Credit: University of Otago
By breaking with conventionality, University of Otago physicists have opened up new research and technology opportunities involving the basic building block of the world – atoms.
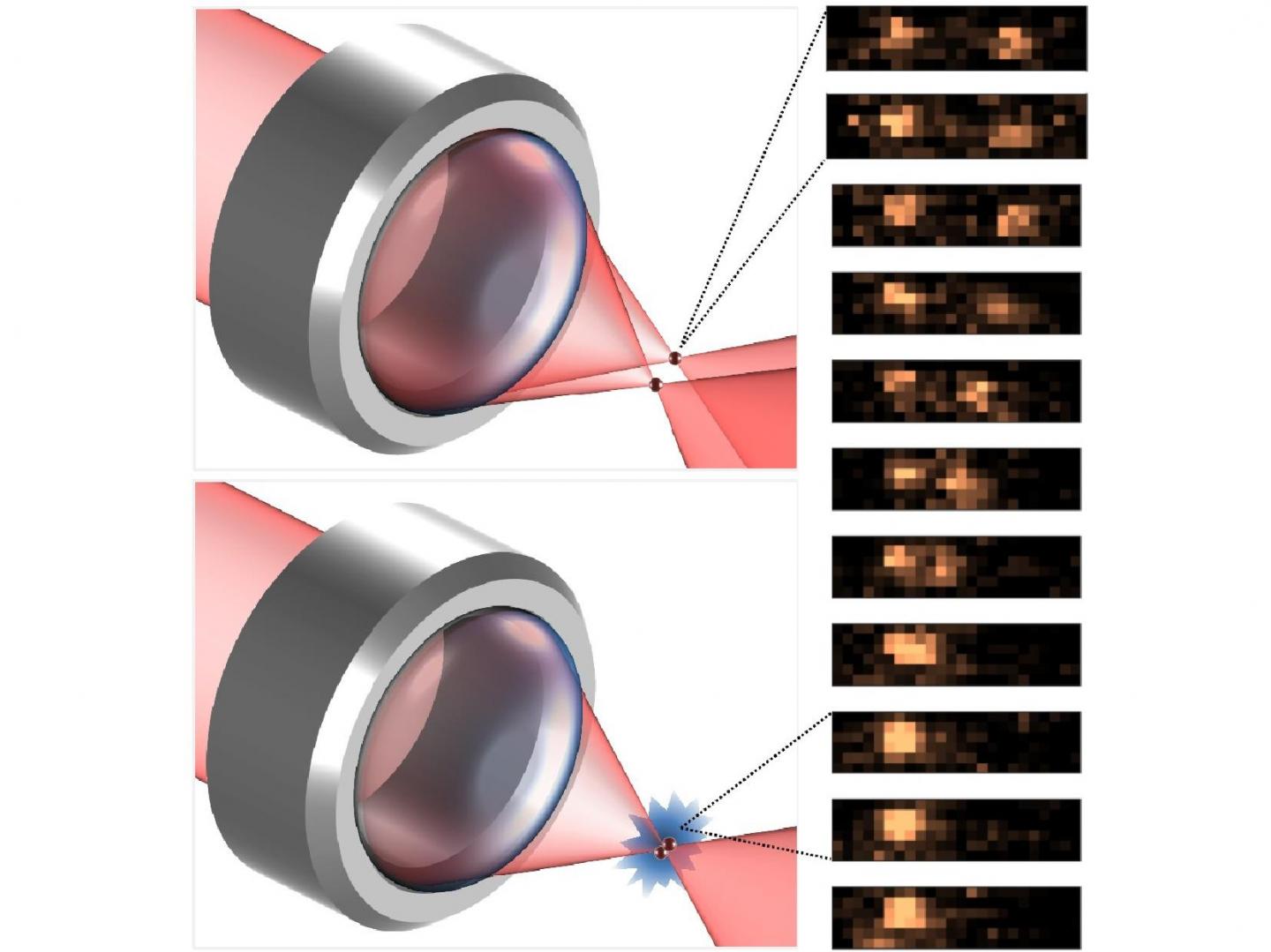
In a study, just published in Nature Communications, researchers put one atom inside each of two laser beams before moving them together until they started to interact with each other.
Co-author Associate Professor Mikkel F. Andersen, of the Department of Physics, says this allows the atoms to exchange properties in a way which could be “very useful” for future quantum technologies.
“Our work represents an important step in our capability to control the atomic world,” he says.
As atoms are like magnets, when the pair start interacting, they start changing each other’s direction, counterbalancing each other.
It is the first time this “pure test of the basic interaction” has been shown in a lab using two single atoms. Previous experiments have been based on multiple atoms, which can result in undesirable outcomes, such as chemical reactions between the atoms.
By showing how to build multi-atom quantum systems from the bottom up, scientists can do things that are not possible using conventional methods.
“Assembling small physical systems atom by atom, in a controlled way, opens up a wealth of research directions and opportunities that are not otherwise possible. It also leads to the atoms displaying different behaviours than if they were one of many in the system,” Dr Andersen says.
This includes a finite-temperature quantum entanglement resource. This is significant because entangled particles remain connected, even over great distances, and actions performed on one affect the other.
Entanglement can be used to enhance technologies as, because the atoms are interconnected, they can co-operate on a set task, rather than operating on its own.
“When we get to the point where we can exploit quantum entanglement, we will have a second quantum technology revolution – like we did with lasers, which made the internet possible.
“This is why making robust entanglement technology is important – and New Zealand is right at the forefront of this research.”
###
Media Contact
Mikkel F. Andersen
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




