Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are novel therapeutics that can be used to treat a wide range of diseases. This has led to a growing demand for selective, efficient, and safe ways of delivering siRNA in cells. Now, in a cooperation between the Universities of Amsterdam and Leiden, researchers have developed dedicated molecular nanocages for siRNA delivery. In a paper just out in the Journal Chem they present nanocages that are easy to prepare and display tuneable siRNA delivery characteristics.
Credit: Image taken from the paper
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are novel therapeutics that can be used to treat a wide range of diseases. This has led to a growing demand for selective, efficient, and safe ways of delivering siRNA in cells. Now, in a cooperation between the Universities of Amsterdam and Leiden, researchers have developed dedicated molecular nanocages for siRNA delivery. In a paper just out in the Journal Chem they present nanocages that are easy to prepare and display tuneable siRNA delivery characteristics.
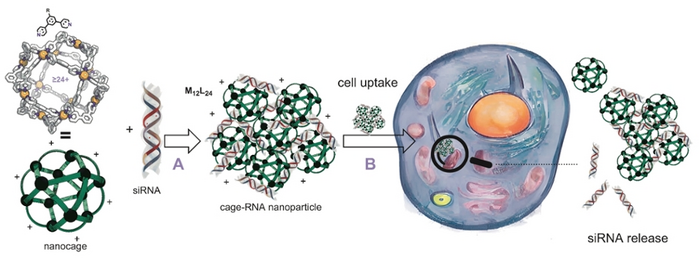
The nanocages were developed in the research group for Homogeneous, Supramolecular and Bio-inspired catalysis of Prof. Joost Reek and Bas de Bruin at the University of Amsterdam’s Van ‘t Hoff Institute for Molecular Sciences, and further studies in the group Prof. Alexander Kros at the Leiden Institute of Chemistry. The researchers were motivated by the potential of siRNA in gene therapy, which requires the need for effective delivery systems. They set out to develop nanocages with functional groups at the outside, making the cages capable of binding siRNA strands. As the binding is based on reversible bonds, the siRNA can in principle be released in a cellular environment. To explore the delivery characteristics of their nanocages, the researchers performed a laboratory study using various human cancer cells.
A range of nanocages
The nanocages are constructions of small molecular building blocks, so-called ditopic ligands, that are connected using metal atoms. A typical cage consists of 12 metal atoms and 24 ligands, hence the abbreviation M12L24. The researchers designed and synthesized five different ligands to form molecular cages with different siRNA binding affinities. They then prepared a range of siRNA binding nanocages using platinum or palladium as connecting metal. The palladium nanocages are less stable in a cellular environment, and decomposition is one of the siRNA releasing mechanisms.
After screening nanocage characteristics such as stability and siRNA binding capability, the delivery characteristics were put to the test in assays based on siRNA-mediated Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) silencing. The cages were used to deliver siRNA to human GFP-expressing cells, so that fluorescence measurements could establish successful siRNA delivery. Two types of human cell lines were used: HeLa and U2Os.
Cage composition determines siRNA delivery
To their surprise, the researchers could not only demonstrate satisfying siRNA delivery, but also discovered a remarkable differentiation depending on the metal used in the nanocage. Where a platinum-based Pt12L24 nanocage showed highly effective siRNA delivery to U2OS cells, it showed little efficiency for HeLa. By contrast, the palladium-based Pd12L24 nanocage, derived from the same ligand building block, delivered siRNA to HeLa but not to U2OS. Such differentiation could not be observed in experiments were a commercially applied delivery system (lipofectamine) was used. The M12L24 nanocages thus introduce the possibility of tuning siRNA delivery characteristics by tuning the nanocage composition.
In their Chem paper, the researchers consider this unique cell selectivity feature of the nanoparticles a promising addition to the field of targeted RNA gene material delivery, whose full potential is yet to be uncovered. Even though the current results were obtained in highly controlled laboratory research, they expect that the tuneable RNA delivery of their nanocages will spawn future developments of highly desirable selective RNA nanomedicines.
Journal
Chem
DOI
10.1016/j.chempr.2023.03.018
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
The application of M12L24 nanocages as cell-specific siRNA delivery agents in vitro
Article Publication Date
18-Apr-2023




