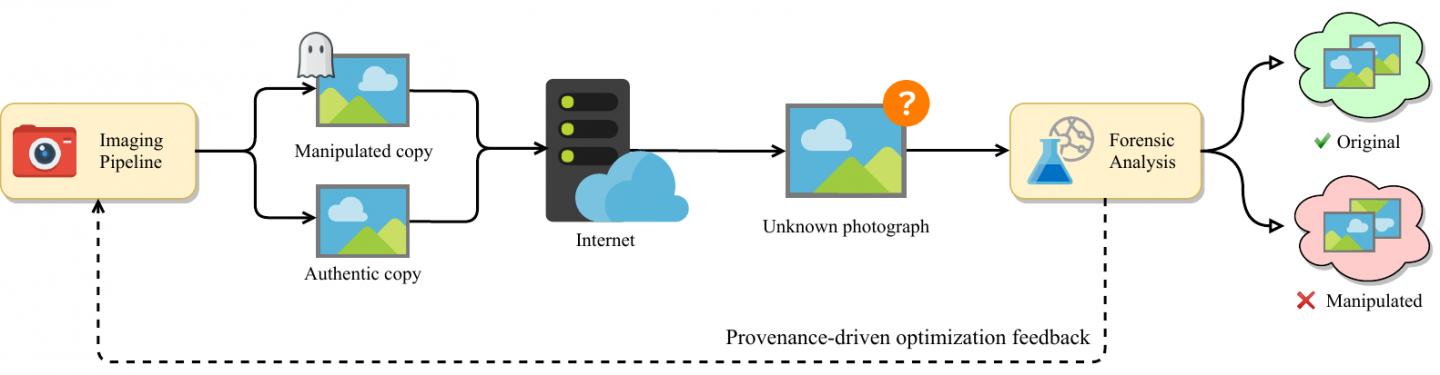
BROOKLYN, New York, Wednesday, May 29, 2019 – To thwart sophisticated methods of altering photos and video, researchers at the NYU Tandon School of Engineering have demonstrated an experimental technique to authenticate images throughout the entire pipeline, from acquisition to delivery, using artificial intelligence (AI).
In tests, this prototype imaging pipeline increased the chances of detecting manipulation from approximately 45 percent to over 90 percent without sacrificing image quality.
Determining whether a photo or video is authentic is becoming increasingly problematic. Sophisticated techniques for altering photos and videos have become so accessible that so-called “deep fakes” — manipulated photos or videos that are remarkably convincing and often include celebrities or political figures — have become commonplace.
Pawel Korus, a research assistant professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at NYU Tandon, pioneered this approach. It replaces the typical photo development pipeline with a neural network – one form of AI – that introduces carefully crafted artifacts directly into the image at the moment of image acquisition. These artifacts, akin to “digital watermarks,” are extremely sensitive to manipulation.
“Unlike previously used watermarking techniques, these AI-learned artifacts can reveal not only the existence of photo manipulations, but also their character,” Korus said.
The process is optimized for in-camera embedding and can survive image distortion applied by online photo sharing services.
The advantages of integrating such systems into cameras are clear.
“If the camera itself produces an image that is more sensitive to tampering, any adjustments will be detected with high probability,” said Nasir Memon, a professor of computer science and engineering at NYU Tandon and co-author, with Korus, of a paper detailing the technique. “These watermarks can survive post-processing; however, they’re quite fragile when it comes to modification: If you alter the image, the watermark breaks,” Memon said.
Most other attempts to determine image authenticity examine only the end product – a notoriously difficult undertaking.
Korus and Memon, by contrast, reasoned that modern digital imaging already relies on machine learning. Every photo taken on a smartphone undergoes near-instantaneous processing to adjust for low light and to stabilize images, both of which take place courtesy of onboard AI. In the coming years, AI-driven processes are likely to fully replace the traditional digital imaging pipelines. As this transition takes place, Memon said that “we have the opportunity to dramatically change the capabilities of next-generation devices when it comes to image integrity and authentication. Imaging pipelines that are optimized for forensics could help restore an element of trust in areas where the line between real and fake can be difficult to draw with confidence.”
###
Korus and Memon note that while their approach shows promise in testing, additional work is needed to refine the system. This solution is open-source, and can be accessed at https:/
About the New York University Tandon School of Engineering
The NYU Tandon School of Engineering dates to 1854, the founding date for both the New York University School of Civil Engineering and Architecture and the Brooklyn Collegiate and Polytechnic Institute (widely known as Brooklyn Poly). A January 2014 merger created a comprehensive school of education and research in engineering and applied sciences, rooted in a tradition of invention and entrepreneurship and dedicated to furthering technology in service to society. In addition to its main location in Brooklyn, NYU Tandon collaborates with other schools within NYU, one of the country’s foremost private research universities, and is closely connected to engineering programs at NYU Abu Dhabi and NYU Shanghai. It operates Future Labs focused on start-up businesses in downtown Manhattan and Brooklyn and an award-winning online graduate program. For more information, visit http://engineering.
Media Contact
Kathleen Hamilton
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/



