Electric vehicles, powered by macroscopic electric motors, are increasingly prevalent on our streets and highways. These quiet and eco-friendly machines got their start nearly 200 years ago when physicists took the first tiny steps to bring electric motors into the world.
Credit: Northwestern University
Electric vehicles, powered by macroscopic electric motors, are increasingly prevalent on our streets and highways. These quiet and eco-friendly machines got their start nearly 200 years ago when physicists took the first tiny steps to bring electric motors into the world.
Now a multidisciplinary team led by Northwestern University has made an electric motor you can’t see with the naked eye: an electric motor on the molecular scale.
This early work — a motor that can convert electrical energy into unidirectional motion at the molecular level — has implications for materials science and particularly medicine, where the electric molecular motor could team up with biomolecular motors in the human body.
“We have taken molecular nanotechnology to another level,” said Northwestern’s Sir Fraser Stoddart, who received the 2016 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work in the design and synthesis of molecular machines. “This elegant chemistry uses electrons to effectively drive a molecular motor, much like a macroscopic motor. While this area of chemistry is in its infancy, I predict one day these tiny motors will make a huge difference in medicine.”
Stoddart, Board of Trustees Professor of Chemistry at the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences, is a co-corresponding author of the study. The research was done in close collaboration with Dean Astumian, a molecular machine theorist and professor at the University of Maine, and William Goddard, a computational chemist and professor at the California Institute of Technology. Long Zhang, a postdoctoral fellow in Stoddart’s lab, is the paper’s first author and a co-corresponding author.
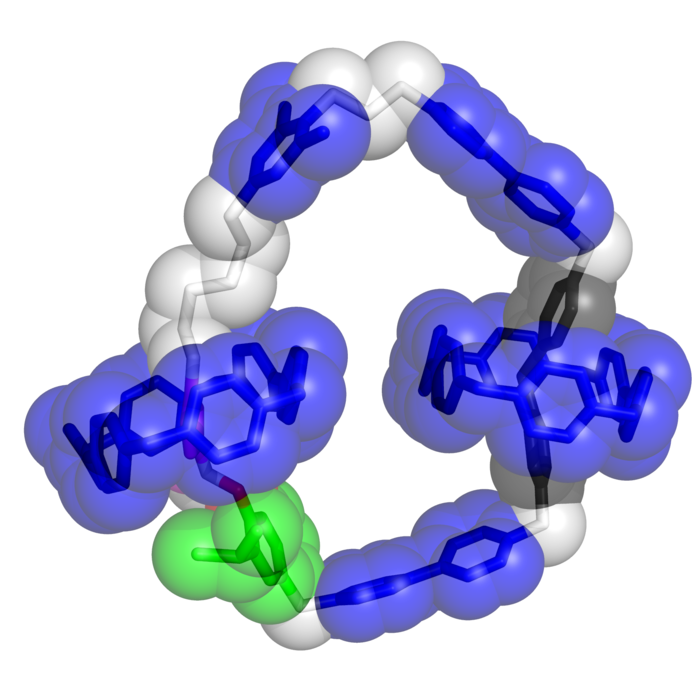
Only 2 nanometers wide, the molecular motor is the first to be produced en masse in abundance. The motor is easy to make, operates quickly and does not produce any waste products.
The study and a corresponding news brief were published today (Jan. 11) by the journal Nature.
The research team focused on a certain type of molecule with interlocking rings known as catenanes held together by powerful mechanical bonds, so the components could move freely relative to each other without falling apart. (Stoddart decades ago played a key role in the creation of the mechanical bond, a new type of chemical bond that has led to the development of molecular machines.)
The electric molecular motor specifically is based on a [3]catenane whose components ― a loop interlocked with two identical rings ― are redox active, i.e. they undergo unidirectional motion in response to changes in voltage potential. The researchers discovered that two rings are needed to achieve this unidirectional motion. Experiments showed that a [2]catenane, which has one loop interlocked with one ring, does not run as a motor.
The synthesis and operation of molecules that perform the function of a motor ― converting external energy into directional motion ― has challenged scientists in the fields of chemistry, physics and molecular nanotechnology for some time.
To achieve their breakthrough, Stoddart, Zhang and their Northwestern team spent more than four years on the design and synthesis of their electric molecular motor. This included a year working with UMaine’s Astumian and Caltech’s Goddard to complete the quantum mechanical calculations to explain the working mechanism behind the motor.
“Controlling the relative movement of components on a molecular scale is a formidable challenge, so collaboration was crucial,” Zhang said. “Working with experts in synthesis, measurements, computational chemistry and theory enabled us to develop an electric molecular motor that works in solution.”
A few examples of single-molecule electric motors have been reported, but they require harsh operating conditions, such as the use of an ultrahigh vacuum, and also produce waste.
The next steps for their electric molecular motor, the researchers said, is to attach many of the motors to an electrode surface to influence the surface and ultimately do some useful work.
“The achievement we report today is a testament to the creativity and productivity of our young scientists as well as their willingness to take risks,” Stoddart said. “This work gives me and the team enormous satisfaction.”
Stoddart is a member of the International Institute for Nanotechnology and the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center of Northwestern University.
The study is titled “An electric molecular motor.”
Journal
Nature
DOI
10.1038/s41586-022-05421-6
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
An electric molecular motor
Article Publication Date
11-Jan-2023




