Credit: Osaka University
Scientists at the Immunology Frontier Research Center (IFReC) at Osaka University, Japan, report a new group of monocytes they call SatM. Studies in mice show that SatM may be responsible for causing fibrosis and creates a new drug target for an ailment that has little effective therapies.
Fibrosis is a form of scarring that could if uncontrolled cause deleterious thickening of tissues. Although it is known that fibrosis is caused by an activated immune system, which specific cells are responsible continuous to elude researchers.
Scientists at IFReC may have found this subgroup, as they report in Nature a class of monocyte cells with strange morphology. "The cells had a bi-lobed segmented nuclear shape and many cytoplasmic granules. We therefore called them 'Segregated nucleus atypical monocytes (SatM)'", said IFReC Professor Shizuo Akira.
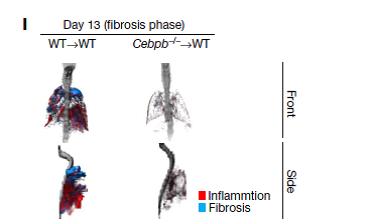
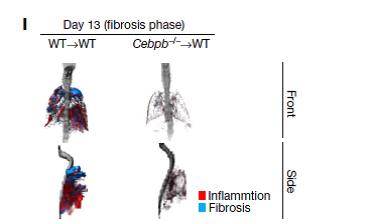
To identify this subgroup, the researchers looked at immune cell subpopulations that predominantly appeared in fibrosis. "These cells were regulated by C/EBPβ," observed Akira.
Detailed examination of immune cells showed that the C/EBPβ mutant mice, unlike normal mice, produced no SatM, whereas no other observed immune cell population was changed. The mice were also significantly more resistant to fibrosis. On the other hand, when the mutant mice were exposed to SatM, their susceptibility to fibrosis rose.
Although Dr. Akira, Dr. Satoh and his colleagues describe SatM as a subset of monocytes, SatM showed characteristics that suggested they were hybrids of different immune cells. According to Akira, gene analysis found SatM "showed granulocyte markers, but SatM are definitely not granulocytes. These cell type is one of monocyte."
Additional study found the progenitor cells responsible for producing SatM. Adoptive transfer of these progenitors into mutant mice unable to produce SatM resulted in a SatM population, and C/EBPβ was found to be essential for maintaining the progenitors.
The ability to isolate cells specifically related to fibrosis gives hope for new therapies.
"Decades of research have shown that immune cells are extremely diverse," said Akira. "Clear definitions of the subpopulations are essential for properly diagnosing and treating diseases. Our discovery of SatM should improve therapeutic strategies against fibrosis."
###
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
@osaka_univ_e
http://www.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag