“In conclusion, our results suggest that STAT3 phosphorylation occurs in livers with NAFLD only in the subset with P2-HNF4α expression, and c-Myc expression is strongly correlated with STAT3 phosphorylation.”
Credit: 2022 Younes et al.
“In conclusion, our results suggest that STAT3 phosphorylation occurs in livers with NAFLD only in the subset with P2-HNF4α expression, and c-Myc expression is strongly correlated with STAT3 phosphorylation.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 6, 2022 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget’s Volume 13 on December 6, 2022, entitled, “Expression of p-STAT3 and c-Myc correlates with P2-HNF4α expression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).”
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with the metabolic syndrome and is rapidly becoming one of the major causes of hepatic cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), although some cases of HCC have developed in non-cirrhotic livers [1–8]. Although the percentage of patients with NAFLD who ultimately progress to fibrosis and later to HCC is relatively small, the number is significant because of the sheer number of patients who have NAFLD. Because there are no reliable biomarkers to predict the risk of HCC in patients with NAFLD, designing effective and cost-effective surveillance programs aimed at prevention and early detection of HCC is difficult, if not impossible. Therefore, there is an urgent need to identify such biomarkers and especially those that may appear at different stages of progression toward HCC.
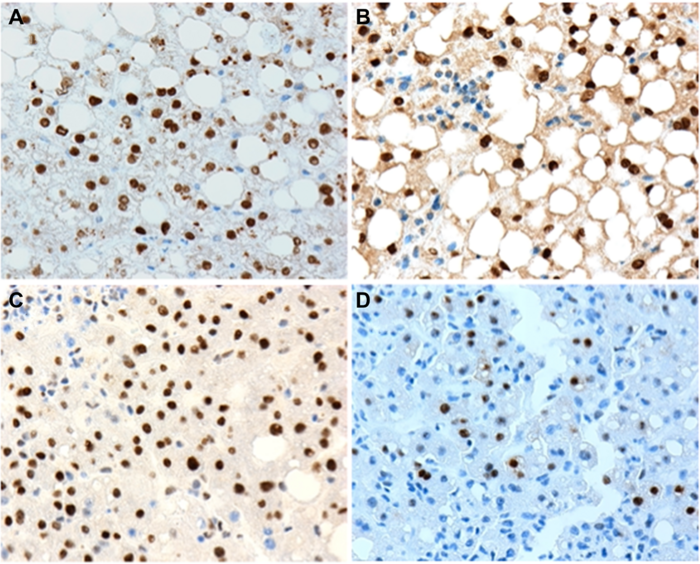
In the current study, researchers Mamoun Younes, Lin Zhang, Baharan Fekry, and Kristin Eckel-Mahan from George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences and McGovern Medical School at the University of Texas Health Science Center (UTHealth) studied the expression of two hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4α) isoforms, p-STAT3. and c-Myc in 49 consecutive liver biopsies with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) using immunohistochemistry.
“The aim of this study was to determine the relationships between p-STAT3, c-Myc and P2-HNF4α expression in biopsies from livers with NAFLD as potential biomarkers of HCC risk.”
All 49 biopsies (100%) were positive for nuclear expression of P1-HNF4α. Twenty-eight (57%) cases were positive for P2-HNF4α, 6 (12%) were positive for p-STAT3 and 5 (10%) were positive for c-Myc. All 6 (100%) p-STAT3-positive cases were also positive for P2-HNF4α (p = 0.03). p-STAT3-positive cases were more likely to be positive for c-Myc (67% vs. 2%, p = 0.0003).
Four cases were positive for P2-HNF4α, p-STAT3 and c-Myc. p-STAT3 expression was associated with hypertension (p = 0.037). All c-Myc positive biopsies were from patients with obesity, diabetes and hypertension. Only c-Myc expression was associated with advanced fibrosis; three (60%) of the c-Myc positive cases were associated with advanced fibrosis in contrast to 7 (10%) of the 44 c-Myc negative cases (p = 0.011).
“Based on these results, we hypothesize with the following sequence of events with progression of NAFLD: P2-HNF4α expression is followed by expression of p-STAT3 which in turn is followed by the expression of c-Myc. Additional larger studies are needed to confirm these findings.”
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28324
Correspondence to: Mamoun Younes
Email: [email protected]
Keywords: hepatocyte nuclear factor four alpha, steatohepatitis, immunohistochemistry, hepatocellular carcinoma, isoform
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
- Twitter – https://twitter.com/Oncotarget
- Facebook – https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget
- YouTube – www.youtube.com/c/OncotargetYouTube
- Instagram – https://www.instagram.com/oncotargetjrnl/
- LinkedIn – https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget/
- Pinterest – https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
- LabTube – https://www.labtube.tv/channel/MTY5OA
- SoundCloud – https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
For media inquiries, please contact: [email protected].
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
Journal
Oncotarget
DOI
10.18632/oncotarget.28324
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Human tissue samples
Article Title
Expression of p-STAT3 and c-Myc correlates with P2-HNF4α expression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Article Publication Date
6-Dec-2022




